From this article you will learn:
- what is superficial caries,
- what is the peculiarity of this form of caries,
- superficial caries - treatment.
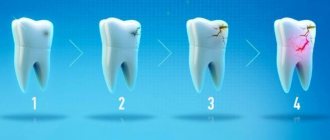
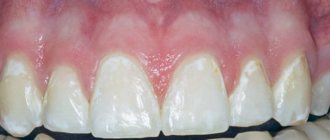
Superficial caries is a form of carious tooth damage in which the resulting carious defect does not extend deeper than the enamel-dentin junction (Fig. 1-3). Thus, tooth decay will only be observed within the confines of the tooth enamel. If the carious process extends to the upper layers of dentin, then in this case medium caries is already diagnosed.
Superficial dental caries usually develops in areas of focal demineralization of tooth enamel, which appear as white chalky spots. Such white spots are nothing more than the initial reversible form of caries. Foci of demineralization occur when there are accumulations of microbial plaque, which metabolizes food debris stuck between the teeth, turning them into acids. Organic acids, in turn, upon contact with tooth enamel, begin to dissolve its mineral matrix.
Superficial caries: photo
Exposure to organic acids does not immediately lead to the appearance of a carious defect. Initially, the structure of the enamel will be preserved, but its surface, due to the loss of calcium and fluoride, becomes chalky white and also loses its shine. If exposure to organic acids continues, then further loss of calcium leads to the destruction of the enamel structure itself over the entire surface of the white spot or in some areas of it, i.e. a superficial carious defect occurs (Fig. 3).
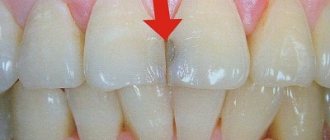
Favorite places for localization of superficial caries are the necks of teeth. This is due to the fact that this is where soft microbial plaque most often accumulates. If the patient has a large amount of microbial plaque (Fig. 4), then after its removal during professional hygiene, almost always on the surface of the teeth you can see foci of demineralization of tooth enamel, or foci of superficial caries, or both.
Accumulations of soft microbial plaque –
Causes of caries
The carious process occurs as a result of the influence of various factors on the human body - external and internal. But the main cause is cariogenic microorganisms, the waste products of which destroy the solid components of the enamel. The acidic environment created by these bacteria corrodes the outer coating of the tooth, which does not have time to recover naturally. There are fewer minerals in the enamel, it softens and cannot fully protect the internal dental tissues from external factors. The area of demineralization gradually increases and forms a carious cavity.
However, microbes alone are not enough to cause caries. There must be factors predisposing to the disease. The main ones are:
- Poor oral hygiene. Food debris stuck in the interdental spaces is a favorable environment for the active proliferation of bacteria. Also, irregular tooth brushing causes plaque formation, and one gram of dental plaque contains over 250 billion microbes. In this regard, caries often affects people who neglect basic hygiene rules.
- Abuse of sweet foods. Sweets disrupt the balance of minerals in the oral fluid. Because of this, trace elements are washed out from the enamel. It becomes vulnerable to bacteria that feed primarily on carbohydrates. For this reason, children who eat sweets in large quantities are more likely to suffer from caries.
- Abnormal structure of teeth: crowding, malocclusion, deep narrow fissures, etc. This complicates the process of cleaning the mouth from food debris and plaque.
- Genetically determined weakness of enamel, congenital pathologies affecting the condition of teeth and bones.
- Decreased salivation. Saliva contains substances that neutralize acids produced by bacteria. With insufficient salivary fluid production, microbes multiply faster.
- Lack of phosphorus, fluorine, calcium and magnesium in the body, which ensure the resistance of enamel to external factors.
Now let's look at the main reasons why superficial caries occurs.
Possible complications
Some parents are in no hurry to visit a pediatric dentist because they consider it useless to treat baby teeth. This approach is explained by the fact that permanent ones will grow instead of them anyway.
Although the carious process itself does not transfer from baby teeth to permanent ones, untreated caries lesions have a detrimental effect on the condition of the latter. If you ignore superficial caries in children , complications may very soon manifest themselves:
- caries progresses rapidly in the absence of adequate therapy. This leads to the development of periodontitis and damage to the molar tooth germ. The inflammatory process significantly slows down the eruption of permanent teeth and complicates their growth;
- premature loss of baby teeth leads to the formation of malocclusion and disrupts the structure of the maxillofacial system;
- If at least one tooth is missing in the dentition, this complicates the process of chewing food. As a result, problems arise with the functioning of the digestive system.
Remember! Even the smallest stain can lead to complete tooth decay. There is no need to risk your child's health. It is much easier to visit the dentist and, if necessary, treat caries.
Reasons for the transition of caries from the first stage to the superficial
The initial stage of caries is called the white or chalky spot stage, when an area of demineralization forms on the enamel. It does not have time to recover and gradually collapses. Externally, the white spot differs from the healthy part of the tooth: it is not shiny and has a rough structure. However, at this stage of caries development there are no complaints from the patient. He does not feel discomfort while eating or brushing his teeth; There is no increased tissue sensitivity or other symptoms. The disease can only be detected during an examination by a dentist.
Lack of treatment leads to further demineralization of the enamel. Bacteria continue to multiply in the oral cavity. Bad habits, consumption of sweets and other factors can aggravate the situation. Superficial caries affects only the enamel; the internal tissues of the tooth are not yet involved in the pathological process. In this case, the patient begins to complain of pain after eating sweets. The pain goes away immediately after the irritant is removed. There may also be discomfort when the tooth is exposed to hot or cold drinks.
At the second stage, it is still possible to stop the pathology through remineralization, that is, without installing a filling. Let's look at the types of superficial caries.
There are two manifestations of average caries:
- Chronic May last a long time and not manifest itself in any way. Layers of dental tissue are gradually affected. Pathology can develop over several years. This is fraught with transition to a more advanced form, deep caries, and even threatens tooth depulpation and canal filling.
- Acute Rapidly developing stage. Perhaps an acute reaction to various irritants, which quickly passes after their removal. This form is characterized by an abundance of softened dentin on the walls and bottom of the tooth cavity with sharp and fragile edges
The chronic form of caries can transform into pulpitis.
Classification of early stages of caries
At the first and second stages, hydroxyapatite, the main substance of enamel, is destroyed. It forms 5 pathological zones, which differ from each other in the depth of penetration into the tooth tissue. Each of these zones has its own characteristics:
- Superficial: stable and dense zone with small microporosity in the area of demineralization.
- Subsurface: in the affected area of the tooth, the calcium content decreases by 15%. Because of this, the permeability of the enamel increases.
- Central: calcium concentration drops by another 25-30%, and the number of micropores increases by 20%.
- Intermediate: mineralization is at a very low level - 2-4%, but the natural process of enamel restoration has not yet stopped.
- Internal: the carious lesion is located closer to the dentin, although within the enamel. There is a risk that superficial caries will progress to the third stage.
Initial and superficial caries can be cured without preparation and filling. However, treatment should be started as early as possible.
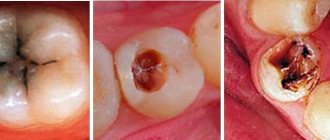
Examples from dentist practice
Unfortunately, even regular visits to the dentist cannot 100% guarantee the timely detection of proximal caries. Very often, especially in the initial stages, teeth look completely healthy.
This is what medium and deep approximal caries looks like upon examination:
But here’s how interproximal caries can be masked, escaping even the dentist’s attention:
It is especially difficult to identify early caries. Therefore, dentists again and again remind us of the importance of preventing oral diseases: even existing caries in the stain stage can be stopped. All you need to do is thoroughly clean the interdental spaces and use fluoride-containing toothpaste.
How is caries diagnosed?
Caries can be detected during an external examination, but some of its symptoms are similar to those of enamel hypoplasia and fluorosis, so differential diagnosis is necessary. To achieve this, dentists use the following methods:
- Treatment of teeth with hydrogen peroxide. Areas of demineralization become more noticeable.
- Caries indicators. The enamel is coated with a special compound that turns the affected areas blue.
- Transillumination is the transillumination of a tooth with a directed beam of light from a special device.
- Fissurotomy: The dentist widens or grinds down the natural grooves on the chewing surface of the tooth to more closely examine the fissures.
- Laser diagnostics. This is the most modern research method. The dentist directs a laser beam at the tooth and illuminates it. The device shows whether there is a carious lesion and how deep it has spread.
- Radiography. It is used for the development of caries at the root or under the gum. The photographs show the carious lesion, its scale and stage.
After the examination, a method of caries treatment is selected.
Diagnostic methods
Clinical diagnosis, carried out as part of an examination of the oral cavity, involves the use of various techniques to determine the degree of development of pathology. Over time, superficial caries can develop into a more severe form that affects dentin and the pulp chamber, so it is important to promptly select the optimal treatment method.
Current examination methods used in clinics include:
- Visual inspection and percussion - assessment of the condition of the dentition by tapping the elements, allowing to identify the patient’s reaction;
- Probing is a technique that allows you to determine the presence of superficial caries by detecting a rough texture on the surface of the enamel;
- Staining – the use of special dyes that form markers in affected areas characterized by insufficient mineralization;
- Antiseptic drying - applying a special composition to the dentition, which, under the influence of a directed light flux, indicates defective areas;
- Differential diagnosis is a procedure that involves comparing the basic symptoms observed in the patient.
The final cost of dental services consists of many factors - as a rule, the price for caries treatment in St. Petersburg clinics is agreed upon based on the results of a preliminary diagnosis, which determines the structure of the treatment plan.
Treatment of superficial caries
For superficial caries, various treatment methods can be prescribed depending on the extent of the carious process. At the very beginning of the second stage, remineralization can be applied, during which a special composition containing large quantities of fluorine and other minerals is applied to the enamel. They strengthen the tooth surface and prevent bacteria from penetrating into dentin.
For home use, the patient is prescribed anti-caries toothpastes, gels and rinses with antibacterial properties: SPLAT Professional “Whitening Plus”, Stomysens® Desensitizing Repairing Treatment, Biorepair Delicate Gums Mouthwash, etc.
Another method of treating superficial caries is Icon infiltration, which does not involve drilling the tooth with a drill. The procedure is carried out in several stages:
- Removal of affected tissue using hand tools.
- Drying the tooth surface with warm air.
- Treating enamel with alcohol or other antiseptic.
- Application of infiltrate - liquid filling.
- Examining the tooth with a lamp, which helps the composition harden.
The procedure is prescribed mainly to children because they are afraid of the drill, but it is also suitable for treating adult patients.
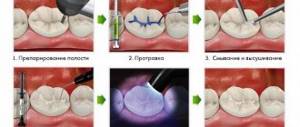
If superficial caries has almost reached the third stage, filling is required. It is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- removal of dental plaque and tartar removal;
- drilling of a carious cavity, preparation carried out using a drill;
- isolation of the tooth crown using an elastic rubber dam;
- antiseptic treatment with chlorhexidine solution;
- applying an adhesive material - a special glue that improves the fit of the filling;
- layer-by-layer filling of the cavity with a filling compound;
- grinding and polishing the hardened filling.
Both procedures are safe and can be completed in 20-30 minutes. They do not cause complications. Filling can be performed under local anesthesia or without painkillers. Modern fillings usually have an unlimited service life. If it is installed correctly, and the patient after treatment is engaged in the prevention of dental diseases, there will be no need to re-treat the tooth.
Diagnosis of hidden caries between teeth
To diagnose the disease, several methods are used that make it possible to detect hidden caries between teeth.
- Visual inspection.
It is carried out to assess the condition of the teeth using a special probe. - X-ray.
On X-rays, carious areas appear as black spots. - Staining or transillumination.
Using staining agents or fluorescent diagnostics, the doctor can detect carious lesions even in the most difficult to reach places.
What happens if superficial caries is not treated?
If there is no treatment, the pathology continues to progress, and the third, middle stage of carious lesion begins. The patient's enamel and tooth sensitivity increases; he reacts painfully to sweet and sour foods, temperature changes and a toothbrush. The carious cavity extends beyond the enamel and penetrates into the dentin. It is no longer possible to do without preparation and installation of a filling.
Then caries begins to destroy the internal tissues of the tooth. The pain is almost constant; it can occur even in the absence of irritants. This suggests that the pathological process is located next to the pulp or has already affected part of the nerve. During treatment it has to be removed. The tooth becomes dead and darkens. There is a risk of losing it: it can break at any moment. In addition, caries can spread to adjacent tissues. Complications from periodontal and bone tissue are possible.
Complicated caries can cause diseases that are not related to teeth, for example, chronic tonsillitis, sore throat or systemic infection. This happens infrequently, but it is better to exclude the possibility of such scenarios and engage in prevention. Let's find out what it is.
Locations
Interdental caries can develop anywhere in the dentition
. Patients turn to dentists both with caries between the front teeth and with damage to the chewing teeth. The photo below shows an example of the development of caries between the chewing tooth and the wisdom tooth.
Also, carious lesions can occur in both the upper and lower teeth. The infection affects not only permanent teeth, but also baby teeth. Therefore, both children and adults are at risk.
Prevention of superficial caries
Caries prevention should be done from childhood. Dental treatment is expensive, so it is better to make every effort to prevent pathology. To do this you need to follow a number of simple rules:
- Brush your teeth twice a day. For additional care, use flosses, rinses and irrigators.
- Limit your intake of sugary foods, including soda. It is better to eat foods that contain nutrients, vitamins and minerals.
- Visit your dentist once every six months for ultrasonic cleaning. This is especially true for coffee and tea lovers.
- Give up bad habits, especially smoking.
At the first symptoms of caries or other dental diseases, consult a doctor. Don't try to treat them yourself. People with healthy teeth should come for a preventive examination to the dentist at least twice a year, children should be examined even more often - 2-3 times a year.
What is the danger of approximal caries?
Often, a carious cavity is hidden under a layer of plaque at the point of contact of adjacent teeth, and it is very difficult to identify it visually during examination.
The presence of a cavity can be reliably determined by taking x-rays. But how advisable is it to regularly perform x-rays of the upper and lower jaw? This issue is still open for debate.
Difficulties in diagnosis lead to the fact that tooth damage is often detected in the later stages, when deep caries or its complications have already developed: pulpitis, i.e. inflammation of the “nerve” of the tooth, and periodontitis – inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth.
How to diagnose the disease in pregnant women?
Caries in pregnant women is one of the most common diseases. Diagnosis of the disease begins with a detailed questioning by the doctor of the patient about the nature and intensity of pain, as well as the presence of other diseases. After collecting information, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity and diagnoses the teeth for the presence of caries using a probe, mirror, dental floss, etc. Pregnant women are not prescribed x-rays to detect the disease, as this can harm the fetus. Usually the dentist limits himself to a visual examination or recommends the Diagnodent device.
Installation of a filling for initial caries
Treatment of initial dental caries in most situations does not require the use of a drill, but in some cases filling is performed. This usually occurs at the dark spot stage, when the doctor is not confident in the success of remineralizing therapy, and for some reason treatment using Icon technology cannot be carried out. Light filling for initial caries is considered the most effective, since it has high functional and aesthetic indicators.