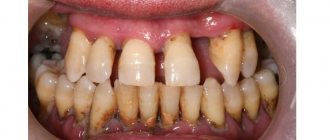
Symptoms of inflammation
During the normal healing process, the pain after tooth extraction lasts 1-2 days, after which it gradually subsides, the wound becomes covered with a blood clot and heals over time. With inflammation, the pain can come in waves, not subside or even intensify. The nature of the pain is pulsating, can radiate to the ear, and manifests itself after eating. Does not respond to painkillers.
When examining yourself, pay attention to the following signs:
- the gums at the extraction site are red;
- the socket is dry, a blood clot does not form or is quickly destroyed;
- there is a gray or yellow coating;
- bleeding from the socket;
- increased body temperature;
- unpleasant taste and odor from the mouth;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
If at least one of the listed signs is present, you should consult a doctor. There is a suspicion of alveolitis.
How not to die from a bad tooth
Cellulitis is a diffuse purulent inflammation, which, in the absence of adequate treatment, leads to death. Quite often, the cause of the formation of phlegmon is a diseased tooth. Igor Panin, head of the department, told the Sibmeda portal how to avoid becoming a victim of a deadly disease. Department of Maxillofacial Surgery of the Novosibirsk Regional Hospital.
– Igor Anatolyevich, is phlegmon a common disease?
– Phlegmons of various localizations, including those of odontogenic etiology, that is, from teeth, are quite common. Patients with phlegmon make up a significant part of the patients in our department.
- What is the reason?
– Despite the rapid development of dentistry, patients with a healthy oral cavity are not as common as we would like.
Diseased teeth are, most often, the cause of the development of severe phlegmons of the face and neck, which regularly lead to death in this group of patients - due to neglect and the development of associated complications.
Such complications include the development of chest inflammation, various types of breathing problems, sepsis, as well as some other conditions that can lead to the death of the patient.
It happens that the development of phlegmon is associated with the removal of teeth, and with the fact that the inflammatory process from the tooth, despite its removal, spreads to the surrounding tissues.
In most cases, the reason for the development of phlegmon is the lack of visits to dentists and late treatment when complications develop.
– Can phlegmon develop from pulpitis?
– It is incorrect to say that phlegmon develops as a result of pulpitis. This is not typical for pulpitis. Still, phlegmon often develops when the pulp is no longer present, and when there is an inflammatory process in the area of the roots of the teeth.
– Does the development of phlegmon often end in death for the patient?
– Unfortunately, every year people die from phlegmon of odontogenic etymology in the Novosibirsk region. I won’t say that such cases are registered every month, but every year.
Fortunately, most patients can still be cured if treated in a timely manner.
But if we talk about advanced cases, when the patient needs to be treated for complications that have already developed, then we have such patients all the time. As a rule, they are in the intensive care unit. Their recovery is a long process; the state has to invest large sums of money for such patients. The process of treating a patient with severe phlegmon can take more than a month.
– It turns out that such dangerous consequences arise simply because of a tooth that is not treated in time?
- More often. There are, of course, other causes of phlegmon - consequences of injuries, various inflammatory diseases of the tonsils, but the most serious problem is precisely those phlegmons that develop as a result of dental disease.
Cellulitis that develops from tonsils or injuries is still of a milder nature than phlegmon from teeth.
The largest group of patients are patients who sought medical help late. When a person has a toothache, he self-medicates: he rinses with soda, takes pills, but the tooth continues to ache, and the inflammatory process extends beyond the boundaries of this tooth into the surrounding tissues, with the development of severe complications.
Less often, situations arise when a patient consults a doctor to remove a diseased tooth or treat it, but despite the fact that the doctor carries out therapeutic measures, the inflammatory process progresses and the patient, as a rule, comes to us.
– How quickly does phlegmon form? This is not an instant process, is it?
– In fact, the microflora in teeth is aggressive, and the development of phlegmon can occur within hours. The speed of development depends on the general condition of the body, age, use of antibiotics and some other factors that can stop this process. But these processes are very serious, and the development of complications cannot always be predicted.
Therefore, if there is a suspicion of phlegmon of the oral cavity and neck, first of all, an urgent visit to the hospital is necessary, where a decision on further treatment tactics will be made.
– By what symptoms can one suspect phlegmon?
– As a rule, the process begins with swelling on the face or neck. The mouth may have difficulty opening, and there may be pain when swallowing. The development of phlegmon is always accompanied by fever, weakness, and sweating.
The presence of swelling on the face and high temperature is a reason to contact a dental surgeon at the clinic as quickly as possible.
In our city, you can get dental care around the clock. And the clinic doctor, even if he cannot provide assistance himself, will assess the patient’s condition and refer him to the hospital if necessary.
– How long does it take for a patient to seek medical help?
– Let’s just say that time in this case does not work for the patient. The faster the better. With timely treatment, you can get by with a smaller amount of surgical intervention. When the situation has not reached the point of phlegmon, and the inflammation is localized in the area of the tooth, it does not spread to the surrounding tissues.
Still, more often it happens like this: the tooth was removed, antibiotics were prescribed, if necessary, and the purulent process stopped there. Most of these patients are treated on an outpatient basis.
But in this group there are patients when the inflammation spreads to neighboring areas, and then the person must be hospitalized in a hospital.
– Is it possible to confuse phlegmon with another acute disease?
– There is confusion with some diseases that are also accompanied by swelling in the neck. If in doubt, it is important to contact the appropriate specialist - a dental surgeon at the clinic, first of all. He will make a decision and, if necessary, send you to the hospital.
– Which medical institutions in Novosibirsk provide assistance to such patients?
– In our city, inpatient care for patients with phlegmon is provided in three hospitals. For the adult urban population - in the department of maxillofacial surgery of the 34th hospital, for the regional population - in the Novosibirsk Regional Hospital and for the children's population - in the 3rd emergency hospital.
– How is the diagnosis of “phlegmon” made or specified?
– As a rule, the diagnosis is made primarily on the basis of clinical data. This does not require any special examination. Tomography can be performed to clarify which areas are affected by phlegmon in a given patient.
– What treatment methods are used for phlegmon?
– The only possible method of treating patients with phlegmon is surgery: wide incisions are required to eliminate the purulent process. No other has been invented yet. No pills or injections will help without surgery.
It is important to know: patients with phlegmon are not treated with antibiotics. Antibiotics are used after surgical treatment, and not instead.
Everything must be combined - surgery, antibiotics, infusion therapy, and many other procedures.
– Igor Anatolyevich, how can you protect yourself from such a dangerous disease as phlegmon?
– It is important to remember that the presence of rotten teeth in the mouth is a time bomb that can explode at any time. There is, of course, an element of luck, but I don’t recommend relying on it in this matter.
Therefore, the main preventive measure is, of course, regular visits to the dentist in order to treat carious teeth, sanitize foci of chronic odontogenic infection, so as not to lead to the development of phlegmon. After all, the strategic task is not to consult a doctor at the right time, when phlegmon has already developed, and not to allow its development, in principle.
Subscribe to our Instagram and Facebook to keep abreast of exciting events and news from the world of medicine, health and beauty.
Causes of alveolitis
- During tooth extraction, tissues are severely injured.
- Reduced immunity.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Intensive rinsing and drinking hot liquids immediately after tooth extraction.
- Elderly age.
- Infection of the hole from neighboring tissues and teeth (for example, in the case of caries in the neighborhood).
- The presence of other diseases of the body at the time of tooth extraction.
- The rest of the root is in the hole.
- Hard pieces of food getting into the wound.
- Insufficient oral hygiene.
- Smoking.
- Creating a vacuum in the mouth (for example, when using a drinking straw).
Most often, alveolitis appears as a result of the removal of “eights”. Since this is a large element, it affects many vessels, which makes healing of the gums after wisdom tooth removal difficult.
Causes of bleeding
First of all, you need to look at the possible reasons why a wisdom tooth has been pulled out and the bleeding does not stop. Depending on this, the algorithm for further actions will differ. So we can distinguish:
- Common reasons
– this includes all factors that do not depend on the actions taken by the patient or doctor. For example, bleeding may occur after special blood thinning medications that may be given before surgery wear off. Complications are also possible when taking medications that reduce blood clotting, such as aspirin. Women need to be especially careful during menstruation, as at this time the level of hormones that impede blood clotting increases. Here it is necessary to mention the presence of chronic diseases, such as hypertension, leukemia, hemophilia, etc.
- Subjective reasons
– here we are talking about specific actions that lead to bleeding. These include non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations (injuring the surgical site, washing out a natural blood clot, etc.). Unqualified or erroneous actions of a doctor can also lead to bleeding.
- Force majeure reasons
– these include excessive damage to gum tissue, blood vessels or even bone tissue caused by individual characteristics of the jaw structure, abnormalities in tooth development and other factors. Here we can also talk about the occurrence of suppuration caused by infection in the wound.
So, if the issue with the cause of bleeding has been resolved, then it is necessary to take immediate action to stop it.
Treatment and prevention of alveolitis
Treatment of alveolitis is carried out by a dentist; self-medication is unacceptable. Firstly, you may make a mistake with the diagnosis, as a result all manipulations will be ineffective. Secondly, traditional methods are not enough, and for professional ones you do not have enough experience and equipment.
How is treatment carried out at the clinic? The doctor numbs the wound, cleans it, and puts a tampon with medicine. If foreign bodies (shards of tooth, root, pieces of food) prevent the socket from healing, the dentist removes them. You may need to take antibiotics, undergo physical therapy, baths with medications, and follow a diet during healing (excluding hard, hot foods from the diet). In advanced cases, additional operations are required. Traditional methods are acceptable with the permission of a doctor. For example, rinses with sage, chamomile, burdock and others. These solutions can accelerate tissue healing and alleviate the patient's condition.
What measures exist to prevent inflammation? In the first days, do not eat hard or too hot foods, and do not rinse your mouth. These actions help flush out the clot, which can cause inflammation. If tooth extraction is not an emergency, it is advisable to take care of the treatment of caries and other oral diseases in advance. Give up bad habits during healing: alcohol thins the blood, which prevents the formation of a clot, tobacco increases the risk of infection of the hole. If your gums hurt on the first day after tooth extraction, you can simply take a painkiller.
Two days after tooth extraction, the pain has not subsided, it has intensified, and its character has changed, which means that you should definitely consult a doctor! Alveolitis does not go away on its own; it can only lead to unpleasant consequences and complicate further treatment. Monitor the condition of your teeth especially carefully if there were other diseases of the oral cavity or the body as a whole at the time of removal. Doctors at Comfort Dentistry give recommendations for further care after tooth extraction. They tell you how to treat gums after tooth extraction, and in what cases to contact a dentist. If you doubt the correctness of self-diagnosis, you can call us and consult with a specialist.
Tooth abscess - symptoms and treatment
A tooth abscess does not go away without treatment. If you open it yourself, the pain may decrease significantly, but this does not eliminate the need for dental treatment. If the abscess is not drained, the infection can spread to the jaw tissue and other areas of the head and neck, which can lead to various complications.
Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
When the veins are located close to the source of infection, a serious complication such as thrombophlebitis develops - inflammation of the vein with subsequent formation of a blood clot. First, the inflammatory process affects the walls of blood vessels (phlebitis), then spreads to the tissue surrounding the vein (periphlebitis) and finally covers the entire wall of the vein. Due to damage to the vessel, blood flow becomes slower, the composition of the blood changes, and clotting increases. All this contributes to the formation of a blood clot. In some cases, blood clots form in the venous sinuses of the brain.
Mediastinitis
Mediastinitis is an inflammation of the mediastinum (a complex of organs located in the chest cavity between the left and right mediastinal pleura, the posterior surface of the sternum and the thoracic spine and rib necks). Can be fatal.
The infection can penetrate into the mediastinum by contact, through the blood or lymph flow. The purulent exudate is so active that it can melt the intermuscular septa and walls of large arteries. In this regard, the infectious process spreads quickly and creates the risk of severe bleeding.
The source of the spread of infection leading to mediastinitis is usually inflammation in the area of the apex of the tooth root (sometimes in combination with infection of the tonsils or damage to the oral mucosa).
Acute or chronic sepsis
Sepsis is the most severe complication of a tooth abscess, which occurs when the immune system fails. The body cannot resist the infection, and it spreads throughout the body. Depending on the speed of onset of symptoms, sepsis can be fulminant (1-2 days), acute (5-7 days), subacute (1-2 weeks) and chronic. First of all, the functioning of the lungs is disrupted, and then other organs: liver, kidneys, etc. Subsequently, septic shock develops: blood circulation in the organ tissues slows down, and failure of several organ systems develops - multiple organ failure syndrome. When this syndrome occurs, most patients die within 2-3 days [8].
Meningeal diseases
Meningeal complications of a tooth abscess (meningitis, brain abscess, etc.) are not so common, but their mortality rate is quite high: it reaches 40-90%. Most often, these diseases arise due to the spread of infection from primary foci, the temporal region, pterygopalatine or infratemporal fossa.
Sinusitis
Appears due to constant inflammation in the oral cavity. The risk is higher if the upper molars and premolars (these are closest to the maxillary sinuses) are affected. The infection penetrates the maxillary sinuses and affects them, causing severe headaches, high fever, and constant purulent mucous discharge from the nasopharynx. Without adequate treatment, sinusitis becomes chronic and can provoke meningitis, sepsis localized near the brain, and damage to nerve endings. It cannot be treated only by relieving symptoms: antibacterial therapy and endodontic treatment are needed.
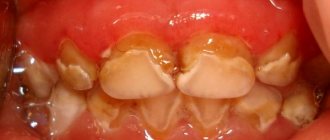
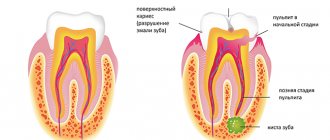
Stages of dental caries
The abscess itself is one of the later stages of caries. The different stages include:
- Enamel decay
: This involves damage to the outer layer of the tooth. In some cases, there are no symptoms, but increased sensitivity to heat and cold may occur. The destruction of enamel is manifested by the appearance of white spots on the teeth. - Dentin breakdown
: This involves damage to the layer under the tooth enamel. At this stage, pain or sensitivity of the tooth is noted. In some cases, there may be a hole or cavity in the tooth. - Pulp damage
: This occurs when bacteria penetrate deep into the inner layer of the tooth. Bacteria inside the tooth pulp damage the nerve, causing severe pain. - Abscess formation
: An abscess develops in the later stages of tooth decay, after bacteria have burrowed into the tooth pulp or deeper into the gums or jawbone. There is pain near the tooth, as well as swelling and redness of the gums. In severe cases, the abscess may also manifest as fever. - Tooth loss
: A severely decayed tooth may fall out.
Prevention of tooth abscess
You can take the following steps to prevent dental abscesses:
- Brush your teeth thoroughly to remove plaque. Pay attention to the area just under the gums where plaque can accumulate.
- Use fluoride toothpaste to fight tooth decay.
- Floss your teeth regularly to remove plaque between your teeth.
- Schedule regular visits to your dentist for thorough cleanings. The dentist can remove hardened plaque or tartar that cannot be removed with a regular brush.
- Treat diabetes or any other underlying condition that may weaken the immune system and increase the risk of infection.
- Treat tooth decay as soon as possible, before bacteria penetrate into the deep structures of the tooth.
Stop bleeding
The best option for what to do if the bleeding does not stop after tooth extraction is to contact a specialized institution. This rule should be taken as the main one and if there is such an opportunity, then it should not be neglected under any circumstances. Qualified specialists will provide assistance much faster and better than what an ordinary person can achieve at home. Moreover, if there is severe bleeding, the cause of which is the use of anticoagulants, then it is simply necessary to go to the clinic, since independent actions will be ineffective.
If the decision is made in favor of a “home” solution to the problem, then here you can mention:
- Vasoconstriction
– before surgery to remove a tooth, doctors often inject a drug into the gums that locally narrows the blood vessels. This can significantly reduce blood loss. At home, a similar result can be achieved by applying ice or other frozen product to your cheek.
- Mechanical impact
- here we are talking about closing the wound in the usual way, which will lead to the appearance of a blood clot that will prevent bleeding. For these purposes, you can use an improvised gauze swab or a special hemostatic (hemostatic) sponge. The tampon must be placed directly into the hole left after tooth extraction and pressed firmly with the jaw.
- Special preparations
– Taking medications that lower blood pressure can be used as one of the measures to stop bleeding. Naturally, before using them, you need to make sure that the indicators are overestimated. As a rule, hypertensive patients always have a tonometer at hand and are aware of their problem. But blood pressure can also rise due to stress.
The listed methods of stopping bleeding after tooth extraction are the main ones and if they are ineffective, you need to contact a specialized clinic, and sometimes you need to go to an ambulance.
In any case, prevention of the problem should be in the first place, and therefore, a few days before the proposed operation, you should refrain from taking blood thinning medications, and after the operation, strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
Tooth abscess - cause
A dental abscess develops when bacteria penetrate deep into the tooth or surrounding structures and then multiply.
The main causes of tooth abscess:
Untreated caries
Bacteria inside the mouth form a biofilm. Regular brushing and flossing removes plaque. However, without proper dental care, tooth decay can get out of control. Over time, plaque bacteria eat away at the tooth, causing tooth decay. If tooth decay continues without treatment, an abscess may develop.
Gum disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontitis
, is the medical term for infection and inflammation of the gums. When the disease is severe, the gums recede from the teeth, revealing deep pockets between the teeth and gums. Food and bacteria getting inside the pockets can cause an abscess.
Oral trauma
Trauma to the tooth or surrounding structures can also increase the likelihood of developing a dental abscess. These lesions can develop as a result of surgery or trauma to the mouth.
The cardiovascular system
Against the background of advanced dental diseases, a number of heart diseases can develop:
- infective endocarditis - inflammation of the heart valves due to infection, which enters them through the bloodstream from the affected tooth, more often occurs when the immune system is weakened;
- heart failure - periodontal inflammation doubles the risk of its occurrence;
- heart attack, stroke. Due to inflammation and the transfer of bacteria through the bloodstream, atherosclerotic plaques form on the walls of blood vessels. The plaque clogs the vessel and a blood clot forms. If it comes off, a stroke or heart attack occurs.
Untreated caries and constant inflammation in the oral cavity increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases by 70%.