In Russia, more than a million people are HIV-positive, and these are only those who know about their status and are registered with a specialized medical center AIDS Center Statistics. . Many people do not yet realize that they are sick.
This is a real epidemic, so fears are understandable. Even at school they tell you that HIV is transmitted through blood and some biological fluids, that you need to use condoms and, of course, not inject yourself with anything. But is this enough?
In the same schools, since the time I was studying, there have been horror stories about contaminated needles, which are deliberately scattered in sandboxes by embittered drug addicts (I must say, used syringes in urban bushes are not uncommon). Adults don’t find themselves in sandboxes as often, but they are no less afraid.
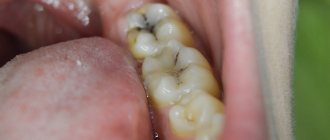
After all, HIV is transmitted through blood. So, any place where blood appears is dangerous? For example, a dentist's chair or a nail salon. You never know who was at the master’s, suddenly one of the infected million.
Lidiya Suyagina
Author of Lifehacker
I gave up trimmed manicure once and for all several years ago, so the chances of picking up something unpleasant have become less. Interestingly, I have not stopped fearing infection. I can’t give any rational explanation for this fear, so I just watch with an eagle’s eye every time what the master has with his tools, and pester me with questions about how it’s all processed. By the way, finding a normal and responsible craftsman who does not neglect the cleanliness of tools is quite a quest.
Let's try to figure out what to be afraid of and what not to be afraid of.
The inertia of stinginess
If the likelihood of becoming infected with HIV at a dentist is very low, then, according to Western studies of hepatitis, in the case of this disease everything is much more serious.
Traditionally, the dentist prepares the tooth structure with a turbine tip to place a filling. The rotor rotates the bur inserted into the handpiece at a speed of 300,000 revolutions per minute, and the rotor itself is driven by a strong stream of compressed air. Actually, this turbine produces that characteristic sound that we associate with a dental office.
When preparing a tooth, the tip is always contaminated with biological fluids: blood, pus, saliva. But the real problem is that when the air supply in the turbine tip is stopped, an aspiration effect occurs: the pressure in the air channel becomes much lower than in the turbine area, and biological fluids are sucked into the air channel.
When you sit down in the dentist's chair or seat your child there, the dentist puts on sterile gloves and unseals a sterile tray of instruments. But the turbine handpiece often remains the same.
When the dentist starts work, he is already in the installation. Unfortunately, in most Russian dental clinics, the handpiece is unsealed from the sterile packaging at the beginning of the shift, and sterilized at the very end - and this is in the best case.
When asked about the sterility of this element, dentists usually answer vaguely: “It’s been processed,” or simply: “It’s clean.” Ignoring the fact that the tip is a reusable medical device that comes into contact with the wound surface, that is, it must be sterilized after each use.
Thus, a recent survey of 467 dentists conducted by researchers showed that 19% of Russian doctors, most of whom specialize in orthopedics and have 10 to 19 years of experience, do not consider it necessary to sterilize small dental instruments between patients.
This is partly due to the fact that when turbine handpieces came on the market in the 90s, they were very expensive and doctors could not afford to see each patient with a separate handpiece. Today, a turbine handpiece costs 2,500–4,000 rubles, which is not much for a dental clinic, but the inertia of specialists’ thinking takes its toll.
Is it possible to get infected with syphilis, AIDS and hepatitis at the dentist?
Doctors won’t let you lie, but most of them almost never encounter patients who come and immediately put a plus in the questionnaire next to AIDS or syphilis. They talk about hepatitis quite often, but everyone ignores the first two points.
And, judging by the morbidity statistics, this is not because these diseases do not exist in the country. Quite the contrary, they exist, but people hide them.
Because there have been plenty of cases when a patient honestly says that he has AIDS, and doctors jump out of the office screaming and refuse to treat him. What will such a person do next time? Naturally, he will remain silent. After all, he has a toothache and he wants to cure it, but he doesn’t want to be looked at like a mad dog that is about to bite, and they refuse to treat him at all.
So it turns out that patients go to private clinics, where they don’t even need to show a passport, call themselves by any left-hand name and have their teeth treated without reporting all the details of their health.
That is why sterilization should be carried out as if every patient were a potential carrier of some disease. And in any modern clinic this has been done for a long time.
Instruments are sterilized in special autoclaves with special marks that change color only when the desired temperature is reached. Then these marks are pasted into a special journal and you can always track how each batch of instruments was sterilized. If at least one mark in at least one corner does not change color, then the entire batch is sterilized again.
Plus, modern autoclaves have a print on the sterilization mode, which completely reflects the entire process.
After autoclaving, the entire instrument remains in sterile Kraft bags, where it can remain sterile for another year.
Needles, threads and even scalpels should be disposable, carpule syringes, after the injection the carpule and needle are thrown away. So the patient cannot become infected with anything at all. It is a fact!
Why are rumors so persistent that some dentist infected a patient with hepatitis or something worse? And everything is very simple!
If a patient becomes infected with something, the epidemiologist must track the entire chain of the disease and identify the source with all connections. This is his sacred duty!
There is an option that the doctor will talk with the patient for a long time and confidentially about all his sexual relationships over the past six months or a year or more, find out about all the friends with whom he was at home and ate and drank something, and perhaps with them slept, checked whether the patient had injected himself with the same syringe with one of his friends, and so on and so forth.
Is there an option that the doctor asks the patient if he has had his teeth treated in the last six months? In 90 percent of cases, people had their teeth treated in the last six months to a year, either went for a follow-up examination, or had professional oral hygiene done. And he says, yes, he went to such and such a dentist!
Ta-da-dam!!! There is no longer any need to ask anything, go to addresses and conduct interrogations with passion about who slept with whom! Here is the culprit on a silver platter! It’s impossible to prove, of course, but go try to refute it!
And now the question is quickly closed, the box is ticked. By no means do we want to say that all epidemiologists work this way! No, most of them take their work seriously. But there are also exceptions.
This is where statistics and the myth emerge that dental clinics regularly infect patients with all sorts of nasty things.
A doctor is much more at risk of contracting something from a patient than a patient is from a doctor. Because it is from the patient’s mouth that splashes of saliva or blood can get into the doctor’s eye, it is the doctor who can prick himself with an instrument that he uses in the mouth of an infectious patient, and it is the doctor who undergoes a medical examination every year and donates blood for any and all tests in order to have a sanitary a book, without which it is impossible to work, and not a patient.
Vacuum of knowledge
However, this issue is regulated by written rules. Thus, the Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated May 18, 2010 N 58 (as amended on June 10, 2016) “On approval of SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities”” indicates that dental handpieces must be sterilized after each patient.
This is also evidenced by modern instructions on the correct and safe processing of dental handpieces. The Kemerovo correspondent for AIDS.CENTER conducted a small experiment: she specifically walked through the city’s dental offices to check how these documents work. It turned out that there was no way. When a woman sat down in a chair and asked uncomfortable questions, the answer, as a rule, in most places was the already familiar “We treated it,” which in practice often meant: they wiped the top twice with a cotton swab containing chloramine.
However, there is no need to panic. Professor of the Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology of the Moscow State Medical University named after A. I. Evdokimov Irina Shestakova answers a question on our site that it is quite difficult to really assess the likelihood of such an infection. And the risk is not as great as it might seem at first glance.
DOCTOR'S OFFICE: DANGER OF INFECTION?
According to the chief physician of the Center for Private Dentistry "DOCTOR LEVIN" Dmitry Levin , infection can occur when the virus enters the blood at once, for example, during the process of removing a tooth with dirty instruments, or when a small amount of it enters repeatedly.
This is only possible in a clinic that does not follow the protocols for sterilization and disinfection of instruments and the doctor’s workspace, offices, chairs, etc., and also ignores the requirements of the Ministry of Health on the prevention of AIDS, and does not use the Anti-AIDS, Anti-Hepatitis first aid kit.
According to Dmitry Levin, the clinic’s own sterilization room protects the patient, as well as the doctor, from possible infection 100%.
“The risk group usually includes patients who prefer to be treated by private practitioners, where there is no way to check whether sterilization and pre-sterilization treatment was carried out and its quality.”
- The immunodeficiency virus lives outside the human body for only a few minutes, but in a closed space - inside a needle, syringe, in the blood - it can remain active for up to several days. HIV is very sensitive to heat: at a temperature of 56 degrees it is inactivated within 10 minutes, and dies within 30 minutes. A temperature above 100 degrees kills him in one minute,” explains the head of the dentistry department at the INPROMED Dentistry Center, orthopedic dentist Tatyana Sidorova . — Quickly dies under the influence of disinfectants: 5% hydrogen peroxide solution, 3% chloramine solution, 70-degree solution of alcohol, ether, acetone.
The virus is resistant to freezing, ultraviolet radiation and ionizing radiation. Infection occurs when biological fluids containing HIV enter directly into the bloodstream, through damaged skin and mucous membranes, and the infectious dose is approximately 10,000 viruses.
WHAT CAN A PATIENT CAN?
The patient is required, first of all, to be attentive when communicating with the doctor and in general when visiting the clinic. If he notices traces of blood left over from a previous patient, if the overall room is dirty and untidy, this should alert him.
Tatyana Sidorova warns that sanitary treatment of the premises should be carried out after each patient, a disposable cup should be in a clean spittoon, and the chair should be wiped with a disinfectant composition. Masks, gloves and aprons for doctors and assistants should also be disposable and changed after each patient.
General Director of the dental clinic “ANATOMY OF A SMILE” Yanna Warkentin recommends paying close attention to the opening of disposable packages of instruments and related materials by the doctor in front of you. The state of sedation or anesthesia, of course, makes such control on the part of the patient difficult.
“When preparing the operating room, a set of necessary instruments is prepared in advance on a sterile table with certain maintained sterile standards,” explains Yanna Warkentin, “however, there is always the opportunity to come to the clinic early and make sure that the instruments are sterile.”
CONTENTS OF A SPECIALIZED FIRST KIT
The contents of the first aid kit are not clearly stated in full, however, SP 3.1.5.2826-10 obliges health workers to carry out certain emergency measures, including treating wounds with a 70% alcohol solution, 5% alcohol solution of iodine, and the mucous membranes of the eyes with 1% boric acid, nose - 1% protargol, mouth - 70% alcohol solution, 1% boric acid or 0.05% potassium permanganate.
In addition, a rapid HIV test should be carried out immediately, and all clinics should have access to it. The regulations do not directly indicate this, but it would be logical to include such tests in the first aid kit for the fastest access to them.
PREVENTIVE METHODS ACCEPTED IN CLINICS
The head of the clinic is obliged to instruct medical workers, as well as personally monitor compliance with the standards of SP 3.1.5.2826-10, which regulates HIV prevention.
Tatyana Sidorova is convinced that strict disinfection rules help modern clinics protect themselves from infection:
— Dental instruments undergo several stages of processing: disinfection, pre-sterilization treatment, sterilization. Sterilization and detection of hidden blood on instruments are monitored. Injection needles, saliva ejectors, dental aspirators, aprons must be disposable, as well as protective equipment for the doctor and assistant: gloves, masks. In dental offices where all these rules are strictly followed, the chance of contracting HIV is reduced to zero.
HIV prevention in dentistry
It is no secret that cases of infection of patients in medical institutions, manicure salons and other establishments have been recorded. The risk group includes all facilities where services involving surgical or cosmetic procedures are expected to be provided.
Dental clinics are no exception. A huge number of people visit their offices every day. It is for this reason that it is especially important to comply with all sanitary standards and sterilize dental instruments. Today, every clinic has a plan of preventive measures. By fulfilling all the requirements, both the private dentist and the doctor at the public hospital protect themselves and the patients in their office from infection.
Briefly about HIV infection
Today, every person knows that the abbreviation HIV stands for “human immunodeficiency virus.” This disease is characterized by the fact that the smallest microorganisms cause disruptions in the protective functions of the body in people. The action of the virus can be described as follows. Once in the body, it affects the immune system, destroying cells responsible for protecting against infections and destroying microbes.
Over time, a person becomes unable to resist either external infections or bacteria or fungi. The virus multiplies only inside a person. Outside the body it dies. The duration of life outside the body is influenced by temperature and humidity. The virus dies when heated (over 56 degrees Celsius). Sterilization of dental instruments completely destroys HIV, because it is designed for more tenacious viruses and bacteria.
Providing dental care to HIV-infected people
Federal law states that preventing the spread of diseases caused by the immunodeficiency virus in the Russian Federation also involves providing medical care. It is agreed to reduce contact with the patient to a minimum. The doctor is obliged to maintain medical confidentiality. The law provides for disinfection measures. In connection with them, the advisability of placing sick patients in separate rooms was noted. At the same time, they must be equipped with the necessary equipment. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to carry out all therapeutic procedures last (after healthy patients).
Patients with HIV infection can receive full dental care provided that the prescribed safety measures are followed. In turn, people with HIV infection must notify staff of their status.
3.How are the tools processed?
To eliminate cases of HIV infection in dentistry, a number of measures have been developed that staff strictly follow. Accounting documentation is maintained - a journal for monitoring the sterilization of equipment.
- After each patient, the instruments are immersed in a special solution, washed and dried.
- Manipulation sets are formed, which are hermetically sealed on both sides. Each of them has an indicator label.
- Sterilization occurs in an autoclave under pressure at high temperature. The indicators on the packaging in each set change color - this is a signal that the sterilization process was successful.
- The log records the time of sterilization.
If you are concerned about whether you can become infected with HIV at a dentist, you should know that work surfaces are also regularly cleaned after each patient with a disinfectant solution or sprays. And in the office quartzing is carried out according to the approved schedule.