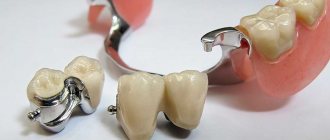
Cantilever prostheses
Designed to replace one tooth.
A distinctive feature of a cantilever prosthesis from a bridge is the support on one side of the defect. It consists of two or three units: 1-2 crowns (placed on the supporting teeth) and a console hanging over the defect site. A cantilever prosthesis is made of metal, metal-ceramics or plastic. Aesthetic ceramics will not be used in this case, since they may not withstand significant chewing loads.
Removable dentures
Prostheses of this type are used in cases of complete or partial edentia. Removable dentures, in turn, are divided into:
- Fully removable.
- Partially removable.
- Conditionally removable.
- Clasp dentures.
- Immediate dentures.
Complete removable dentures
Prostheses of this type are installed in cases of total adentia, that is, complete loss of teeth. They are made of plastic and are fixed in the oral cavity due to the effect of suction of the prosthesis to the surface of the jaw. There are cases when this method of prosthetics is the only one that can make life easier for the patient. But if there is an opportunity and a satisfactory state of health, it is much more effective to insert an implant into the jaw bone and attach a removable denture to it. This way, the fixation of the prosthesis will be better and the level of discomfort caused to the patient will be reduced.
Partially removable dentures
Prostheses of this type are used to correct defects in incomplete dentition, when not all, but most of the teeth are missing. Typically, partial dentures are made of plastic and are secured to the remaining teeth using hooks made of stainless steel. The fulcrum for partial dentures is the gums.
Clasp dentures
Dentures of this type are made of a metal arch to which a gum cuff and artificial teeth are attached. The entire structure is fixed in the oral cavity using a lock, one part of which is mounted into the crowns of the supporting teeth, and the second - directly into the prosthesis. Thanks to reliable fastening, the prosthesis is easy to use, durable and evenly distributes the load on the teeth.
Conditionally removable dentures
Dentures of this type are usually used when one tooth is lost. They are fixed to adjacent teeth using metal claws or special glue; the use of reflective cement is also allowed.
Immediate dentures
These types of prostheses are temporary; they are made of plastic and are used until a permanent prosthesis is made in the laboratory.
Types of dental crowns by material
Metal
Previously, a full metal crown was placed on a tooth because there was no alternative. But its aesthetic properties left much to be desired. Fortunately, thanks to modern technology, you no longer need to cover your mouth with your hand for fear of showing off your prosthesis. Nowadays metal is still used, but only as a base, which is hidden by a coating similar in color to enamel.
Metal-plastic
The cheapest option for crowns is metal products coated with plastic; they last about 5 years.
Disadvantages of combining metal and plastic:
- short service life,
- low strength,
- susceptibility to staining,
- possibility of poor biocompatibility with gum tissue.
- low price,
- possibility of restoration directly at the dentist’s appointment
- low weight.
The last point is sometimes of great importance. For example, a doctor can cover a newly inserted implant with a crown. Ceramics weighs heavier and will put pressure on the sore spot where the “roots” of the prosthesis have not yet taken root in the jaw. The metal-plastic construction will not cause such concern.
Metal-ceramic
Metal-ceramic crowns are heavier than those with a plastic surface. Firstly, their basis is a medical alloy. It may include chromium, cobalt, nickel and precious metals. A natural ground tooth is hidden under a “box” made of medical or precious metal, onto which several layers of ceramic composition are applied.
The positive aspects of installing such structures:
- the ceramic surface is closer in color to enamel than plastic,
- greater compatibility of materials with body tissues,
- service life is about 10 years or more.
Here it is worth clarifying about color and biocompatibility. These points are true only if the crown is made with high quality and using precious metal alloys. Other bases may show through the ceramic and cause an unpleasant taste if the coating is damaged. In addition, an individual allergic reaction of the patient cannot be excluded.
Negative side: not very high reliability of ceramic cladding. This is the main disadvantage. After all, if the ceramics crack and the metal is exposed, then all the aesthetics come to naught. When using non-precious alloys, damage at the base can provoke a painful gum reaction. To avoid this, you should order a crown with a shoulder mass, a ceramic projection that covers the base.
Metal composite
Metal-composite crowns are similar in structure to metal-ceramic crowns; they differ only in the composition of the coating, which is a photopolymer material.
- thinner base
- more natural color
- more options for installation (can be “put on” on different teeth),
- can be placed on an implant.
The properties of the composite material allow the use of a thinner metal base that does not show through the photopolymer layer. As a result, the thinness of the frame and the flexibility of the photopolymer make it possible to place a crown on any tooth: incisor, canine, molar, and even an implant. The latter is especially important, because after implantation the body needs time to engraft. The metal-composite crown is light and strong enough to protect the implant during this period.
- the composite coating is quickly painted,
- possibility of individual reaction to metal.
After installation, doctors warn that the patient will have to exclude coloring foods and drinks from the diet. But in modern life it is difficult to give up drinking tea or coffee. Therefore, composite orthopedic products often darken quickly.
Metal-free
The above types of crowns have a common drawback - the presence of a metal base. Its negative properties manifest themselves in different ways: the metal becomes translucent, the coating on it cracks, and an allergic reaction occurs to it. Modern technologies have given the world metal-free dental crowns, but they are also divided into several categories:
- ceramic,
- based on zirconium dioxide,
- based on aluminum oxide.
Important: when installing a metal-free crown on any tooth, it is subjected to grinding to a lesser extent.
Ceramic
All-ceramic crowns without a metal frame look the most natural. Ceramics transmit light through themselves and are practically indistinguishable from enamel.
The main positive qualities of the design:
- aesthetic appearance,
- hypoallergenic.
They are perfect for patients whose body reacts painfully to a metal foreign body. Even a “living tooth” with pulp can be covered with a completely ceramic crown.
The disadvantage of this design is its lower strength compared to metal-ceramic products. Therefore, they are installed on the front incisors, which bear less load. The best crowns for teeth are made of pressed ceramic, which has a higher density. But still, dentures are often placed on chewing teeth, under the ceramic shell of which a zirconium base is hidden.
Zirconium dioxide
Zirconium dioxide is much more reliable than ceramics and cermets. Crowns made from it are the most modern development in orthopedic dentistry.
Advantages of a protective structure made of zirconium dioxide:
- hypoallergenic,
- high strength,
- possibility of installation on implants
- the most natural look (if it is premium zirconia).
Premium zirconia has amazing reflective properties. Using modern equipment and technology, crowns of increased strength and the most natural appearance are created. They can be placed on the front and lateral chewing teeth, and even on implants.
A simpler option is to combine a zirconium dioxide base and a pressed ceramic coating.
Aluminium oxide
Aluminum oxide and zirconia have several properties in common. They are both metal oxides, hypoallergenic, and can be virtually indistinguishable from the color of enamel. Aluminum oxide is less durable and is not typically used to protect posterior teeth—only the front teeth. But this characteristic can also be given to pressed ceramics, which are already widespread in orthopedic dentistry. Aluminum oxide is still rarely used.
Our dentists care about the quality of prosthetics, so ready-made structures last for 10 years.
Particular attention is paid to the preparation of the root canal (cleaning and filling) - in order to avoid inflammation, loss of the prosthesis and other negative consequences.
To buy crowns for molars and consult their cost in Moscow, make an appointment with our doctor by phone.
You can make an appointment by phone. Consultation is free if treatment is started on the day of treatment.
Who has a cantilever crown?
I am treating my teeth for prosthetics. The situation is this: the four on top is alive, without fillings, the five is gone, the nerve of the six was removed today, the doctor said that he would install a crown - a console, unlike a bridge, the crown over the missing tooth is attached to the tooth on one side. I read that this design is extremely unreliable, it destroys the tooth on which it is attached and for some reason the tooth that is next to the crown, in my case a four. Please tell me who installed this design and how long it lasted? What are the consequences for teeth?
I'm thinking about this myself. I read that a cantilever crown, when chewing, seems to screw the tooth in because there is no second support. I don’t even know what to do either. I’ll probably put up a bridge anyway, although it would be a pity to cut down terribly healthy teeth. Do you already have bridges? I have none.
If we consider it from the point of view of strength of material))), who has not yet forgotten it after studying at a technical university, then yes, the cantilever mount in this case is a definite evil, if the tooth is chewing, then doubly so. The load on the supporting tooth increases by about 1.8 times relative to normal
I stood there for 16 years until the tooth under the crown started to hurt. When biting, chewing did not feel anything. At first it was just not familiar. If the prosthetist is good everything will be fine.
I'm thinking about this myself. I read that a cantilever crown, when chewing, seems to screw the tooth in because there is no second support. I don’t even know what to do either. I’ll probably put up a bridge anyway, although it would be a pity to cut down terribly healthy teeth. Do you already have bridges? I have none.
No, there are no bridges, but there are three holes, around two holes the teeth have already been ground, and around the third hole the teeth were healthy ((
I stood there for 16 years until the tooth under the crown started to hurt. When biting, chewing did not feel anything. At first it was just not familiar. If the prosthetist is good everything will be fine.
Wow, 16 years old! Not all bridges cost that much.
I asked the doctor: Is it better to place an implant? And he: If the tooth under the crown is destroyed, then you’ll put it on.
I had the gold console for about 20 years. My husband is already over 20. Listen to the doctor
I asked the doctor: Is it better to place an implant? And he: If the tooth under the crown is destroyed, then you’ll put it on.
He's a good doctor, he doesn't spend money on him.
I asked the doctor: Is it better to place an implant? And he: If the tooth under the crown is destroyed, then you’ll put it on.
Will the tooth under the crown be a six? Why is there a crown on it? What is the reason for refusing an implant instead of an A? Maybe you still don’t have the closure of the sixes when chewing? Then they will fix it with a crown! Implants are sometimes contraindicated.
Will the tooth under the crown be a six? Why is there a crown on it? What is the reason for refusing an implant instead of an A? Maybe you still don’t have the closure of the sixes when chewing? Then they will fix it with a crown! Implants are sometimes contraindicated.
Yes, there will be a six under the crown, but there will be no five tooth. Three, not only are they alive, they are also healthy, without fillings. And there was a seal on the six. I don’t know about the closure, but it seems to be there, based on the sensations. He didn’t say any reasons why he shouldn’t have the implant; he’s generally not very talkative. They don't do implantation in their clinic.
I had the gold console for about 20 years. My husband is already over 20. Listen to the doctor
How good! This means that not everything is hopeless. I like the doctor’s behavior, businesslike, silent, he does everything confidently. I’m just used to not trusting dentists, but it’s probably in vain, like it or not, I’ll have to trust it; you can’t fix your own teeth.
Who has zirconium crowns?
Who has bridges and crowns?
Anyone who has crowns on their teeth, please come in!
Who has bridges and crowns, come in
Who has metal-ceramic crowns?
Yes, there will be a six under the crown, but there will be no five tooth. Three, not only are they alive, they are also healthy, without fillings. And there was a seal on the six. I don’t know about the closure, but it seems to be there, based on the sensations. He didn’t say any reasons why he shouldn’t have the implant; he’s generally not very talkative. They don't do implantation in their clinic.
My daughter kept saying that it was not convenient for her to chew. They were getting their breeches on. When she got into dentistry from the medical academy, it turned out that braces were contraindicated in her case! The bite is irregular, but the correct one is rarely found in nature. Not comfortable, no closure. The tooth was filled (because there was a hole), with some kind of gasket, which increased the height of the tooth. Maybe this is the case for you too. And how is the six sealed? What part of your tooth is intact, a crown on it can be a chance to save the tooth. As the professor told us about his tooth, even with a crown it’s better, and you should save it while you can, and you’ll still have time to be without teeth.
The fact of the matter is that there was a small filling on the six and he was alive until today; today they put the medicine on him. It would be more humane to leave him alive, but in this clinic crowns are only placed on teeth without nerves.
I had the gold console for about 20 years. My husband is already over 20. Listen to the doctor
You have a living tooth - a support, or the nerve has also been removed.
If we consider it from the point of view of strength of material))), who has not yet forgotten it after studying at a technical university, then yes, the cantilever mount in this case is a definite evil, if the tooth is chewing, then doubly so. The load on the supporting tooth increases by about 1.8 times relative to normal
Prosthetic options for one missing tooth
When one or more teeth are missing, dental bridges are attached to natural adjacent teeth or dental implants. The method of attachment and the type of bridge depends on many factors (except the patient’s wishes), which include the person’s financial situation, as well as the preference of the orthopedic dentist.
If you have one missing tooth, the ideal solution would be to install an implant, but for a number of reasons this option may not be suitable for everyone, so technologies that allow you to correct the dentition without it come to the rescue.
Structure of a dental bridge
A traditional dental bridge consists of two components:
- A fixing crown that is adjacent to the edentulous space. Placed over existing teeth on both sides of the edentulous space.
- An artificial tooth that replaces a missing natural one.
The entire system is rigidly connected. A dental bridge is permanently attached to the supporting teeth. All chewing forces pass along the supporting teeth to the jawbone. The more artificial teeth there are, the stronger the forces acting on the supporting teeth. To avoid severe overstrain on the replacement part of the teeth, it is not recommended to do it for more than four teeth.
To ensure the integrity and rigidity of the bridge, it is necessary to properly prepare the abutment teeth. They must be depulped, i.e. the tooth structure must be removed. This is the biggest drawback, as it leads to the loss of a large amount of healthy tooth tissue. This deficiency is especially noticeable when the supporting teeth are completely healthy without any fillers or cavities. Therefore, implant technology has the great advantage that the teeth adjacent to the gap remain intact.
Special bridges
Dentistry offers several types of bridges that differ from the general standard.
1. Bridge with inserts. Instead of having crowns fixed to existing teeth, this type of bridge has two inserts attached to a tooth replacement prosthesis. These inserts are fixed in specially prepared cavities inside the teeth.
The aesthetics are excellent, but it lacks strength and stability; therefore, this prosthesis can only be used for small restorations.
2. An adhesive bridge , also known as a Maryland bridge, is a conservative alternative to a traditional bridge. It is usually used when a front tooth is missing; can serve as either a permanent or temporary solution.
This design is essentially a crown with “wings” on one or both sides, allowing the crown to be attached to adjacent teeth on the back side.
The bridge frame can be made from a variety of materials, including metal, composite, zirconia, and even reinforced porcelain.
An adhesive bridge is a relatively quick solution and requires little or no preparation of adjacent teeth. However, it is only supported by the back of the adjacent teeth; therefore it can only be used in a limited number of situations, with careful planning.
3. Cantilever bridges are dental bridges that are designed for cases where abutment teeth are prepared on only one side of the missing edentulous gap.
When might such circumstances arise?
- when, for aesthetic reasons, it is undesirable to prepare the teeth on both sides of the violation
- when there are no teeth on one side of the break
- when teeth suitable for supporting the bridge on one side already support another prosthesis, which for various reasons cannot be replaced
In such a bridge there is no distribution of the load on the teeth as in the traditional design, so cantilever bridges must be calculated correctly and carefully; otherwise there is a risk of compromising the stability of the supporting teeth.
There are two types of cantilever bridges based on their location on the dentition - anterior and posterior.
When constructing a cantilever bridge in the front of the mouth, the gap is located in front of the supporting teeth. This is a favorable situation due to the fact that the impairment of chewing decreases as we move towards the front of the mouth.
However, chewing forces still act outside the axis of the bridge and therefore place additional pressure on the supporting teeth. Therefore, the design must comply with certain rules:
- There can only be one artificial tooth in a bridge.
- It may be ideal if the missing tooth is either a premolar or a lateral incisor, and only in limited situations if other teeth are missing.
- Typically, at least two abutment teeth are needed to support a bridge.
A cantilever bridge in the back of the mouth on molars is not recommended, since the chewing forces are much higher there. Large loads acting on the supporting teeth will, after some time, lead to looseness of the teeth under the crowns, and this can jeopardize the entire restoration.
There are several situations where these types of restorations may be indicated:
- temporary restorations
- if back teeth are missing and patients do not want (or cannot afford) more expensive restorations: removable dentures, dental implants
The life expectancy and prognosis of these restorations are usually very short. With the development of dental implants, such solutions are rarely used.
We are about health
Cantilever bridge
Almost everyone knows that dental prosthetics can be done with crowns and bridges, but few have heard about another type of structure - a cantilever prosthesis.
However, of course, no one will accuse patients of ignorance: firstly, the console is the same bridge-like prosthesis, only in a specific design, and secondly, in comparison with the classic bridge, this prosthesis is inferior.
Nevertheless, when a person hears about such a prosthesis, he wants to consider the prospects for its installation.
This means that it is in his interests to know in advance what a dental console is and when it is appropriate to use such a prosthesis.
Lumi-Dent dentistry knows how to work with such material, and is always happy to tell patients about its features in detail.
What is a cantilever prosthesis?
So, a cantilever for teeth, also known as a cantilever bridge, is a type of orthopedic dental structure that is designed to replace one missing tooth.
Its main distinguishing feature is one supporting side (fulcrum) instead of two, like a classic bridge.
In other words, a cantilever is like a balcony in a building.
The treatment process in which the console is involved looks like this:
- one or two supports (healthy or in need of treatment teeth in a row, the crown part of which is at least 80% preserved) takes on the main load;
- the cantilever denture itself is an artificial tooth, only without a root;
- the console is securely fastened to the supporting part and forms a single cantilever bridge.