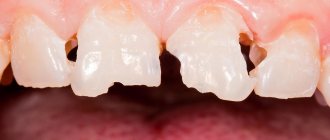
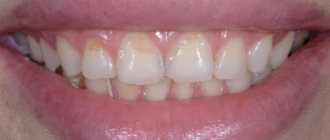
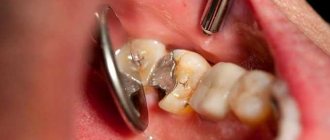
Loose teeth and sore gums are signs of serious health problems. In most cases, this factor is associated with dental diseases, but there are many other reasons that have a detrimental effect on the condition of the teeth.
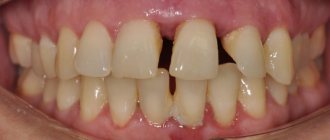
Often, a loose tooth looks like this: the gums around it are inflamed or have a “loose” texture, there is bleeding, discomfort when chewing food, and toothaches may appear. If any of the above symptoms occur, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Symptoms
In the vast majority of cases, teeth become loose due to advanced caries and the presence of tartar. Clear signs that you will experience periodontal problems in the coming months:
- dark spots on tooth enamel;
- bleeding gums;
- high sensitivity of teeth to cold/hot;
- pain when chewing.
At the initial stage, the amplitude of tooth loosening does not exceed 1 mm. Subsequently, it increases, and the tooth wobbles in all directions. Biting or chewing with it is uncomfortable or even impossible.
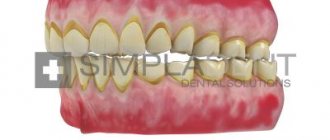
Periodontal diseases are most often accompanied by atrophy of the jaw bone. That is, the volume of bone tissue in which the teeth are anchored gradually decreases. This is clearly noticeable by the “sagging” of the gum line, the formation of gum pockets and the increasing exposure of the necks of the teeth. If no measures are taken, bone volume can decrease catastrophically, leading to loose teeth. And this already threatens their loss.
Causes
Dental
The most common disease, one of the consequences of which is loose teeth, is gingivitis - a disease that occurs as a result of insufficient oral hygiene, metabolic disorders, a weakened immune system, or due to a hereditary factor. Gingivitis is characterized by inflammation of the gum lining, bleeding, bad breath, and weakening of the tissue at the root of the tooth (causing the teeth to become loose).
Untreated gingivitis develops into periodontitis - inflammation of the periodontium (the tissue that holds the tooth in the alveolus). This disease is much more serious and more difficult to treat.
Another cause of loose teeth is periodontal disease, a non-inflammatory periodontal disease. It develops over years, eventually affecting the entire dentofacial apparatus.
Not dental
- Injury. Teeth may begin to become loose due to mechanical damage.
- Osteoporosis. Resorption of bone substance can also occur in the bone tissue surrounding the tooth.
- Chronic diseases. Arthritis, thyroid diseases, mineral metabolism disorders, psoriasis, and diabetes mellitus negatively affect the health of teeth and gums.
- Eating disorder. Anorexia and bulimia have a detrimental effect on the condition of bone and muscle tissue.
- Pregnancy, hormonal imbalances. During pregnancy, dental problems are caused by a lack of calcium, and any hormonal fluctuations in the body also affect the condition of the teeth.
- Heredity.
To prevent loosening of teeth and strengthen them in time, you need to pay attention to the body’s signals. If an unpleasant odor appears from the oral cavity, traces of blood are visible on the toothbrush, then it is worth taking measures: improving hygiene, analyzing your diet and lifestyle, eliminating bad habits. However, before starting treatment, you should definitely go to the clinic to make an accurate diagnosis and choose a therapeutic course that will restore and strengthen loose teeth.
Teeth started to loosen: what to do?
The sooner you go to the dentist, the greater the chance of saving the tooth. The doctor will suggest taking a targeted or panoramic X-ray, depending on how many teeth are loose. They can be used to determine the degree of periodontal damage and bone loss.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to carry out professional oral hygiene - clean the teeth (including under the gums) from hard deposits (tartar) and bacterial plaque. This is a standard procedure performed with an ultrasound machine. Ideally, such cleaning should be carried out once every six months.
If necessary, the patient also undergoes systemic diagnostics and consults with specialized doctors. Further treatment depends on how loose the teeth are and what the causes of the loosening are.
Preventive actions
To prevent the problem, it is recommended to use preventive action tips:
- It is necessary to brush your teeth thoroughly every day, morning and evening.
- It is necessary to rinse with special means - this will kill the infection in hard-to-reach places.
- Proper nutrition will provide the body with all the necessary beneficial elements.
- Visits to the doctor should be at least 2 times a year.
- It is recommended to quit smoking in order to strengthen the walls of blood vessels and prevent bleeding gums.
Preventive measures are quite simple and do not require much effort to follow.
What will the doctor do if the tooth is loose?
In modern dentistry, tooth-preserving methods are practiced, so a tooth is removed only if it is very loose and cannot be restored. When an adult’s teeth become loose, treatment depends on the causes and course of the pathological process.
If the loosening is still minor and is caused by weakening of the gums, it is necessary to clean the periodontal pockets from bacterial deposits. For this purpose, therapy is carried out using the Vector device. The doctor directs a healing mixture into the pockets, which acts simultaneously with ultrasonic vibrations and effectively cleanses the teeth down to the roots. The procedure is painless and promotes gum healing. Also, many dentists use lasers for the same purposes.
After this, the doctor prescribes therapeutic treatment:
- applications with antiseptic drugs;
- applying medicinal gels to the gums that relieve inflammation and restore tissue;
- strengthening gums with rinses - herbal infusions (aloe, oak bark);
- taking vitamins;
- gum massage, which needs to be performed 3-4 times a day on your own;
- if there is inflammation with purulent discharge, the dentist will recommend antibiotics.
In severe cases of periodontitis, when the gum pockets are deep (more than 7 mm), surgical intervention may be necessary - open curettage. During this procedure, the surgeon opens the gum, clears the pocket of infection, applies medication, and sutures the tissue.
Content:
- Why is there a problem?
- Other reasons
- Is it necessary to remove a loose tooth?
- How to save a loose tooth
Only children with primary occlusion can react calmly to a loose tooth. For everyone else, this is a serious problem that requires immediate dental attention. If measures are not taken in time, you may encounter partial edentia - the movable unit will simply fall out at some point, which will negatively affect the functioning of the maxillofacial apparatus and, of course, the appearance of the smile. You should not decide on your own whether to remove a loose tooth. Only a qualified dentist, after an in-person examination, can tell you what to do correctly in a particular situation. Today, thanks to a large number of innovative treatment techniques, doctors most often manage to save even loose units.
What to do if the tooth is very loose?
An effective method of strengthening teeth is splinting. It returns teeth to their functions and allows you to avoid extraction for a long time. Tires are most often made from safe fiberglass material; aramid threads, metal and ceramics can be used. The purpose of the procedure is to fasten the mobile teeth between themselves and the adjacent healthy teeth.
The splint is installed on the inside of the dentition by drilling shallow grooves in the teeth. Fiberglass tape or aramid cord is secured into these grooves with dental adhesive, and then they are filled and polished. Durable and aesthetic materials prevent teeth from loosening further, and therapeutic methods help strengthen periodontal and gum tissue. In many cases, it is possible to significantly reduce the degree of mobility.
Treatment of loose teeth
How to treat front and side loose teeth on both jaws
When splinting incisors, aramid threads or fiberglass tape are used. To connect the lower teeth into one block, grooves are drilled on the lingual surface of the enamel and a reinforcing thread is passed through them. When splinting the upper front teeth, the enamel is drilled from the front. For injuries, a temporary splint is placed on one or both jaws.
A crown, bridge or clasp prosthesis is installed on premolars and molars. A bridge is suitable if one tooth or several adjacent ones are loose. If there are not all teeth in the mouth, a clasp denture is placed.
Prevention
The best prevention of tooth mobility is good oral hygiene. To do this, the doctor will recommend special products and instruments: paste, balm, rinse, dental floss, irrigator. Regular (once every 6 months, and in case of gum problems - once every 3-4 months) visits to the dentist for professional teeth cleaning are required. You should also pay attention to proper nutrition, rich in calcium, vitamins and minerals.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Author of the material: Igor Skripnik
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sensitive teeth and damaged gum tissue require special care. ASEPTA SENSITIVE paste with a high content of enzymes, thermal mud and herbal extracts has been developed especially for them. The balanced chemical composition of the paste relieves inflammation, increases the strength of tooth enamel and destroys the vast majority of harmful microorganisms in the oral cavity, and also carefully whitens the enamel.
Repeated clinical studies have proven that regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA SENSITIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 62%, reduce sensitivity of teeth and gums by 48% and reduce inflammation by 66%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
Degrees of mobility
Before determining the reason why the molar began to loosen, it is necessary to find out the degree of mobility of the element of the oral cavity. Everyone can become a little loose, but with certain diseases, such as periodontitis, the movement is clearly pathological. There are 4 degrees of tooth mobility; upon examination, the doctor independently determines which the patient currently has.
When teeth become loose due to periodontitis and periodontal disease, you need to change not only the toothpaste, but also the toothbrush.
It should be soft so as not to injure the gums. It is best to start using an irrigator - a device for cleaning teeth using a stream of water, the strength of which can be adjusted.
Dentist
Novikova Olga Alexandrovna
8 years of experience
The first degree means the movement of the element towards the adjacent tooth by no more than 1 mm. But there may be a tilt towards the tongue or the inside of the cheek.
The second degree determines the movement of the element by more than 1 mm. At this stage, the tooth may begin to move in a vertical plane.
The third degree occurs when the tooth moves freely in all directions, but sits tightly in place. If there is no adjacent element of the oral cavity near the problem area, then the problem area may have a slope.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
The final fourth degree implies, in addition to the above movements, also circular ones. The tooth practically does not stay in the socket and requires its removal.
To determine the degree of mobility, dentists use tweezers or conduct a palpation examination. To prevent the last stage, you should immediately consult a doctor.
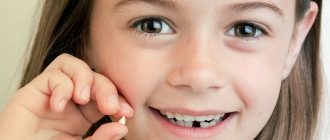
How to pull a tooth without pain for children using gauze
First, make sure that the tooth is not deep enough in the gum, and that the gum itself is loose. To do this, you will need clean gauze and an antiseptic. Using moistened gauze, grab the tooth from the sides and slowly rock it in different directions. If the gums are plastic, there is no swelling or redness, you can safely proceed.
- Set your child up for positivity and distract him from obsessive thoughts.
- Feed the baby, because after pulling out, you will not be able to eat for 2-3 hours
- Clean and rinse your baby's mouth.
- Place him on a chair so that the oral cavity is well lit.
- Take the tooth by the tooth with gauze soaked in antiseptic, and begin to slightly swing it in the direction from the gums.
- As soon as you feel that the tooth is not offering much resistance, pull it out with a sharp movement.
- Carefully monitor the condition of the wound after tooth extraction. To do this, you need to apply a cotton swab with an antiseptic, for example Chlorhexidine, to it and hold it for half an hour. It is important that it does not get infected.
In the first day after the intervention, the gums may become inflamed. Procedures for cooling it will help - compresses lasting up to 10 minutes. If necessary, the child can be given an anesthetic in an age-appropriate dosage. Then the mouth can be rinsed with chamomile or mint decoctions with a strong disinfectant and analgesic effect.
In what cases should you not pull out a child’s tooth yourself?
If the gums are dense and the tooth cannot be loosened, there is no point in experimenting. Artificial intervention can injure the oral cavity. Part of the dental crown may remain in the gum, and this is fraught with serious consequences. In addition, suppuration, swelling and redness in the area of the baby tooth are dangerous. Here you cannot do without consulting a dentist.
In any case, before pulling out a child’s tooth and relieving him of pain, it never hurts to consult a pediatric dentist. The specialist must confirm that the tooth needs to be removed. In modern medical offices, baby teeth are removed without pain - this is much less traumatic from a psychological point of view for both the child and his parents.
How to remove a molar
At home, a molar can be removed only if it is mobile. In this case, the soft tissues must be treated with a local anesthetic. The diseased tooth is grabbed with gauze and then rocked.
All actions must be extremely careful so that the tooth does not crumble.
Permanent teeth have powerful roots that are designed to hold the tooth in place as firmly as possible. Therefore, there cannot be a painless and safe tooth extraction outside a medical office.
Preparing for permanent tooth extraction
There are a number of conditions that must be met before proceeding with removal:
- Psychological aspect. Tooth extraction is always associated with nervous tension. The patient must sensibly assess his capabilities, the feasibility of the operation and the opportunity to visit the dentist’s office.
- Hygienic preparations. The oral cavity should be as prepared as possible. First of all, it is important to get rid of plaque and food debris. This can be done using regular paste and a brush, as well as rinse aid. In the area of the diseased tooth, special care is important.
- Taking painkillers and sedatives. This can be any drug that can relieve pain. It may also be a good idea to take a sedative to reduce nervousness before surgery. Taking any medications should be reasonable, you need to study the instructions and strictly follow the instructions.
Tooth extraction can be performed at home if you have the following items:
- Mirror to ensure a good view.
- Antiseptic, sterile gauze pads, tampons.
- A place where you can sit for the removal procedure.