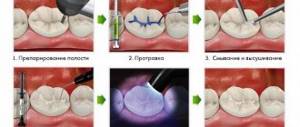
Nowadays, dental problems are one of the common problems among both adults and children. Dental diseases, in particular caries, are suffered no less often than colds. There are several reasons for this - improper dental care, poor heredity, weakened immunity. But, as you know, a disease is easier to prevent than to treat, and it will be easier when you know all its features.
What does early stage psoriasis look like: photo
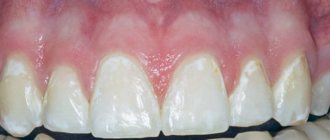
Initially, the patient experiences a sudden appearance of reddish rashes on the arms, legs, elbows, torso and part of the head covered with hair. When the disease manifests itself in young children, the signs may be mistaken for diathesis. Sometimes the baby begins to be actively treated for an allergic reaction. Symptoms in children may appear in atypical places. Typically, the disease affects areas that are most often subject to friction from clothing.
Of course, the insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that correct diagnosis does not always occur in a timely manner. Meanwhile, the further outcome of the disease depends on the correct decision of the doctor. With prompt help, psoriasis can subside for a long period.
The primary element is a red-pink pimple with clear boundaries and a rounded shape. The plaques are covered with gray scales that can be easily separated. Inflammation is noted at the site of the pathological process, and swelling can be visualized on the skin. Often the formation of a specific rash is accompanied by severe itching.
To accurately diagnose the disease, the papule is scraped. With this manipulation, characteristic symptoms appear, called the psoriatic triad.
- Stearic stain phenomenon. If you scrape the plaque, its surface will be white, and the scales covering it will peel off. The treatment area will resemble a drop of stearin that has been thoroughly ground.
- Thermal film phenomenon. If the scraping is prolonged, then after removing the scales, a reddish surface is clearly visible on the skin.
- Blood dew phenomenon. Prolonged mechanical contact with the papule provokes the formation of very small drops of blood. This sign indicates that the patient has pinpoint hemorrhages.
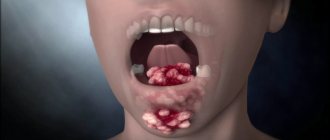
In some cases, the manifestation of psoriasis at the initial stage is accompanied by the presence of exudative complications. That is, the scales will absorb serous fluid and form a rough crust on problem areas. When such a defect is removed, a weeping island of skin remains.
The danger is that type 2 bacterial infections can penetrate through such wounds. The progression of the disease is characterized by the formation of plaques of impressive size, which affect large areas of the patient’s body.
Causes and types of complications
The culprits in the development of caries and its complications are streptococcus bacteria – Streptococcus sanguis, mutans, viridans. These pathogenic microorganisms oxidize and destroy tooth enamel, and then penetrate deep into the hard tissue through the dentin canals.
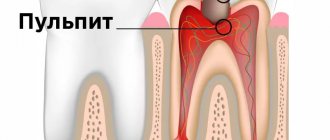
In the absence of proper treatment, the infection affects the coronal part of the soft tissue, the pulp, and the first stage of complicated caries occurs - acute pulpitis.
Pulpitis
When the infection reaches the pulp, an inflammatory process begins in the neurovascular bundle of the tooth in the form of:
- acute focal;
- diffuse (general) pulpitis,
a characteristic symptom of which is severe, throbbing pain in the tooth and increased sensitivity to cold.
If you do not go to the dentist with pulpitis in the first 2-3 days, the acute stage of the complication becomes chronic and develops:
- fibrous;
- hypertrophic;
- concretory;
- or gangrenous chronic pulpitis.
With chronic pulpitis, the inflamed tissue of the neurovascular bundle degenerates and is gradually destroyed, dentin formation in the tooth stops, and it becomes dead.
Over time, decay processes reach the peri-apical tissues and ligamentous apparatus - periodontium.
Periodontitis
Between the root of the tooth and the alveolus there are periodontal tissues, they act as a shock absorber during chewing and hold the tooth in the socket.
With periodontal inflammation, periodontitis, the integrity of the tooth ligaments is disrupted, the jawbone becomes infected and damaged.
Symptoms of acute periodontitis:
- acute pain when biting or touching a tooth with the tongue;
- pain is transmitted along the trigeminal nerve - to the temple and jaw;
- general malaise, deterioration of health;
- increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees.
The acute phase with severe pain lasts from 2 to 14 days, after which the disease takes on a chronic form.
With chronic fibrous or granulating periodontitis, a fistula, that is, a through hole, can form in the gum. Patients also complain of a feeling of the diseased tooth moving out of its row and attacks of aching pain.
Granuloma
An advanced form of chronic periodontitis, granulomatous, leads to the formation of a capsule with exudate (pus) at the apex of the tooth - granulomas.
The gums of the diseased tooth become inflamed, patients complain of a feeling of bulging bone and persistent, severe pain.
A granuloma that is not eliminated in time can cause the formation of gumboil or a cyst at the root of the tooth.
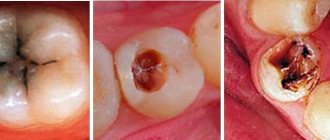
Multiple caries
Another common type of complication is multiple (acute, blooming) caries, in which the infection simultaneously affects the coronal part of eight or more teeth.
In record time, caries destroys the enamel-dentin junction, penetrates the pulp and leads to tooth loss. The infection affects the cement on the roots of adjacent teeth, and the patient feels as if the entire dental arch hurts. Most often, multiple caries is detected in people with diabetes and preschool children.
Stages of psoriasis: photos
With psoriatic disease, patients experience 3 stages of development:
- Progressive. The onset of the disease can be very violent, and suddenly the skin is dotted with nodular-type rashes. They are smaller than the head of a pin. On the top of each papule, a gray scale is visible. As psoriasis spreads, the rash will begin to grow, intense itching occurs, and plaques will form. Due to the possible weeping state of the inflamed area, an infectious lesion is often associated with the disease.
- Stationary. After a period of time, the inflamed nodules stop developing. They do not disappear, but the formation of new foci is not observed. A crust may appear on the plaques, but there is no inflammatory process.
- Regressive. The final cycle of the disease begins; it should not be confused with recovery. The process may appear again as soon as a provoking factor arises. Resorption and reduction of plaques occurs from the middle of formation, therefore, by the end of the stage, the patient may have rings or other strange shapes on the skin. Pretty soon all the papules will disappear, and there will be no trace of inflammation and itching.
How do dentists define the concept of caries and its causes?
Dental caries is known as one of the most common dental diseases that almost every person on the planet has encountered. This pathological process is caused by microorganisms that live in the oral cavity. They process the carbohydrates we eat and produce organic acid. It is this acid that contributes to the destruction of enamel, dentin and other tooth tissues.
The more carbohydrate foods (sweet, starchy) in the diet, the more comfortable cariogenic microbes feel, the more actively they multiply, and the more acid they produce. Therefore, the carious process is more active.
On hands
Initially, clear papules of a bright color appear on the skin; they can be moist and covered with silvery scales. The inflamed area is limited, swelling and hyperemia are noticeable on it. The patient complains of constant itching at the site of the lesion. It is noted that the problem is localized on the part of the palm or elbows where flexion movements occur.
Subsequently, the patient’s process stabilizes, and no new foci of psoriasis are detected. The scales spread over the entire surface of the problem area. The skin is light in color and thin in places. This stage can last more than one month.
After each new relapse process, the manifestation of psoriatic disease will intensify. The disease that affects the patient’s hands can lead to significant coarsening and thickening of the skin at the sites of the pathological process.
Caries: what is it?
Caries leads to the destruction of hard dental tissues and the appearance of a hole in the tooth. This process occurs due to harmful bacteria. Here are just some of the reasons that can lead to caries:
- Poor nutrition.
- Untimely and improper dental care.
- Bad ecology.
These reasons can influence the formation of caries even in childhood; by the way, it is in childhood that the risk of caries is most likely and common - more than 70% of children suffer from this disease.
On foot
The onset of the disease begins with the formation of pimples, which are covered with small scales. As psoriasis progresses, the fusion of papules and the formation of new inflamed areas are noted. The active development of the problem is accompanied by significant itching.
In the acute course of the disease, skin problems begin to develop in places where the skin is injured. In this case, old papules may be inactive, differing only in peeling.
The transition to the stationary stage is characterized by the cessation of the formation of new manifestations of the disease, and the scales almost completely disappear from the problem areas. Where there were previously papules, a different pigmentation is noted.
The onset of the regressive stage means an improvement in the patient's condition. Psoriatic plaques almost completely disappear, there is no itching or flaking on the skin.
Diagnostic methods
To accurately determine the nature of dental damage, doctors use many methods. The main types of diagnostics include:
| Inspection of the tooth surface with staining to identify carious spots. |
| Probing. Allows you to determine the depth of the carious cavity, assess the condition of the pulp chamber, the density of the affected tissue, and the degree of pain. |
| Electroodontometry. A test to determine the degree of excitability of the pulp. Normally, in an inflamed or necrotic state, it reacts differently to irritation. |
| Percussion (tapping). In case of caries, the procedure is painful for the patient; a healthy person will not pay attention to it. |
| X-ray. Using interproximal radiography, it is possible to identify hidden caries and determine the depth and extent of tooth damage. The method is used only in combination with other diagnostic methods. |
These methods are applied only to carious teeth; healthy teeth are not subject to unnecessary diagnostics. Only a doctor with special education can determine what the research should be like. The patient can assist by providing the results of previously performed diagnostics. Using them, dentists determine how long ago the problems arose, how quickly dental caries and its complications develop.
Complications of caries
The destroyer of tooth enamel and dentin, caries, can lead to tooth loss and also cause severe inflammation of the pulp, peri-apical tissues and jaw.
Cariogenic bacteria streptococci, which form hollow cavities in untreated teeth, tend to infect the connective tissues that make up most of our organs. And this is fraught with the development of diseases such as endocarditis, chronic tonsillitis, lymphadenitis and abscess.
How quickly advanced forms of caries develop
Typically, from the moment a carious spot appears on the enamel to the formation of deep caries, it takes from 1 to 4 years; the infection affects root canals 2 times faster.
But there are cases when complete tooth destruction and the formation of complications occur in just 3-4 months; this is acute caries. The reason for this is individual resistance, that is, the susceptibility of teeth to caries.
Signs that caries has reached the deep layers of dentin:
- the appearance of short-term pain;
- increased sensitivity to cold and hot;
- bad breath.
And not always, when the form is neglected, the tongue rests on a deep relief cavity in the tooth - sometimes it is just a small hole in the enamel, behind which lies an almost completely destroyed tooth.
On the head
When psoriasis begins to develop, the patient notices that inflamed areas appear at the edge of the scalp. There is peeling on them, the plaques will quickly increase in size. In this case, entire plates of problem areas are possible, noticeable in the forehead area.
After a month, the patient does not notice the growth of new plaques, but the old ones will begin to become intensively covered with scales. Since the problem is localized on the entire surface of the head, some people mistake this symptom for dandruff.
With adequate therapy, symptoms can be completely relieved and problem areas can be cured within a few months.
Rules for treatment at home
Today, it is not necessary to treat psoriasis in a hospital setting. Modern medicine can offer many techniques that allow you to stop the manifestation of the disease at home. Moreover, psoriatic disease does not go away completely, but only goes into remission.
The purpose of the manipulations is to control the course of psoriasis and increase the period without exacerbations.
The following forms of medications are suitable for treatment:
- lotions or shampoos;
- herbal infusions or baths with the addition of herbs;
- UV irradiation.
To obtain a pronounced therapeutic effect from the therapy, the patient must adhere to certain rules:
- All prescribed medications must be used as prescribed, without deviation from the dosage schedule.
- If there are no severe symptoms of the disease, then treatment with mild herbal remedies is possible. Provided that the course of the disease is determined to be severe, it is mandatory to take medications containing hormones.
- The skin in places of the pathological process should be sufficiently moisturized.
- The crusts of the plaques will gradually become softer; they must be removed in a timely manner if they have moved away from the skin. By regularly cleaning the inflamed area from scales, the absorption of medicinal forms will occur more quickly.
- At home, treatment is expected using simplified regimens. Complex therapy, including several medications and ointments, is not recommended.
- There must be a period of time between courses, usually the break can be up to 12 months.
- In case of psoriatic disease in a child, it is necessary to exclude factors that can provoke a relapse. Sometimes the therapeutic effect is achieved through dietary adherence.
- The disease requires observation, therefore it is necessary to regularly visit specialized centers. In this case, treatment tactics should be discussed with a dermatologist, after which possible adjustments are made.
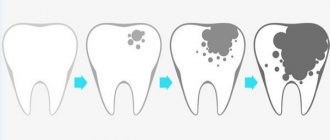
Development of caries using the example of tooth structure
To understand the process of caries development, it is worth first studying the structure of the tooth. Human teeth consist of several “layers”:
- The outer, strong one is enamel. It is with damage to the enamel that caries begins - the tooth begins to decay. If this process is not stopped in time, the destruction will spread to the next layers, and this is fraught with complete loss of the tooth.
- The second layer is dentin. This is soft tissue, when damaged, the sensitivity of the tooth to hot, cold, sweet, and any mechanical influences significantly increases.
- The dental pulp is the next layer. This is loose tissue in which nerve endings, blood and lymphatic vessels are located. If the pulp is damaged (this is no longer caries, but pulpitis), doctors open the tooth and remove the nerves, clean the canals, treat it with medications and put a filling. They do this in order to preserve their tooth for as long as possible and not replace it with an artificial one. Over time, such a “dead” tooth without nerves begins to darken and should be covered with a crown.
It is extremely important not to lead caries to pulpitis, to treat minor enamel damage immediately. This will help prevent tooth loss.