The face and neck are those parts of the body that should be not only healthy, but also beautiful. This moment greatly influences how a person perceives himself and whether he has the opportunity to realize himself in society. All diseases and defects affecting these parts must be resolved with the help of specialists.
Most of the problems occur in the field of maxillofacial surgery. This is a branch of dentistry and surgery that covers the treatment of inflammation of various types - both soft tissues and bones. Surgeons help eliminate not only inflammation, but also their consequences, benign and malignant tumors, defects of any kind: congenital and acquired as a result of illness, injury. The surgery section covers everything related to the facial part of the head, neck, oral cavity, and jaw.
The concept of maxillofacial surgery
An oral and maxillofacial surgeon is a specialist who combines a plastic surgeon and a dentist, as he can solve problems in both areas. As for dentistry, maxillofacial surgeons are used for surgical treatment in the presence of impacted teeth and other serious pathologies. These specialists help eliminate problems associated with tumor formations in the face, as well as pathologies of the facial bones. This can already be attributed to the field of plastic surgery.
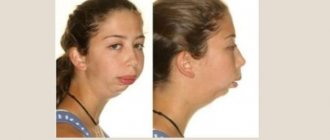
The areas of the face, neck and jaw are what are constantly in sight, and the slightest defects will be visible to others. This can cause a person both psychological and social problems. Defects of the maxillofacial region can be congenital (for example, cleft lip) or acquired, for example, as a result of trauma. Correction of such pathologies is the field of activity of the maxillofacial surgeon.
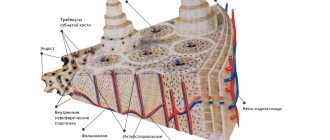
A specialist in this field must have extensive experience, as he has great responsibility. There are many blood vessels and nerve endings in the facial area, and the slightest carelessness can lead to serious negative consequences. Therefore, when choosing an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, it is very important to pay attention to his work experience and patient reviews.
Dentists at our clinics refer patients to an oral and maxillofacial surgeon at the Central Research Institute of Dentistry.
Examples of diseases for which an oral and maxillofacial surgeon can help
It is quite difficult to list all the cases, so we can name a few as examples:
- Abscess. Purulent inflammation of tissues can occur in the muscles, subcutaneous area, bones - this is a dangerous phenomenon that requires the immediate intervention of a qualified doctor, otherwise the consequences can be unpredictable.
- Lymphadenitis. A disease associated with inflammation of the lymph nodes. Such nodes are found throughout the human body, but most often this diagnosis concerns the head and oral cavity.
- Periodontitis. This disease is associated with a violation of the integrity of the ligaments that hold the tooth. It can have two acute stages and several chronic ones. But common symptoms include severe pain, fever, and general malaise.
There are many such examples. In each of them, the help of a surgeon is required at different stages and in different volumes, but it is impossible to do without it.
What types of procedures are classified as maxillofacial surgery?
The activities of a maxillofacial surgeon can be divided into two main areas according to the criterion of urgency.
First, he surgically rids patients of birth defects and provides routine treatment. Preliminary preparation for such operations, including examinations, takes some time. Such “non-urgent” problems include many dental diseases, congenital defects, tumor formations, etc. As for congenital pathologies (“cleft palate”, “cleft lip”, tongue aplasia), they should be eliminated in early childhood during avoiding the development of psychological problems in the child.
Secondly, oral and maxillofacial surgery deals with emergency cases when, as a result of injury, accident or accident, a person acquires a defect in the face, neck or jaw, and when it is necessary to restore vital functions (respiratory, chewing, speech) and correct appearance through surgical intervention .
The scope of practice of an oral and maxillofacial surgeon includes procedures such as:
- taking anamnesis;
- external examination of the patient;
- conducting diagnostic studies and making a final diagnosis;
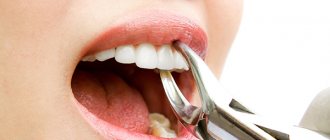
- surgical intervention;
- monitoring the healing process;
- carrying out preventive measures to avoid complications, etc.
Among the most popular surgical procedures in the maxillofacial area are:
- rhinoplasty;
- otoplasty;
- blepharoplasty;
- maxillary sinusotomy;
- prosthetics;
- osteosynthesis;
- removal of various tumors;
- circular facelift;
- contour plastic surgery.
During surgery, surgeons use the most modern equipment and materials, making operations less traumatic. This shortens the recovery period and helps reduce the likelihood of noticeable tissue scarring after surgery.
When should you contact an oral and maxillofacial surgeon?
Most often, a referral to a maxillofacial surgeon is written by a dentist or therapist when he sees that only this specialist can solve the patient’s problem. Among the most common indications for maxillofacial surgery are the following pathologies:
- Periostitis - often after a tooth is removed, its root or part of it remains in the canal, which can cause inflammation. In this case, the inflammatory process can spread over a fairly large area and cause the appearance of compaction in the gums, and subsequently lead to problems with the soft tissues of the face.
- Periodontitis - with this pathology, as a result of pressure on the nerve endings, the patient experiences severe pain, and the teeth begin to loosen and change color.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw - necrosis of the pulp leads to infection and inflammation, first in the soft tissues of the jaw, and then in its bone. Necrotic tissue must be removed as quickly as possible to avoid this problem. This disease manifests itself as severe throbbing pain in the teeth and head, chills and elevated body temperature.
- Abscesses - these include suppuration in the maxillofacial area for a variety of reasons. In cases where pus is released from the soft tissues, the patient's temperature rises, he experiences severe weakness and headache. Often there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth associated with purulent discharge.
- Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the lymph nodes located in the maxillofacial area and next to it.
It is necessary to contact a maxillofacial surgeon for surgical treatment in the following cases:
- when for any reason the facial part of the skull was deformed;
- if there is a serious malocclusion, and the existing problem cannot be dealt with using braces and other orthopedic devices;
- if there is an inflammatory process on the jaw bone and surrounding soft tissues;
- when there are complications associated with tissue suppuration in the face or neck area;
- if as a result of an accident or injury the maxillofacial bones have been deformed and their urgent restoration is required;
- if the patient wants to get rid of any aesthetic defect in the maxillofacial area.
Maxillofacial Surgery
Maxillofacial Surgery
- a branch of medicine that deals with the treatment of various diseases and injuries of the head and neck. The range of these pathologies can differ significantly from each other depending on the specific medical institution and the competence of the individual doctor, which leads to the fact that not only patients, but also doctors of other specialties do not know where to refer a patient with a “non-obvious disease”.
We will try to briefly describe what pathologies we will deal with at the S.V. Center for Cosmetology and Plastic Surgery. Nudelman.
Diseases of the oral mucosa
, incl. both potentially malignant diseases (various erosive and ulcerative lesions, “white” and “red” diseases of the mucosa), and an established diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma.
Any ulcers, formations on the mucous membrane of the tongue, cheeks, lips, oropharynx, floor of the mouth.
Diseases of the salivary glands.
Benign and malignant tumors. Salivary stone disease. Systemic diseases associated with damage to the salivary glands (invasive diagnostics).
The appearance of formations or enlargement of large salivary glands - parotid (located “under the auricle, behind the lower jaw”), submandibular (under the lower jaw), sublingual (under the tongue).
Formation of soft tissues of the head and neck.
Skin formations and everything that is under it.
Congenital neck diseases.
The most common are thyroglossal duct cyst (median neck cyst), lateral neck cyst.
Long-term enlarged lymph nodes of the neck.
Diseases of the jaws. Cysts associated and not associated with tooth roots. Damages due to medication. Radiation damage to the jaws.
Abnormally positioned and supernumerary teeth.
Injuries of the upper and lower jaw, orbital walls, nasal bones.
Consequences of trauma to the bones of the facial skeleton and cranial vault.
Deformations and “retraction” of tissues and the eyeball (enophthalmos) due to a violation of bone anatomy.
Pain syndromes in the facial area.
Diseases of the temporomandibular joint.
Surgical treatment of endocrine ophthalmopathy.
A number of pathologies have a “vivid” clinical picture (for example, salivary stone disease), and a fairly clear and well-established treatment strategy. In other situations, it is necessary to “go to the diagnosis” for a long time and persistently, including invasive manipulations and operations to obtain cytological and histological material.
In all cases, the basis of treatment will be a correct diagnosis.
We actively discuss diseases that are at the “junction” of specialties, and there are definitely more than half of them. These consultations are carried out in our clinic and in some cases can be joint (neurologist, orthopedic dentist, orthodontist, ENT).
We carefully study imaging data (computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging) with the involvement of leading specialists.
It is possible to discuss the case with your attending physician (oncologist, dentist, neurologist, rheumatologist).
This surgical procedure is aimed not only at “selecting” patients for surgical treatment, but also at “strategic” planning and long-term observation of diseases that are chronic in nature and require monitoring (photo recording of clinical manifestations, biopsy, etc.).
Pathology of the bones of the facial skeleton
Jaw formations
Operation options: - incisional surgical biopsy (taking a section of pathological tissue for the purpose of subsequent histological verification, if without this it is impossible to immediately determine the extent of the operation) - cystectomy - removal of the cyst membrane (if the formation is of such a nature), may differ in significant variability in volume, complexity and duration - cystotomy (cyst marsupilization) - an operation to create an anastomosis of the cyst cavity with the oral cavity - used both as an independent surgical intervention and in combination with a biopsy.
— partial resection of the jaw along with the tumor
Chronic osteomyelitis of the lower jaw (in the absence of an acute inflammation phase), incl. radiation and drug-induced injuries (depending on a number of conditions, the operation can be performed both under local anesthesia and general anesthesia)
— necro- or sequesterectomy (removal of altered bone tissue)
Abnormally located and supernumerary teeth - removal of abnormally located and supernumerary teeth under anesthesia
Diseases of the temporomandibular joint - arthrocentesis, lavage of the temporomandibular joint
Surgical treatment of endocrine ophthalmopathy - bone decompression of the orbit (outer, lower, medial wall and their combinations)
Injuries of the upper and lower jaw, orbital walls - osteosynthesis of the lower jaw (mainly through intraoral access) - osteosynthesis of the upper jaw - plastic surgery of the orbital walls
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, SPECIALIST CONSULTATION IS REQUIRED
Preliminary preparation for procedures
It is necessary to carefully prepare for surgery. Preliminary preparation includes a full range of diagnostic measures, including the collection of various tests. Mandatory laboratory tests include clinical and biochemistry blood tests, as well as a general urine test. The doctor may prescribe a hormonal examination, scrapings from the epidermis in the affected area, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, radiography or radiovisiography. All this will help the maxillofacial surgeon see the exact picture of the disease and select the most appropriate treatment.
Before the operation itself and in the postoperative period, you must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations to avoid complications.