27.11.2019
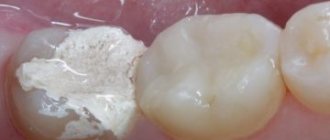
Dental fillings are one of the most common dental procedures. Tooth filling is resorted to in case of damage to the dental crown - to prevent infection from entering, to restore the integrity of the tooth in case of injury, and so on. Currently, doctors use a wide variety of materials to make fillings, and in each specific case the choice depends on many factors - the nature of the filling, the location of the tooth, as well as the wishes and financial capabilities of the patient.
Choosing a filling for molars
For most people, dental fillings are their first dental procedure. It allows you to preserve the organ, its aesthetics and functionality. The latter is especially important for molars. The inability to chew food normally affects a person’s general well-being, not to mention possible diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. This means that fillings for molars must have special requirements. In order to choose the most suitable one from several materials offered by modern dentistry, it is worth knowing the types of fillings, as well as the qualities they require.
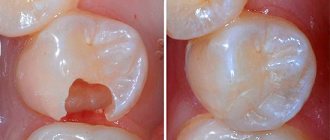
The filling on the front teeth interferes after treatment
In some cases, the design on the frontal incisors prevents the mouth from closing completely; the roughness injures the tongue or the mucous membrane of the lips.
Causes
Trouble arises if sufficient grinding and grinding of the excess surface has not been carried out.
Much less commonly, the cause is an excess of applied material when correcting the interdental gap on the front teeth.
The rarest situation occurs when the wall between the filling and the pulp chamber is thinned. There is a feeling of discomfort that irritates the nerve.
Complications
Ignoring pathology can lead to unpleasant consequences. For example:
- The high position of the artificial structure causes a lot of pressure on the jaw. Pulpitis and periodontitis gradually develop.
- Increases the likelihood of chipping.
- Uneven closing of the jaw contributes to its dislocation and other diseases of the temporomandibular apparatus.
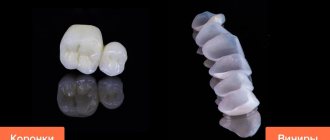
What are fillings?
Dentists have several materials at their disposal with different properties, qualities and prices. Which one to use for chewing teeth is determined by many circumstances, including the size of the cavity being filled.
Sometimes it makes sense to install a tab. But if it is possible to get by with filling, then the choice is made among cement and composite materials, which also come in several types.
Cement
Such fillings have been used for a long time, since there are three subtypes of them, which to varying degrees satisfy the requirements of modern dentistry:
- Silicate. One of the oldest products, consisting of special glass and phosphoric acids. The material is characterized by the release of fluoride ions, which prevent bacteria and the reappearance of caries. A negative quality of silicates is also the formation of phosphoric acid, which can damage the pulp. Therefore, simultaneously with such a filling, an obstacle is installed between it and the nerve in the form of a special gasket;
- Phosphate. From the name it is clear what constitutes the basis of this filling material. This determines its qualities: loose fixation to tooth tissues, fragility, and rapid abrasion. In addition, phosphate fillings are toxic and allow bacteria to enter the cavity, causing caries;
- Glass ionomer. The chemical composition is similar to tooth tissue, which allows for a tight fit during installation. This is also facilitated by the method of hardening the glass ionomer filling under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The dentist has time to carefully fill the tooth cavity with the material. This way, the likelihood of secondary caries is reduced, and the lifespan of the organ is increased. Among glass ionomer cements there are so-called hardened ones. They contain particles of metal or ceramic, which makes the material particularly resistant to any impact, and therefore desirable for filling molar chewing teeth that are subject to heavy loads. The same can be said about nanoionomers. They emit less fluoride, but such fillings firmly “sit” in the tooth cavity, giving bacteria and caries no chance.
Composite
Relatively new materials for filling have already received their share of recognition among dentists and patients.
There are also several subspecies, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages:
Acrylic-containing. They contain a toxic compound, which is why they are not suitable for everyone. This feature becomes a common cause of pulpitis, since acrylic has a very negative effect on this part of the tooth. The material is quite durable, wears out slowly, but absorbs everything that happens in the oral cavity. This increases the risk of caries not only for the filled tooth, but also for those nearby. Acrylic fillings tend to quickly become deformed and “eaten”;
Epoxy. Less toxic and also resistant to abrasion, but break quite easily. The advantage of such fillings is their rapid and uniform hardening, which allows them to fill large cavities in the teeth. But this same quality can be considered negative if an inexperienced dentist does not manage to install it correctly within a certain time. In addition, epoxy resin fillings release substances that can destroy the pulp. It will last for 3-4 years, provided there is no heavy load on the tooth;
Light-curing. They are quite durable, due to the fact that their final appearance is obtained as a result of polymerization under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. They tend to shrink over time, although not as much as other composite fillings. Only 70% hardened. To ensure they last longer than 5 years, careful grinding and polishing is required during installation.
There is an even more modern subtype - nanocomposites. The material consists of tiny particles that provide reliable adhesion to tooth tissues and the strength of the filling itself. This is the most suitable option for treating molars. Dentists consider it universal.
Compomers
This material took all the best from composite compositions and glass ionomer cements, from which it received its name. Compomers consist of a monomer, a resin and polyacrylic acid, benzoyl peroxide and an amine. When installed, such a filling polymerizes evenly, which gives it density and ensures uniformity regardless of size.
Despite this, compomers are used mainly for filling anterior teeth. The load falling on the chewing teeth is too great for them. Therefore, dentists are confident that this filling material is not suitable for molars.
Rules for caring for fillings
Despite the fact that many fillings can theoretically last for years, it is recommended to change the materials every 10-12 years. It is recommended to visit a doctor once every six months for hygiene measures. You should also make an appointment with a doctor if:
- short-term pain in the treated area;
- detection of cracks;
- presence of a chip in the filling material.
The dentist can easily replace a bad filling with a new one.
If there is a large amount of restoration material in the cavity, you can ask the specialist to prescribe a gel with a high fluoride content. Its regular application will help strengthen the hard surface and prevent caries from forming again. Filled teeth may also be coated with fluoride varnish during the examination.
At home, it is recommended to use mouth rinses. With their help, you can significantly reduce the number of microbes that cause caries.
Summarizing the above, I would like to note that filling is a serious procedure. To prevent dental treatment under anesthesia from ending with repeated fillings and a double waste of time and money, you should seek help only from reliable, experienced specialists.
What is important for filling molars?
To decide how to heal chewing teeth, it is necessary to highlight what qualities fillings for them should have:
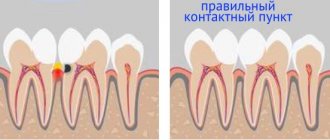
Strength. We are talking about resistance to fracture, minimal deformation over time and low abrasion. The mechanical load on molars is high, so the listed properties are of paramount importance; Tight fit. The presence of this quality will ensure the safety of the tooth, since it is practically impossible for infection, food debris and the development of secondary caries; Unaffected by saliva. The filling should not be easily soluble; Neutrality of the material. Dentists prefer not to depulpize chewing teeth, if possible, in order to preserve them longer. A filling that releases harmful compounds to nerve endings negates these efforts.
Disadvantages of durable fillings
The first and second types of fillings have disadvantages. For example, acrylic fillings are quite toxic and can cause complications after their installation, such as inflammation of the tooth nerve, pulpitis, and secondary caries. Fillings based on epoxy resins have less toxicity, but darken over time.
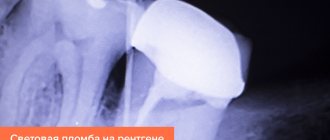
The most used today are light-curing dental fillings (light-composites, gel fillings). Such a filling undergoes polymerization under the influence of ultraviolet light and hardens, although the lamp is also used when installing some cement fillings.
The light filling looks good and aesthetically pleasing, since it can be modeled to match the anatomical shape of the tooth, and it is also possible to choose a shade that matches the shade of the enamel on the patient’s teeth. Over time, the color of the light-curing filling does not change. Such a filling is non-toxic, stable, durable and allows you to restore the shape of even a significantly damaged tooth.
Is it worth filling teeth for free?
It is believed that it is impossible to receive decent dental treatment under the compulsory medical insurance policy either in a state clinic or, especially, in a private clinic. Sometimes this corresponds to reality. But in fact, in the “List of medications for the provision of free outpatient dental care” there are several names of composite and cement filling materials, which may well be used in the treatment of chewing teeth.
The first include:
- Ketak Molar;
- TaLan;
- UniRest;
- FlowRest;
- Evicrol;
- Valux.
These are light-curing materials characterized by low abrasion and shrinkage. A correctly installed photocomposite filling will last up to 10 years. In addition, its aesthetic qualities are beyond praise: there is a large selection of shades, the structure after polishing is similar to enamel.
To ensure that the appearance of the filling remains the same, this procedure is recommended to be done every six months. But since we are talking about molars, for which aesthetics is not of great importance, this is not necessary.
The list of filling drugs that medical institutions must provide to patients free of charge includes glass ionomer cements:
Such materials adhere well to the walls of the cavity, are not subject to rapid abrasion, and are not afraid of a humid environment. Among the disadvantages is their external unattractiveness, but for molar chewing teeth this is not so important.
Unfortunately, among the free drugs there are no strengthened glass ionomer cements, as well as nanocomposites. But if the patient does not have the opportunity to pay for filling out of his own pocket, it makes sense to choose one of the listed materials for the treatment of molar chewing teeth.
The list of drugs for dental treatment for which the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund pays also includes silicate cements Silitsin and Silidont. In the absence of other possibilities, it is permissible to use them in filling primary chewing teeth in children. It is better not to put such a filling on adults. Even if it lasts longer than 3 years, caries will probably develop underneath it.
After teeth filling
In some cases, after applying a filling, the sensitivity of the sealed tooth to external factors may increase: it may “ache” unpleasantly with any temperature change or when air enters. This most often happens when using composite materials. If the tooth remains sensitive two weeks after treatment, you should immediately consult a doctor.
A common cause of pain that occurs immediately after the anesthetic wears off can also be an excessive filling height. In this case, it should be reduced by the dentist.
The application of a filling is always accompanied by final grinding, during which the edges may remain sharp. Due to the action of the injection, this is often not felt immediately. If you notice protruding edges after the anesthetic has worn off, you should contact a dental clinic as soon as possible and make an appointment to straighten the tooth surface.
What is the best filling material?
Many dental clinics offer fillings using several different filling materials. Price lists (including those posted on websites) are also often replete with various commercial names of fillings: Filtek, Spectrum, Aesthetics, Charisma (Karizma), Vines (Venus), Gradia, Estelite, Herculite, Point, Tetrik, Admira, Brilliant, Enamel Plus and others. Patients are asked to make a choice, but this requires dental-level knowledge, which most people, of course, do not possess.
Light
In the professional language of dentists, there are several variations of names for this filling: light, light-composite, gel filling. These terms have a direct connection with the method of curing the filling material. The light seal hardens when exposed to ultraviolet radiation from a special lamp. The hardened material looks natural and aesthetically pleasing. It fits tightly to the edges of the teeth and guarantees long service life.
The difference between light and conventional fillings also lies in the speed at which the material hardens. The components of the light filling polymerize under ultraviolet radiation and harden much faster than the ingredients of the chemical composition. It is very important for a dentist to do everything in 40 seconds. Otherwise, the filling material will begin to crack, since during the hardening process the dental canals are subjected to enormous stress from the inside. Dentists try to avoid this complication. To reduce the risk of cracks, filling material is applied to the canals in stages, in layers.
Attention! The main advantage of a light-curing filling is the ability to restore broken and completely destroyed teeth. The dentist can restore the natural shape of the tooth, its relief, and select the desired shade for full compatibility with the natural color of the enamel.
The light filling literally returns to the patient what seemed hopelessly lost - a realistic tooth and a smile without complexes. But there is also a minus. If the carious cavity is very deep, the dentist will not be able to perform light polymerization and will place a conventional chemical filling in the tooth.
Types of dental fillings
Dental fillings can be temporary or permanent. Temporary fillings are installed for a short period during treatment to protect the pulp (for example, during multi-stage treatment of deep caries) or to retain a medicinal substance in the tooth. Such fillings are made from lightweight, quickly hardening compounds that can be easily removed at the end of treatment. Permanent fillings are designed to restore the function of a damaged tooth. They are installed to last for many years and are made using durable, wear-resistant materials that can withstand natural chewing stress, while being non-toxic and not damaging the edges of the crown. If fillings are installed on the front teeth or premolars, the aesthetic characteristics of the material are also taken into account - compliance with the natural shade and texture of the tooth.
Currently, fillings made from the following types of materials are used in dentistry:
- metal (amalgam);
- cement;
- self-curing composites;
- composite light-polymer;
- glass ionomer;
- combined.
Metal fillings are the simplest and cheapest option. Amalgam contains metals such as silver, copper, zinc and tin. This combination provides the filling with all the necessary characteristics - copper gives it strength, silver increases resistance to corrosion and has an aseptic effect, zinc gives it plasticity, and tin accelerates hardening. Such fillings are strong, durable, abrasion resistant and inexpensive. However, they also have a lot of disadvantages - high thermal conductivity, severe shrinkage during hardening, low level of adhesion (adhesion) to the crown, as well as the risk of poisoning if the production technology of the filling composition is violated.
In addition, they are contraindicated for people who already have metal structures in their mouths - in order to avoid the accumulation of galvanic currents in the oral cavity, the so-called galvanism. Therefore, today such fillings are not very popular and are being actively replaced by other materials.
Cement fillings are still popular today. They are made from a special dental cement that is non-toxic, flexible and easy to harden. Such fillings are inexpensive, their installation is simple and quick, and if necessary, they can be easily removed. However, the advantages of cement fillings also have a downside: light and brittle cement is not very durable, wears out quickly and has poor adhesiveness.
Self-curing composite fillings are made from special composite materials (consisting of more than one component) that contain silicon compounds. Thanks to this, fillings made from such materials have high strength, are resistant to abrasion, but during hardening they shrink significantly, and in addition, they are quite toxic.
Light-curing composite fillings are made from silica and are a more modern version of composite fillings that are more durable and less toxic. Such materials harden only when exposed to special visible blue light, which allows the doctor to adjust the shape as accurately as possible. Today this is the most modern type of filling. However, it also has disadvantages: a certain degree of shrinkage (although much less than that of self-curing composites), as well as incomplete curing - only 70% of the material hardens under the light of a blue lamp.
Glass ionomer fillings are another new development in the field of dentistry. They are made from glass ionomer cement, a plastic, non-toxic material that bonds well to tooth tissue. Glass ionomer cement is actively used in pediatric dentistry due to its high (up to 15%) fluoride content, which prevents the re-development of caries. At the same time, it is very fragile, wears out quickly, and also poorly imitates the natural color of the tooth, which is why the filling does not look very aesthetically pleasing.
Also in modern dentistry, combined fillings are used, combining several types of the listed materials.
Cement materials
Cement differs significantly from composite in its lower hardness, however, it is able to protect the tooth from repeated carious development. A disadvantage is the high density of cement compared to tooth tissue: over time, this contributes to the thinning of the crown surface adjacent to the filling.
Cement compositions have three subtypes, according to additives to the main ingredient:
- silicate;
- phosphate;
- glass ionomer.
Silicate compounds are the oldest of all. The material contains special glass mixed with phosphoric acids. The silicate composition has a different release of fluoride, which prevents the development of dental caries. The harmfulness of the material lies in its aggressive phosphoric acid, which destroys the pulp. To neutralize the effect of acid on the pulp tissue, a special gasket made of safe substances was installed.
Phosphate compounds are characterized by fragility and fragility, weak adhesion (adhesion to tooth tissue), and high abrasion. The peculiarity of these fillings is their high toxicity, which provokes the proliferation of aggressive bacteria. This substance (phosphate) does not protect well against the re-development of caries.
Glass ionomer cement is used to treat children. The substance is as close in texture as possible to dental tissue, has high adhesive characteristics and safety. The glass ionomer is illuminated with a special ultraviolet lamp, which promotes rapid hardening of the material and high-quality tooth protection from infection. The advantages of this material include the fluoride contained in the composition, which protects against the development of recurrent caries.
The disadvantages include fragility - softness and instability of the composition. In modern dentistry, strengthened glass ionomer is used, the composition of which is supplemented with metal or ceramic particles. This material is used for filling chewing molars; it is most resistant to abrasion. The last word in the development of dental materials is the production of nanoionomer, which reliably protects dental tissue from infection and the development of caries.
Which filling is better to put?
The answer to this question depends primarily on where the tooth is located and the extent of its damage. The choice of technical characteristics of the material depends on the location of the tooth.
On molars
Permanent (molar) teeth can be filled with almost anything - the choice depends solely on the priorities of the patient.
The universal requirements for filling materials are non-toxicity and durability, therefore, it is best to give preference to materials with high abrasion resistance and a significant degree of adhesion.
However, in conditions of a limited budget, for small damage, a conventional cement filling with average characteristics is also suitable.
For baby teeth
Filling baby teeth has its own characteristics. Firstly, the tooth enamel in children is less mineralized than in adults and is more susceptible to caries, including secondary ones. Secondly, fillings on baby teeth are weaker. Therefore, a material with high adhesiveness is needed, preferably with an aseptic effect, easy to process and install.
On the front teeth
Placing fillings on your front teeth is not an easy task. What is important here is, first of all, the aesthetic component - the filling material should recreate the natural color and texture of the enamel as much as possible. However, since the load on the front teeth is not as great as on the molars, less durable materials can be used. Composites are best suited - both self- and light-curing.
On chewing teeth
It is necessary to place fillings on the chewing teeth made of a material that can withstand constant load and is resistant to abrasion.
The aesthetic side is not so important - the filling on the surface of the molar is practically invisible.
For molars, amalgams, cement, and composite materials (especially light-curing ones) are well suited.
In what cases is it necessary to install a filling?
The installation of restorative material is carried out not only in the treatment of carious lesions. The procedure is also performed when:
- presence of chips and cracks;
- elimination of consequences after mechanical damage;
- intense loss of hard tissues, leading to almost complete wear of the upper part of the teeth (for example, due to involuntary grinding of the jaws).
It is worth noting that any dental clinic performs filling only in cases where the destruction of the coronal part is insignificant. If the surface of the tooth is damaged by more than a third, it is replaced with an artificial substitute - a prosthesis.
The use of modern materials helps restore the beauty of the smile and chewing function, and also prevents further destruction of the mineralized coating.
Reviews from patients and dentists
Dentists have different opinions about various fillings, but they agree that it is not so much the material that is important, but the quality of the installation. A cement filling installed in free dentistry can last more than twenty years, provided that the procedure is carried out competently and in compliance with all technologies. At the same time, a filling made from an expensive photopolymer, if installed incorrectly, can fall out of the tooth in just a couple of weeks. Experts advise paying attention first of all to the doctor who will perform the procedure and his level of professionalism.
Varieties
Such composites contain:
- silicates – almost 45% consist of silicon, which gives the mass transparency and shine after it has completely hardened. It has a high coefficient of mechanical stability and good strength.
The main difference from other cements is the complete absence of the zinc element in them, which results in its disadvantage - low adhesion to enamel tissues.The process of complete crystallization is about 28 days, which is much slower than analog mixtures. It includes silicic acid, which releases toxins, so when installing such a filling, a gasket is required that does not allow direct contact of silicates with the pulp;
- phosphates – modified zinc-based cements. In terms of their basic physical and chemical characteristics, they are somewhat better than silicates.
At the same time, they are very inferior to them in terms of aesthetics, so they are practically not used for frontal filling. The consistency is more viscous.Such compositions are an ideal option for subsequent covering with decorative crowns. They finally harden just a few hours after the manipulation.
In demand in pediatric dentistry. For complete hardening, it is advisable to exclude direct contact of the composite with saliva;
- glass ionomers – belong to the modern and widely used cements by Russian doctors. They represent an almost ideal ratio of liquid and powder.
It is characterized by good transparency and resistance to the acidic environment contained in saliva, which increases the durability of the material.It does not irritate the natural tissues of the organ and adheres well to them. The material is safe for the pulp. Gives low shrinkage during operation.
Almost all of them, with the exception of the last material, are chemically active components and harden naturally.
Glass ionomer hardens only when interacting with an acidic environment or light wave flows.
What types of fillings are there and which are the best?
Usually at the dentist's office you will be asked, “Which dental filling should you get?” And this question is often confusing, because there are many types of fillings.
In order not to get lost in this issue anymore, let’s figure out what types of dental fillings there are, what are the most reliable and the best types.
In dentistry, they are distinguished by composition and use. These can be plastic, ceramic fillings, as well as temporary and permanent.
Temporary ones are used for long-term treatment, when it is necessary to use drugs inside the cavity, and permanent ones are used for instant treatment at a time.
Dental filling is a classic of dentistry, but it is used for not very large damages; if the defect is particularly large, then an alternative to fillings is used - inlays that can cover larger sizes.
Today, clinics use several different materials to make fillings.
Lost filling on a front tooth
Causes
The reason for material loss may be:
- Neglect of oral hygiene and, as a result, plaque formation.
- Untimely removal of tartar.
- Inflammation of the pulp.
- Mechanical injuries.
- Chewing food with frontal incisors.
- Poor tooth preparation before the procedure.
- Eating seeds, nuts, etc.
- Excessive load on the front units. For example, opening lids, chewing threads, etc.
Elimination methods
With high-quality elimination of carious cavities, correction is carried out within a month. If the product was placed in the treatment of deep caries, then you should immediately contact the dentist to exclude an infectious process.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the cause of the loss. If there is repeated caries or loss of a pulpless tooth, re-installation does not make sense. The doctor suggests installing a pin or crown.
What to do if a piece of the filling breaks off
In this case, you should immediately visit a dentist
. The doctor will correct the problem in one visit if no spread of secondary caries is noticed.
If the chip occurs from the edge, then the restoration is carried out with the same material that was originally used. If a significant part has broken off, the doctor suggests changing the material or performing a complete restoration and extension.
Materials from which fillings are made
All modern materials are divided into several groups. Let's look at the types of dental fillings.
Cement (silicate and silicophosphate) fillings
This material is also able to resist the re-development of caries, however, it is very fragile and may not last very long, or can be used as a temporary option.
Although this material has outlived its best years of popularity, however, it is not forgotten in some cases, since it has a low cost and is easy to use.
Plastic
Their popularity is explained by the same factors as the previous ones - low price and quick, simple installation.
However, they have many disadvantages:
- when the material hardens, severe shrinkage occurs;
- after a while, a color change occurs;
- increased abrasion of the material;
- secondary occurrence of caries is often possible.
Such fillings are the prerogative of free medicine.
Amalgams or metals
This material includes silver and mercury, or other alloys containing the second element. It is distinguished by its hardness and service life of up to 10 years. This material is dangerous due to its mercury content and the possible harmful effects of this element on fillings. It hardens for a long time and is difficult to use; the dentist must have high professionalism in order to place a filling from such a material.
Note: When installing a product made from this material, the dentist should take into account the fact that it expands greatly during the curing process, and accordingly, a fragment of the tooth wall, which is located near the filling itself, is possible.
Their use is popular on chewing teeth, as well as under crowns, when the composite will not be visible.
Composite
What dental fillings are considered the best of the inexpensive options are composite ones. They include plastic in their composition, but their distinctive feature is quartz powder, which provides them with the desired hardness. In addition, they are distinguished by relatively good color fastness and strength. Their service life is on average 2-5 years.
Light-curing composites
This is a group of materials that require special equipment in the form of a halogen lamp, they are also known as solar curing or photopolymer. It is with its help that the lamp is given the necessary hardness. When asked which fillings are the best, we can accurately answer that these are those made of this material.
Important: However, in order for a product made from this material to be as strong, durable and aesthetic as possible, it is necessary to carry out careful grinding and polishing.
If polishing is carried out once every six months, the color will last much longer. The most memorable feature of such materials is the mandatory use of special-purpose adhesives that can secure the raw material “tightly”.
It consists of various fillers and polymers that harden under the influence of that same blue lamp.
It has a fairly wide color palette, thanks to which you can choose any desired color and shade, as a result - as close as possible to a healthy tooth.
This material will last at least 5 years.
But such a seemingly flawless material has three main drawbacks:
- Shrinkage due to the chemical composition can be up to 5%, which reduces the quality of the installed filling. That is why it is better to use such material in small areas;
- with severe shrinkage, deformation is possible to such an extent that the thin wall of a natural tooth breaks off;
- incomplete hardening. Hardening of this material occurs only by 70%; more is impossible due to the peculiarities of using the lamp.
Glass ionomer cement
Dental fillings, which are considered the best for use in pediatric dentistry, since they contain 10-15% fluoride, which helps protect against re-infection. In addition, they are chemically bonded to the natural tooth, and therefore the likelihood of various cracks appearing is minimal. The coefficient of expansion under temperature is as close as possible to that of dental tissue, therefore minimizing the risk of the tooth cracking.
However, even this seemingly ideal material has its drawbacks. These are reduced strength indicators, both in abrasion and in bending. In addition, they do not look particularly attractive, and therefore are better used with more aesthetic fillings.
Chemically cured composites
This material was developed to replace conventional cement options. Their fundamental difference is the filler used, in this case it is porcelain. These composites can be further divided into:
- Light-curing.
- Acrylic-containing.
- On epoxy resin.
Composites that contain acrylic are highly durable and resistant, but they are also very toxic. It is often noted that after installation of fillings made from this material, a large number of pores appear. And the consequence may be the development of pulpitis or secondary caries both on this tooth and on neighboring ones.
Resin composites are more fragile, although they wear out less. They are not as toxic as their acrylic counterparts, however, they inevitably darken several years after installation.
Plastic, metal and ceramic compounds
Plastic fillings are also at the peak of popularity, also due to their low price. Plastic has many disadvantages:
- gives significant shrinkage after curing;
- changes its color over time;
- quickly wears out and becomes unusable;
- poorly protects against secondary caries.
Important! Cement and plastic fillings are placed in free dental clinics.
Ceramic compositions
The distinctive characteristics of this material are high strength, lack of shrinkage and aesthetics. Ceramics does not darken during use and is not painted. In modern dentistry, ceramics is considered an almost ideal filling material. Types of ceramics include:
- transparent material;
- pressed material;
- metal ceramics.
The disadvantages include the difficulty of installation: the composition fills the hole in the tooth, like an inlay. The inlay is formed using an impression of a previously sanitized tooth.
Metal alloys
Amalgam material includes a mercury compound along with silver. The dangers of exposure to mercury in the body pose a certain health risk. The advantage of amalgam is its long service life and abrasion resistance.
Another disadvantage of this material is expansion during hardening. If the dentist does not correctly calculate the volume of the filling, the possibility of slight destruction of the crown cannot be ruled out.
Due to the unaesthetic appearance of metal structures, they are used on back teeth or the hidden surface of the crown.
How much do the products cost?
Which fillings are best to install based on their cost? It seems that the only correct answer to this question is that all good things come at a price. However, this is not so; in each specific case, one must start from specific features, and only they will dictate the future price of the filling.
However, in order to get at least a little orientation in the pricing policy, you should know that inlays cost in the range of 3000-14000 rubles, compomers from 650 to 1000 rubles, chemically cured composites from 600 to 800 rubles.
Staging process
The procedure for installing a filling is perhaps the most common dental procedure. Due to their low cost, two out of three patients in domestic clinics choose such materials.
The specialist’s step-by-step algorithm is as follows:
- Preparation of the cement composite is done on site, immediately before installing the filling. Using a special spatula, the doctor mixes the powder with liquid with constant wave-like movements and brings the composition to a uniform paste-like consistency.
- Composite application – is performed one-time, therefore it requires precision movements and a certain dexterity.
In a fairly short period of time, it is necessary not only to restore the coronal area of the destroyed organ, but also to make it an exact copy of the lost tooth.Unlike cement, glass ionomers are applied in stages, in several layers. Each of them undergoes a polymerization procedure with a special lamp.
Each layer takes no more than 40 seconds. During this time, the layer has time to crystallize.
- Checking the correct placement - the patient is given a piece of copy paper and asked to bite on it.
All inaccuracies and protruding fragments will appear on the carbon copy - the sheet in these places will become lighter, and the cement mass, on the contrary, will acquire a zonal coloring of the excess areas. They are removed with a drill using a fine-grained thin attachment. - Polishing, grinding - the finished filling is carefully ground on all sides, bringing it to an almost smooth state, and polished with pastes.
Upon completion of all work, the outer surface is covered with a protective varnish, which increases the service life of the material and prevents too active shrinkage and the manifestations of secondary caries.
What is the best filling for a child’s tooth?
When choosing a filling material for a child, it is important to consider additional factors. For example, in order to minimize the discomfort from the procedure, light-curing compounds are recommended. An equally important point is the minimal toxic impact of the material.
Pediatric dentists successfully use glass ionomers in their practice . The advantages of such materials include the effect of enamel remineralization, and the disadvantages are rapid abrasion.
How the procedure works
For uncomplicated caries, filling is carried out after removing pathologically changed areas of the tooth, cleaning and treating the resulting cavity. Photopolymer fillings harden under the influence of light radiation.
In case of pulpitis, the doctor, after treating and cleaning the canal, fills it with plastic material - gutta-percha - this is a special rubber that hermetically fills the canals of the tooth. First, the doctor may place a temporary filling for a couple of weeks, or sometimes even a month, to make sure that the treatment was successful.
Treatment of caries using filling is carried out in one visit. With superficial and medium caries, there is practically no pain. In the case of its deep form, there is a need for local anesthesia. The key to success in such treatment will be a well-prepared, absolutely clean and dry tooth surface. And as a result, the service life of the filling will be as long as possible.
Types and classifications of fillings
The filling can be made of plastic or metal. Plus, seals include self-adhesive tapes, which are mainly polymer-paper. According to one classification, indicator seals are divided into:
- universal - made from polymers, easy to install manually, disposable (a striking example: Tailsil, a flag seal with a tightening, locking device);
- plastic bags - here the seal's locking device is often a tape with special spikes, which, after closing, do not allow the seal flag to be turned in the opposite direction;
- metal - can be installed manually, but sometimes they require special tools, these are the most reliable and durable power seals, a metal cable is passed through the body of the seal, after which it cannot be pulled back out (carriages are often sealed with such seals);
- metal strip seals - here the locking mechanism is not a cable, but a tinned steel strip; such seals have gained great popularity in the field of maritime cargo transportation;
- self-adhesive - disposable universal seals, which are a piece of self-adhesive tape that can be glued to any object that has doors (the tape cannot be removed unnoticed - marks will remain on the product, or the inscription “opened” will appear on the tape).