Echo of childhood
Milk teeth are something from the realm of a carefree and touching childhood, most of us are sure. It is not for nothing that the Scottish writer James Barrie, in the fairy tale about Peter Pan - a boy who did not want to grow up and remained forever young - specifically mentions that “his mouth was full of pearly milk teeth. None have fallen out yet.” Replacing baby teeth with permanent ones is the same step into adulthood as first grade and first grade.
The change of teeth begins at the age of 5–6 and usually ends by the age of 14–16. Moreover, according to the observations of doctors, children are currently replacing their baby teeth with permanent ones at a younger age than several decades ago. But sometimes baby teeth persist into adulthood. People encounter similar cases at 20, 30, and even 50 years old! Why does this happen and what should be done in this case?
Prevention is the best solution
So that you do not have to worry about treating or removing baby teeth, organize proper nutrition for your child and oral care.
Try to prevent your baby from consuming a lot of sweets; if possible, reduce the amount of sweet juices and carbonated drinks in the diet. And, of course, take care of regular and proper brushing of your teeth.
The child should brush his teeth 2 times a day: morning and evening. At the same time, do not allow any snacks after brushing your teeth in the evening. If your child is under two years old, brush his teeth yourself. At this age, by the way, be sure to use special toothpastes recommended for children over 0 years old, for example, ASEPTA baby.
Older children should brush their teeth themselves, but always under adult supervision. From the age of two, also visit the dentist at least 2 times a year. This is the only way you can prevent the development of serious dental diseases and ensure timely resolution of all emerging problems.
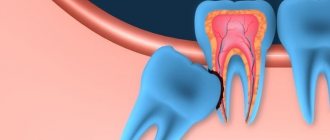
Why didn't my baby tooth fall out?
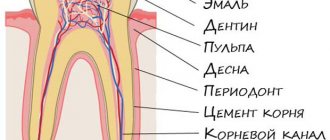
The structure of temporary and permanent teeth has certain differences. Dairy teeth have the same shape as molars, but they are smaller in size, their roots are much shorter, and they grow in the amount of only 20 pieces versus 32 permanent ones, including wisdom teeth. The service life of “children’s” teeth is also short: their roots begin to dissolve (dentists say “resorb”) approximately 2 to 3 years after they are fully formed. The process begins from the area where the crowns of the permanent teeth growing underneath touch them.
However, it happens that the rudiments of molars do not form for some reason. In this case, the roots of the milk teeth most often dissolve under the influence of the rudiments of adjacent permanent teeth. But sometimes this does not happen, and then “children’s” teeth are preserved in adults - doctors call them persistent, from the Latin persistere - to remain, to remain.
The reasons for the absence of permanent tooth buds can be different. Sometimes these are hereditary characteristics, metabolic disorders or disorders of the endocrine glands, trauma and osteomyelitis of the jaws. Chronic and acute inflammatory processes in baby teeth, in particular, periodontitis that is not cured in a timely manner, can also lead to damage and death of the rudiments of permanent teeth.
It also happens that the rudiments of permanent teeth, although they are formed, lie very deep, without touching the roots of milk teeth. This may be caused by insufficient space or misalignment of the permanent tooth. In these cases, milk teeth can remain in an adult.
Differences between permanent and temporary units
Temporary and permanent elements of the jaw row are almost identical in shape, but there are some differences:
- dimensions;
- root length;
- chemical composition;
- number in a row;
- life time.
Temporary elements of the jaw rows are designed in size for a growing organism. The jaw of a child or teenager is much smaller than that of an adult.
For a comfortable life, so that the milk units do not put pressure on each other, do not cause pain, inconvenience when chewing food, and do not injure the surrounding tissues, nature prescribes a smaller size.
The shortened length of the root and differences in composition are provided for by the replacement mechanism, for a relatively painless and traumatic passage.
A child grows only 20 milk units, and after the formation of a permanent bite, 32 or 28 elements erupt (not everyone grows four eights or wisdom teeth).
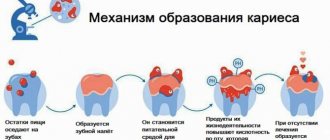
The service life of a temporary unit is reduced due to the difference in composition, their greater susceptibility to various diseases, and lower resistance to caries. That is why it is not recommended to give children a lot of sweets to maintain health.
Stages of formation of permanent dentition and its characteristics.
Read here about possible anomalies that develop with mixed dentition.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/profilaktiki.html we will talk about a kit for the prevention of malocclusions.
What to do if an adult’s baby teeth don’t fall out?
Of course, baby teeth often cause problems in adults. Firstly, they are designed to have a short lifespan, and therefore their resistance to caries is much lower than that of permanent teeth. Secondly, baby teeth that do not fall out in time can interfere with the growth of permanent teeth and lead to their incorrect location. However, this does not mean that a baby tooth found in an adult must necessarily be removed. It all depends on each specific case. Most often, doctors recommend keeping well-preserved baby teeth in adults - let them last as long as they can. After all, the permanent ones may never emerge in their place.
In any case, the question of the fate of a baby tooth in an adult is decided only after an x-ray is taken. This will help to find out whether there are rudiments of an unerupted permanent tooth, as well as whether the roots of the baby tooth are being reabsorbed. If there are no rudiments and the roots of the baby tooth have not resolved, while the baby tooth is motionless and looks quite aesthetically pleasing, then it is not worth removing it. The same applies to cases when the permanent tooth, judging by the x-ray, is in such a position that it is impossible for it to erupt even after the removal of the milk tooth.
Features of the structure of persistent units
It would seem good that the tooth is in no hurry to fall out, but why are adults whose baby teeth have not fallen out very worried about this? And dentists themselves treat this situation with extreme caution and advise monitoring it over time. The thing is that milk units have a number of distinctive features:
- short roots, wide and straight dentinal tubules, and a thinner enamel-dentin layer: compared to permanent units, they are more vulnerable and susceptible to any external influences (mechanical damage, bacteria, food temperature). And any destructive or inflammatory process occurs faster on them. As a result, caries of a baby tooth may occur in an adult, which will quickly become complicated by pulpitis or periodontitis,
- small crown size: permanent units are very massive, they have a large coronal part. What are the disadvantages here for adults? The first is that if several milk units are preserved in the bite, then they will stand out strongly against the background of the rest, permanent ones. For example, in the smile area - it will look, at a minimum, strange or ugly. Secondly, if adult molars are preserved (by the word “molars” we mean chewing teeth), their small size can lead to malocclusion, uneven distribution of the chewing load, and again to premature wear of both them and their neighbors.
Is it possible to grow a baby tooth on an adult?
If the baby tooth is mobile or does not suit you from an aesthetic point of view, you still need to start with an x-ray examination. If the x-ray reveals that there are no permanent tooth buds, and the roots of the baby tooth have resolved, while the baby tooth has mobility of 3–4 degrees (that is, the tooth is very mobile), then it should be removed and further decide what type Prosthetics are more suitable for you to replace the loss.
If you are not satisfied with the appearance of the tooth, it is necessary, again using an x-ray, to determine the condition of the rudiments of the permanent tooth and the roots of the baby tooth. Further decisions will depend on each specific case, including the age of the patient and the place in the dentition of the baby tooth. If there are no rudiments and the roots of the baby tooth have not resolved, then you can install a veneer on it or carry out a tooth restoration, which will make it invisible in the dentition. And for those who want to completely transform their hair, we can recommend getting lumineers.
If there are rudiments of a permanent tooth, in this case it is worth assessing how much time they need before erupting and making a decision about removing the baby tooth and “pulling out” the permanent one.
Although milk teeth in adults are an anomaly, this is not a reason to necessarily part with them - they can serve you well for many years to come. However, it is possible that this “greetings from childhood” prevents the permanent tooth from growing. So, if you suddenly have a baby tooth, be sure to take an x-ray and consult a specialist.
What to do after tooth loss
If this does happen, you also need to see a doctor. Loss of teeth with blood accompanied by swelling and inflammation of the gums indicates the development of periodontitis. If the inflammatory process is not stopped, over time it will lead to further loss of teeth.
If advanced caries led to the problem, it also needs to be treated. Since the inflammatory process that develops in the affected tooth roots, gum tissue and jaw bone can result in serious complications.
And finally, it creates aesthetic and physiological problems. The loss of a front incisor is an unpleasant event for any person, even those who are not too attentive to their appearance. And the loss of one of the chewing molars can disrupt the health of the entire dentition. Thinning of the chewing surface leads to a redistribution of the load on adjacent molars, which accelerates their wear. If not one tooth, but several are lost, the quality of food grinding in the mouth changes. This disrupts the functioning of the digestive system and can lead to the development of diseases of the stomach and intestines.
In addition, it is important to remember that the dentition is not a static system. And if free space appears between the teeth, imperceptibly, millimeter by millimeter, the remaining molars and incisors will strive to fill it. As a result, gaps will appear between them, the smile will change, as will the bite. And here different scenarios are possible - from the appearance of psychological discomfort due to changes in the appearance of the dentition to physical discomfort due to malocclusion and redistribution of the load on the teeth during chewing. And even to the deformation of the jaw, which leads to both external changes and physiological disorders.
The solution to the problem will be dentures. Modern techniques allow you to restore your teeth, correct bite and the beauty of your smile. And crowns and implants are completely indistinguishable from “real” teeth in appearance.
pixabay.com/
How long do eights grow?
The process takes place individually. At what age a wisdom tooth can erupt depends on its readiness. By the age of 17, its main part (crown) is just beginning to form. The roots are still in progress. This will continue for about 3-4 years. In the range of up to 40 years, you can expect its appearance from the gums. For each person, this process occurs differently in terms of time and symptoms. The Guinness Book of Records records the latest case at 94 years. Some people experience a whole list of unpleasant symptoms with pain and fever, while for others everything happens quietly and calmly. At what age wisdom teeth erupt is a secondary matter. The speed of appearance is influenced by the size of the jaw. If there is not enough space, it will be difficult for the crown to come out of the gums.