Surgeries and manipulations in the oral cavity almost always require anesthesia. For different procedures, different methods of anesthesia are used, for example, when performing cosmetic procedures (plaque removal, teeth whitening), an application technique is sufficient, when the anesthetic is applied to the gums in the form of a gel or spray. This method allows you to neutralize the pain sensitivity of the upper layers of the mucosa.
Swelling of the upper lip
More serious procedures (treatment and extraction of teeth, operations on the mucous membrane) require the introduction of an anesthetic deep into the tissues using an injection (infiltration and conduction techniques). Each type of anesthesia can cause swelling of the soft tissues of the face and oral cavity, including the lips. The reasons why the lip is swollen after anesthesia may be different.
Allergic reaction
Anesthetics are a common cause of allergic reactions, including manifestations in the form of tissue edema. As a rule, with allergies, after the administration of an anesthetic, swelling appears quickly, within the first thirty minutes and quickly spreads to the surrounding tissues. The patient himself, under the influence of anesthesia, may not feel any changes and notices that the lip is swollen only after the effect of the drug has stopped. An allergic reaction, accompanied by tissue swelling after anesthesia, will be noticeable to the dentist, he will take emergency measures and give recommendations for treatment.
In addition to a reaction to the anesthetic, the cause of allergic swelling of the lip can be an allergy to other agents used during the treatment process (filling material, antiseptics, and even latex gloves on the dentist’s hands). As a rule, allergic swelling is not accompanied by pain.
Why does lip swelling occur due to anesthesia, and what measures should be taken?
Surgeries and manipulations in the oral cavity almost always require anesthesia. For different procedures, different methods of anesthesia are used, for example, when performing cosmetic procedures (plaque removal, teeth whitening), an application technique is sufficient, when the anesthetic is applied to the gums in the form of a gel or spray. This method allows you to neutralize the pain sensitivity of the upper layers of the mucosa.
More serious procedures (treatment and extraction of teeth, operations on the mucous membrane) require the introduction of an anesthetic deep into the tissues using an injection (infiltration and conduction techniques). Each type of anesthesia can cause swelling of the soft tissues of the face and oral cavity, including the lips. The reasons why the lip is swollen after anesthesia may be different.
Allergic reaction
Anesthetics are a common cause of allergic reactions, including manifestations in the form of tissue edema. As a rule, with allergies, after the administration of an anesthetic, swelling appears quickly, within the first thirty minutes and quickly spreads to the surrounding tissues. The patient himself, under the influence of anesthesia, may not feel any changes and notices that the lip is swollen only after the effect of the drug has stopped. An allergic reaction, accompanied by tissue swelling after anesthesia, will be noticeable to the dentist, he will take emergency measures and give recommendations for treatment.
In addition to a reaction to the anesthetic, the cause of allergic swelling of the lip can be an allergy to other agents used during the treatment process (filling material, antiseptics, and even latex gloves on the dentist’s hands). As a rule, allergic swelling is not accompanied by pain.
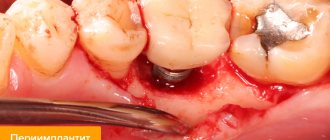
Infectious process
The patient the next day after visiting the dentist may notice that the lip is swollen or pulled to the side if infectious complications have developed both after pain relief and the operation itself. In case of infectious inflammation, swelling of the lips will be accompanied by pain at the injection site or along the nerve fiber. The lip will be hot and tight to the touch. Body temperature may rise, and symptoms of intoxication will appear: weakness, chills, dizziness, nausea.
Due to the proximity of the oral cavity to the brain and other vital organs, if the symptoms described above appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid progression of the infection.
Hematoma
A patient may experience a feeling that the lip is swollen if, during anesthesia, a needle enters a vessel and a hematoma forms in the tissues. In this case, the lip will have a local seal; if blood has accumulated near the surface of the skin, a bruise may be visible. The hematoma is accompanied by pain and tenderness when pressed.
The formation of a hematoma does not require treatment; the blood will gradually resolve and the swelling will subside. If pain and swelling persist for several days, their intensity does not decrease or increases, you should consult a doctor, as the bruise may fester.
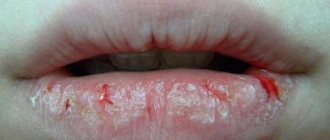
Mechanical damage
Often the effects of anesthesia continue for several hours after surgery, accompanied by a lack of sensation. In this case, a person can injure his lip by biting it, or cause damage with cutlery or a cup of tea. After the anesthetic wears off, the lip will appear swollen.
Damage to the nerve trunk
As a rule, the patient may notice that the lip is swollen and the face is distorted if, during the process of conduction anesthesia, damage to the nerve trunk innervating the lower jaw and soft tissues of the lower lip occurs. Such an injury will manifest itself as pain in the area of innervation of the damaged nerve; symptoms will persist for a long time (several months). The feeling that the lip is swollen may be accompanied by impaired sensitivity and limited range of motion in the mandibular joint.
Treatment of neuritis and neuralgia of the mandibular nerve is carried out by both maxillofacial surgeons and neurologists. As a rule, restoration of function will require long-term combined treatment with medications and physical procedures.
Infectious process
The patient the next day after visiting the dentist may notice that the lip is swollen or pulled to the side if infectious complications have developed both after pain relief and the operation itself. In case of infectious inflammation, swelling of the lips will be accompanied by pain at the injection site or along the nerve fiber. The lip will be hot and tight to the touch. Body temperature may rise, and symptoms of intoxication will appear: weakness, chills, dizziness, nausea.
Due to the proximity of the oral cavity to the brain and other vital organs, if the symptoms described above appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid progression of the infection.
Lip frenuloplasty
Another operation that requires surgical intervention is plastic surgery of the frenulum of the upper lip. It is carried out on the recommendation of an orthodontist (for example, if the patient needs to correct the bite in the future using a plate or braces) or a speech therapist (if the frenulum interferes with articulation).
The labial frenulum is responsible for additional attachment of the upper or lower lip to the jaw bones. Most often the upper frenulum undergoes surgery. This operation does not take long and does not have any negative physiological or aesthetic impact on the patient’s health and appearance.
Rules of care after frenuloplasty
If you have undergone this minor operation, then you need to know about the rules of oral care for the first time after the operation.
Two to three hours after the operation, you can apply cold to the lip. It is strictly forbidden to consume hot food on the day of the operation. Brushing your teeth in the next 24 hours is also undesirable, as is rinsing your mouth. Every other day, you can rinse your mouth with chamomile infusion.
Avoid contact of the operated surface with the tongue and dirty hands. Do not touch the wound. If you feel itching and burning at the operated site, you can take a pain reliever. But remember that taking aspirin is strictly prohibited, since it affects blood clotting.
Hematoma
A patient may experience a feeling that the lip is swollen if, during anesthesia, a needle enters a vessel and a hematoma forms in the tissues. In this case, the lip will have a local seal; if blood has accumulated near the surface of the skin, a bruise may be visible. The hematoma is accompanied by pain and tenderness when pressed.
The formation of a hematoma does not require treatment; the blood will gradually resolve and the swelling will subside. If pain and swelling persist for several days, their intensity does not decrease or increases, you should consult a doctor, as the bruise may fester.
What does flux look like?
It is of infectious origin, the process occurs against the background of inflammation of the body of the jaw or in the periosteum. Flux is formed not only after dental surgery, but also after furunculosis or tonsillitis. If the cheek and gums are swollen, there is throbbing or mild pain, in advanced stages pus may appear and the temperature may rise. On the upper jaw, the flux covers the lip, cheek, gum and nasolabial area. In addition to the face, the infection often spreads to the neck.
Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are used for treatment. After using topical medications, you should not eat or drink liquids for 2 hours.
Mechanical damage
After anesthesia, numbness may persist for several hours
Often the effects of anesthesia continue for several hours after surgery, accompanied by a lack of sensation. In this case, a person can injure his lip by biting it, or cause damage with cutlery or a cup of tea. After the anesthetic wears off, the lip will appear swollen.
Damage to the nerve trunk
As a rule, the patient may notice that the lip is swollen and the face is distorted if, during the process of conduction anesthesia, damage to the nerve trunk innervating the lower jaw and soft tissues of the lower lip occurs. Such an injury will manifest itself as pain in the area of innervation of the damaged nerve; symptoms will persist for a long time (several months). The feeling that the lip is swollen may be accompanied by impaired sensitivity and limited range of motion in the mandibular joint.
Treatment of neuritis and neuralgia of the mandibular nerve is carried out by both maxillofacial surgeons and neurologists. As a rule, restoration of function will require long-term combined treatment with medications and physical procedures.
Surgery
After surgery, swelling and tenderness may persist for several days
Tissue swelling is a natural reaction of the body to surgery. If complex treatment or removal of a molar tooth was performed in the oral cavity, extensive surgery on the mucous membrane, swelling of the lip may be a consequence of such intervention. In addition to swelling of the soft tissues, the patient notes pain in the surgical wound. In this case, the symptoms should go away on their own within a few days without consequences.
After tooth extraction, the cheek is swollen: how to get rid of the swelling on your own?
It is necessary to strictly follow the rules: exclude physical activity immediately after the operation, completely abstain from food for three hours (and until complete healing, eat only soft food), do not touch the hole (neither with your tongue nor with your hands). If, even if you follow all the rules, swelling occurs, but it is not so large and painful that you need to see a doctor, you can easily cope with it yourself by using one of the following methods:
- Cold compress.
Cold can deal with both swelling and pain, you can use: a bottle of water, a damp cloth, ice cream, and so on.
- Compress “soda + salt”.
1 spoon of soda + half a spoon of salt. This mixture must be applied for 10-20 minutes every 1-1.5 hours.
- Decongestants.
Gels and ointments help cope with swelling that occurs even after difficult removal. The main thing is to consult a doctor before use.
- Don't worry and take sedatives.
Tooth extraction is always stressful, and as is known, it has a detrimental effect on the general physical condition.