Content
- Causes of tooth decay
- Signs
- Dental diagnostics
- Methods of dental treatment
Pathological changes in teeth restored with crowns are an extremely unpleasant situation and, moreover, dangerous for the health of the entire body. With the correct use of a well-made and installed crown, the likelihood of such problems occurring is minimized. However, cases of tooth decay under crowns still occur. It is important to recognize the problem in time and seek help from a doctor.
PROMOTION
Zirconium crowns and bridges
RUB 12,500
Carrying out restoration
Prosthetics are possible provided that the root is not destroyed, is preserved, and is strong enough. An orthopedic design replaces the visible part of a tooth, repeats its original shape, size, relief, and exactly matches the dentition in color, parameters of light reflection, light transmission, and surface gloss.
Before prosthetics, preparation is carried out: sanitation of the oral cavity, preparation, turning (needed to form a base for installing a crown). In case of severe damage, it is possible to use inlays for additional strengthening.
If your own tissues have been preserved to a minimum extent, restoration is performed in the following order.
Diagnostics. Inspection, control of the condition of the tooth root. During diagnosis, the doctor assesses the degree of destruction of hard tissues and decides on the possibility of restoration and prosthetics.
Formation of an order for a dental laboratory. Orthopedic structures are made individually, repeating the size and shape of lost teeth. To restore it most accurately, photographs and casts are taken. Design is carried out using CAD/CAM technology, which allows you to build a three-dimensional model. Its use allows design and further production to be carried out with high precision - so as to reproduce all the nuances of the form, the original surface topography, ensure correct occlusion, and carry out the restoration discreetly, with an aesthetic result. Production in the laboratory is carried out within a few days.
Preparation for prosthetics. At this stage, the doctor removes damaged tissue, performs trimming, and forms a base for installing an orthopedic structure. Additionally, periodontal and endodontic treatment can be performed. They are completed before prosthetics to minimize the risk of complications.
Prosthetics. The finished structure is installed on the prepared base. It is attached after turning using special compounds. If there are several gaps in the dentition at once, it is possible to install bridges.
Do you have questions about dental crowns?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7
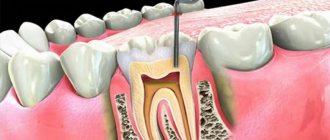
Why does a tooth rot under a crown?
The emergence of a pathological process occurs for a number of reasons. All of them are united by the same outcome - the penetration of pathological microorganisms. Among the most common causes of rotting are:
- Poor hygiene. If the patient does not keep his teeth clean and his oral cavity healthy, plaque accumulates on the teeth and tartar forms. These processes are accompanied by damage to the gums that protect the cervical part. The root of the tooth and the junction with the crown are exposed to destructive effects.
- Bad habits, unhealthy diet.
- Lack of calcium, bone tissue pathology.
- Secondary caries, decementation and food getting under the crown. Food rots, causing tooth decay.
Benefits of prosthetics
Crown installation is safe and the likelihood of complications is minimal. If the preparation for prosthetics is carried out efficiently, the destruction of hard tissues stops and stops progressing.
This restoration provides:
- aesthetics: complete restoration of the dentition. The artificial structure matches the dentition in shape and size, and the shade of the enamel;
- restoration of the functions of the dental system. After restoration, the tooth root receives the correct chewing load. This stops the process of bone regeneration, ensures proper chewing, and does not provoke an increase in chewing load on other parts of the dentition;
- preservation of dentin. Without treatment and restoration, the destruction of hard tissues will continue: the process will go to the root, and serious complications are possible. Installing a crown stops this process: after sanitation and preparation, only healthy tissue remains, the crown completely covers them.
Signs of tooth decay under the crown
The first thing the owner of a crown notices is bad breath. Brushing, rinsing, and flossing do not help eliminate it, or give short-term results. Manifestations other than odor:
- Mobility of the crown or tooth.
- Darkening of the visible part.
- Recession of the gums, exposure of the cervical area.
- Unpleasant, purulent taste in the mouth.
- Discharge of pus.
- Redness of the gums.
Defects in metal crowns
Defects in metal crowns
Class I cavities also include defects in metal crowns. Such defects most often occur on the chewing surfaces of premolars, molars and the cutting edge of the anterior teeth.
The cause of metal abrasion can be even a slight increase in the bite on individual cusps of the crown, especially if a sharp cusp of a stable tooth antagonizes the crown.
An even more common cause of metal abrasion is the closure of the crown with the artificial teeth of a removable antagonizing denture. Violation of tactile reception due to the presence of a removable denture in the mouth eliminates the dosing of the chewing load, which is the reason for the very rapid erasure of the masticatory surface of metal crowns by porcelain teeth. Sometimes the same thing is observed when dentures antagonize plastic teeth, despite the fact that plastic is many times softer than gold and steel.
The third reason that causes the formation of a defect in metal crowns is their long-term use. Crowns become thinner from mechanical stress during chewing and from a toothbrush.
Leaving a crown with a defect is unacceptable, since the cement that fixes the crown inevitably begins to dissolve, followed by decalcification of the tooth, and a carious process develops in the area of the crown defect.
Conventional filling of a carious cavity through a defect does not stop the resorption of the fixing cement under the crown, since it is impossible to create a seal between the edge of the defect and the filling.
Previously, the only reliable means of preserving the abutment tooth was to replace the entire bridge. Often, replacing an old bridge or crown is extremely undesirable, since it may entail alteration of a plate or clasp prosthesis if defective crowns cover the abutment teeth for a removable denture. Using an inlay, you can easily eliminate a small defect in a metal crown while preserving the bridge or crown.
To decide whether it is advisable to restore the crown, it is necessary to comprehensively examine and evaluate it from the point of view of its further suitability. If the crown completely covers the neck of the tooth, is securely fixed with cement and is not thinned over time, then restoration of such a crown with an inlay is advisable.
It is better to replace a single defective crown with a new one, except in cases where it is a support for a full-fledged clasp or plate prosthesis.
It is possible to form a cavity in the presence of a defect in the metal crown only in cases where the tooth is not affected by caries or if the resulting carious cavity is surrounded on all sides by still healthy tooth tissue (Fig. 19, a).
If there is no layer of healthy tooth tissue left between the metal crown and the formed cavity, then such an inlay will not hold (Fig. 19, b).
If a crown covers a badly damaged tooth and only a thick layer of cement is found under the defect of the crown, then in this case the fixation of the inlay will be unreliable and it may be considered more appropriate to replace the crown.
Consequently, a well-preserved bridge prosthesis in the presence of strong walls of the abutment tooth should be considered an absolute indication for restoring a defect in a metal crown with an inlay.
A gold crown is restored with a gold or plastic inlay, and a steel crown is restored with steel, plastic or alloys made from Lipets, Citrine, etc.
Since when forming a cavity, the walls of the tooth should be preserved on all sides of the inlay, the direction of the walls may deviate from strictly vertical. At the same time, one should not forget about the topography of the pulp.
For good fixation of the inlay, taking into account the layer of cement under the crown, it is advisable to give the cavity a well-shaped shape.
It is necessary to begin the formation of the cavity with a slight expansion of the defect, since the edges of the crown around the defect are usually thinned. It also helps determine whether the cement is retained under the crown.
It must be especially emphasized that the cavity cannot be given the correct geometric shape (square, circle, triangle, etc.), as this makes it difficult to orient the position of the inlay during fitting and cementing.
If it is not possible to create guidelines that determine the position of the tab in the cavity itself in the form of additional bays, then you can make a small depression at the bottom of the cavity, protecting the pulp from accidental opening. The protrusion on the finished tab corresponding to this recess will serve as a guide (Fig. 19, a). If a very deep well-shaped cavity is needed, the walls should diverge slightly (see Fig. 15, a).
The formation of the cavity ends with the creation of a fold in the thickness of the metal so that the future inlay, having the shape of a rivet, moves 0.5-1 mm onto the surface of the crown.
How to place a crown
If installation is required on the front teeth, the nerve must be removed, because when grinding the structure, the pulp can be burned. In premolars and molars, soft tissues are left if they are not involved in the pathological process.
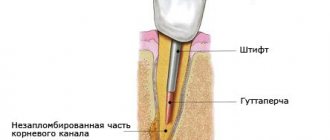
After treatment, preparations begin for installation and production of the prosthesis. First, the doctor cleans the tooth surface and strengthens the remains of the tooth. If this is not possible and it is almost completely destroyed, a pin and a temporary crown are installed. After this, the laboratory prepares a permanent structure based on the casts. The specialist must accurately make the prosthesis not only in shape, but also in color, so that it does not differ in appearance from other teeth. Next, the temporary crown is replaced with a permanent one. Now we will find out whether caries can develop under it.
Symptoms
The following symptoms may be a signal that a prosthetic molar covered with a crown has begun to rot:
- a very heavy, putrid odor that does not go away after cleaning and rinsing the mouth;
- black color of the tooth covered with a crown;
- sharp pain from the prosthesis (as a rule, occurs if the canals of the prosthetic molar are not removed);
- severe swelling of the muscle covering the gum near the implant, as well as the cheeks;
- a cavity under the crown that can be felt with tongues. It is in it that pathogenic bacteria develop, causing the process of decay.
Important: if any of the above symptoms appear, you must visit the dental office as soon as possible. Delaying or completely ignoring the problem can result in it rotting completely and having to be removed.
Can there be caries on the crown?
Many patients are concerned about whether caries can develop on a crown that was installed instead of the coronal part of the tooth. The microprosthesis is a composite material on which bacteria cannot grow. To do this, they need organic tissue, not artificial. The crown can break off as a result of injury or fall out if it is not installed correctly, but it is not susceptible to cariogenic bacteria and their metabolic products.
If you notice a chip or other defect on the structure, contact your dentist. If the damage is not your fault, the crown will be replaced under warranty.
Advantages of treatment at the GDenta clinic
GDenta dentistry installs crowns on 1 tooth using high-quality materials and advanced equipment. We provide a guarantee for prosthetics services and related manipulations. Do not delay treatment if installing a prosthesis is currently beyond your means: our clinic provides interest-free installments.
We try to make prosthetics a gentle procedure, therefore we ensure the physical and psychological comfort of patients. Our doctors develop an individual treatment plan for each patient. Sign up for prosthetics by calling: +7 (495) 312 2504 and +7 (925) 891 8353. We are waiting for you at the address: Moscow, st. Podolsk cadets, 3.
Causes of darkening of enamel
Discoloration of enamel and dentin can be caused by:
- carious lesion,
- pulp necrosis,
- long-term use of tetracycline antibiotics in high dosages,
- violation of the acid-base balance in the oral cavity,
- overdose of fluoride or zinc,
- smoking,
- some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract,
- improper filling,
- excessive consumption of coloring foods and drinks - black coffee, strong tea, pomegranate and grape juice, soy sauce, blueberries and blackberries.
To return the enamel to its natural color, you need to make an appointment with a dentist. The doctor will determine why the crown of the tooth has darkened and will suggest the optimal restoration method, taking into account the age and health characteristics of the patient.