Content:
- Peculiarities
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Operation
- Removal methods
- Difficult removal
- Stages
- Diagnostic value
- Does it hurt to remove
- Possible complications
Wisdom teeth or “eight” teeth, located at the edges of the jaw, erupt much later than their counterparts. Moreover, this often happens in adulthood, causing a person many unpleasant moments. The fact is that the structure of the human jaw does not provide enough free space to comfortably accommodate an additional pair of teeth. Therefore, “eights” often put pressure on “sevens”, they grow at an angle, their roots become curved, and it can be difficult to provide them with proper hygienic care, as a result of which caries develops. The peculiarities of the location do not allow for high-quality treatment of the wisdom tooth, and the optimal solution is its removal, since it bears neither a functional nor an aesthetic load.
Risks
There are genetic features that do not change, but there are those that depend on various factors, including age.
Facial structure
One of the easiest ways to determine whether there is a greater or lesser risk of problems with wisdom teeth is through a mirror. Let's pay attention to the face. If it is elongated from bottom to top, has narrow cheekbones, and people say a small, neat face, then there may not be enough space for wisdom teeth. But the wider the cheekbones, the wider the “bone”, the more space there is for cutting figure eights.
Also, sufficient space in the jaw reduces their crowding and creates conditions for good hygiene. And this is the best prevention of caries, not only of the seemingly unnecessary tooth that we inherited from our ancestors, but also of all other teeth.
A consultation with an orthodontist and radiation diagnostics (X-ray/MRI) will help you understand the situation.
Age dependent
Problems that can arise with wisdom teeth at different ages can vary significantly2.
In youth, the main problem is inflammatory processes during the eruption of wisdom teeth. As well as the need to remove them for orthodontic treatment.
In adulthood, those who have retained their teeth begin to experience caries. The occurrence of pulpitis and cysts usually leads to a surgeon for removal.
In old age, the main problem is periodontal disease, which usually also leads to the removal of wisdom teeth. Or it becomes a preparation stage for prosthetics.
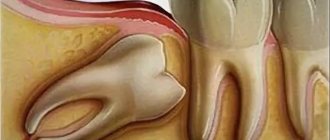
Features of the structure of wisdom teeth
The structure of a wisdom tooth is no different from other molars and consists of a neck, a root system (4–5 pieces) and a crown. In some cases, root development is disrupted and a single conglomerate is formed, that is, a tooth grows with one root.
Its only difference from its neighbors is that recent studies recognize the wisdom tooth as a rudiment that has lost its functional purpose during the evolutionary development of man. Scientists do not consider it as a full-fledged organ, since some part of humanity does not grow it at all.
However, the wisdom tooth has several parameters that distinguish it from the same “seven”:
- lack of milk precursors, which ultimately complicates eruption and impedes growth. There is no room left for it on the dental arch, which is why various developmental pathologies arise;
- the number of roots is greater than that of other molars - up to 5 pieces. In this regard, problems often arise when removing a wisdom tooth;
- significantly curved roots of the “eights” make cleaning and treatment of root canals very difficult;
- poor blood supply compared to other teeth leads to rapid aging, accompanied by fragility and susceptibility of tissues to caries, despite minimal load;
- many pathological conditions, for example, pathologies of the masticatory muscles, malocclusion, pericoronitis, are associated with the growth of “eights”.
Thus, the appearance of third molars has many more negative consequences than positive ones. Many patients are forced to see a dentist even before they can be seen in person.
Changes in soft tissues
Attached soft tissues also change when bone volume changes. The gums shrink in volume and become thinner. In the lower jaw, the layer of attached soft tissue may be very thin or almost absent.
Periodontal nutrition is disrupted and blood supply deteriorates. This further accelerates destruction: surface tissues become thin, susceptible to inflammation and irritation. In advanced cases, bedsores form. Destructive processes provoke the development of chronic periodontal diseases. These, in turn, can lead to the loss of adjacent teeth.
If toothless ridges of bone tissue on the jaw have already formed, the tongue can gradually increase in size: it fills the space that was previously occupied. With the loss of one tooth, such manifestations are minimal; if there are several gaps in the dentition, the enlargement of the tongue will be clearly visible.
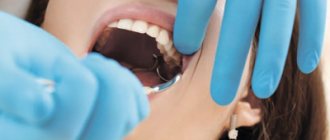
Indications for wisdom tooth removal
Treating third molars is a challenging task, but a competent dentist will try to keep the unit relatively healthy. However, in practice, even relatively healthy “eights” are extremely rare.
Most often, problems begin at the teething stage, which is associated with pain, fever, swelling and other troubles. The doctor prescribes wisdom tooth removal if:
- an unerupted molar is incorrectly positioned in the jaw, injuring neighboring teeth and soft tissues;
- extensive caries damage with significant destruction of the crown;
- pericoronitis (presence of an inflamed hood);
- installation of a bracket system. Sometimes only the removal of a wisdom tooth can ensure the correct movement of other molars;
- presence of a cyst;
- the trigeminal nerve is pinched;
- pulpitis, periodontitis.
Most experts are inclined to believe that the “eight” should be under the supervision of a doctor from the moment of eruption. An x-ray is sufficient to assess the development of the tooth and assess future prospects. This needs to be done immediately, if only because for young people the rehabilitation period is much easier and the likelihood of complications is minimal.
Is it necessary to remove figure eights before installing braces?
Since braces are installed for a long period of time, a thorough examination of the oral cavity is carried out before this and, if necessary, any existing problems are treated. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove teeth before braces:
- For large carious cavities that cannot be filled.
- In the presence of cysts.
- For osteomyelitis and chronic periodontitis
- Teeth with damaged roots.
- Severely loose teeth.
Healthy teeth are removed when there is crowding, and the choice most often falls on the “fours” - the first premolars. They have short roots and removal is easy. In addition, the first premolars are least involved in chewing.
In rare cases, “sevens” are removed - only if the function of the chewing tooth and support for the brace can be taken over by a healthy wisdom tooth. It is also rare that fangs and incisors are removed - only in cases of severe destruction of the root and dental crown or significant deformation. Which teeth need to be removed largely depends on the individual characteristics of the bite. As for the eights, it makes sense to pull out teeth if they grow at an angle and cause severe pain when erupting. Removing figure eights for braces is not necessary if the wisdom teeth are not causing problems, do not affect neighboring teeth, and grow relatively evenly.
Before deciding to remove teeth, the doctor conducts a thorough diagnosis and takes panoramic photographs of the jaw. If braces are placed on a teenager whose wisdom teeth have not yet erupted, in most cases the dentist will not remove them. The rudiments of eights are located under the bone layer in a teenager, and serious surgical manipulation will have to be performed to remove them. After it there may be severe tissue swelling, pain, and difficulty opening the mouth. Until the eights have erupted, it is difficult to predict whether they will be problematic or not. Therefore, the orthodontist most often will not remove unerupted wisdom teeth for a teenager before installing braces.
The exception is cases when the x-ray shows that the third molars are located horizontally in the jaw and can lead to the destruction of the “sevens”. For such indications, the doctor may recommend the removal of unerupted wisdom teeth, even if installation of braces is not planned.
Contraindications to wisdom tooth removal
Despite all of the above, there are situations when the mouth cannot do without the “eight” or the operation cannot be performed for other reasons:
- you need to install a bridge supported by the third molar;
- adjacent molars become loose, and a wisdom tooth is used as a base for applying a splint;
- due to the absence of chewing molars, the chewing function falls on it;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- impaired blood circulation;
- allergy to anesthetic;
- hypertensive crisis.
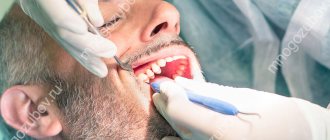
Simple wisdom tooth removal method
For a simple operation, the surgeon uses forceps and an elevator without resorting to incisions or drilling into the bone. This method allows you to extract a molar if:
- the upper wisdom tooth needs to be removed;
- there are no significant developmental deviations;
- there are no complicating circumstances.
Wisdom tooth removal proceeds as follows:
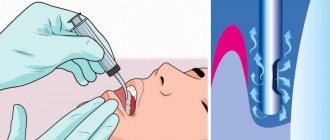
- 1. The dentist collects anamnesis, inquires about the patient’s allergic reactions to medications, and selects the optimal anesthesia;
- 2. an anesthetic drug is administered, its effect begins after about 5 minutes;
- 3. the surgeon prepares instruments, the sets of which differ depending on the location of the tooth, its condition, and the presence of inflammation;
- 4. Using forceps or using an elevator, the tooth is removed from the socket;
- 5. The doctor treats a fresh wound with antiseptic drugs;
- 6. If necessary, an anti-inflammatory agent is placed in the hole.
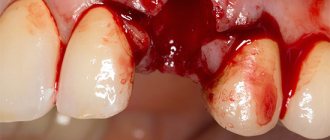
After the removal of wisdom teeth, large sockets remain, so the surgeon sutures the tissue to prevent infection and speed up healing. In the presence of purulent processes and inflammation, suturing the hole is not advisable, since the contents must have an unimpeded outflow. The manipulation usually takes no more than 10 minutes. To monitor the patient’s condition, the doctor schedules an examination a few days after the operation to remove the diseased wisdom tooth.
Will dental prosthetics prevent facial oval deformation?
If you want to avoid changes in the shape of your face after teeth removal, you should not delay with prosthetics, since it not only allows you to preserve the beauty of your smile, but also preserves your dentition, which will help you avoid jaw deformation.
Timely and competent prosthetics of extracted teeth will preserve the youth of the face and prevent the appearance of wrinkles.
The method of dental prosthetics does not matter in this case; any dental implants will help maintain the same distance between the teeth, preventing the jaw from deforming. In addition, the chewing muscles and jaw joints will work as before, as a result of which the oval of the face will remain unchanged, and the appearance of new wrinkles will be avoided.
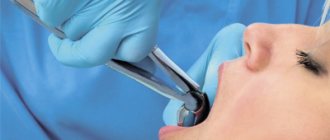
Complex wisdom tooth removal
During such an operation, the surgeon uses many more instruments and performs more complex manipulations, in particular, cutting soft tissues and suturing the incision without fail.
Complex removal is carried out if:
- we are talking about removing the lower wisdom tooth;
- there is an abnormal root system;
- the coronal part is severely destroyed;
- impacted, dystopic molars.
Preparation for the operation follows approximately the same pattern as for simple wisdom tooth removal, but this is where the similarities end. This is noticeable already at the initial stage: more time is allocated for the effects of anesthesia - about 10 minutes.
Missing teeth: consequences for the body
The next segment that can be considered is the condition of the oral cavity and the entire body. What else does missing teeth affect?
- speech : undoubtedly, you will not be able to pronounce many sounds, because from childhood you get used to the fact that for high-quality speech you need not only your mouth and tongue, but also teeth;
- decreased immunity : no teeth - no dense food. The logical conclusion follows from the fact that there will simply be nothing to chew solid foods with. But they contain vital vitamins that support the health of our body and, again, the beauty of our body;
- diseases of the stomach and intestines : even if you want to eat something tasty, you are unlikely to be able to chew a solid product well. It will be difficult for the stomach to digest the food taken, and over time, new diseases will appear, only now of the digestive system.
By the way, the presence of “holes” in the mouth will certainly affect the condition of the remaining teeth in the oral cavity. Previously, they had support on all sides, and when there is none, the only way is to move towards the vacated space. Over time, due to the displacement of teeth, it will be possible to observe gaps between the teeth and protrusion of opposing teeth.
Well, it’s worth talking about the discomfort caused by missing teeth. Psychologists note that due to bad teeth, not enough snow-white or slightly crooked, people smile less because they are embarrassed. But what about if the smile is ruined by holes? We smile less, communicate even less, and the result is a lack of personal life and problems in career development.
No teeth: what to do?
If teeth are missing, it is very important not to put off their restoration to the furthest drawer - it is better to start prosthetics within a couple of months at most after losing a tooth, otherwise the jaw will become increasingly deformed and the process will be much more difficult to stop.
You may prefer a removable denture or a bridge structure. These are inexpensive options, but they are not recommended by doctors, since they rely on supporting living teeth - the load on them is double, so it’s not far from loosening of natural teeth, deformation and inflammation of the gums. In addition, dentures allow you to restore only the tops of the teeth, but not the roots. Therefore, bone deformation gradually continues - over time, this will affect the aesthetics of the updated dentition. After all, the denture remains in place, but the gums recede: a gap will appear between them.
According to dentists, dental implantation is the most natural way to restore the dentition, since not only the apex, but also the root of the tooth is replaced. This means that the bone receives a load and the metabolic processes inside it continue to work: the deformation is stopped.
Do not forget that the creation of dentures should be trusted only to experienced specialists, and even more so when it comes to dental implantation. If installed incorrectly or poorly prepared for surgery, the implants may not take root and will have to be reinstalled. In addition, crowns should be comfortable and accurately matched in color.
Stages of complex wisdom tooth removal
The methodology may differ for each specific case, but in general terms several approximate stages can be outlined:
- 1. local anesthesia;
- 2. incision of soft tissues, peeling them off the bone;
- 3. sawing, drilling out the proper bone tissue;
- 4. extracting the “eight”;
- 5. treatment of a fresh hole left after the removal of a diseased wisdom tooth;
- 6. suturing with non-absorbable suture material;
- 7. The doctor will remove the stitches only after the edges of the wound have completely fused.
The duration of the procedure depends on the situation and can last from 30 minutes to 2 hours. After the operation, the doctor advises the patient regarding wound care, prescribes medications and informs the date of the next appointment.
The value of x-ray diagnostics when removing wisdom teeth
No qualified doctor will remove wisdom teeth “blindly”. You cannot rely on external indicators. A clear assessment of the condition of the root system and the development of the tooth is necessary in order to eliminate complications that could arise after the operation. An x-ray must be taken to assess the feasibility of removing a particular wisdom tooth.
X-ray examination provides an informative picture that allows you to see:
- the presence of curved roots;
- number of root shoots;
- structural features.
Based on the results of X-ray diagnostics, the doctor will be able to draw up a surgical plan and eliminate errors in the form of bone fragments remaining in the gum.
Why are braces needed?
Braces are an orthodontic structure that consists of a metal arch and small plates with locks. The orthodontist attaches braces to the teeth and connects them together with metal wire with shape memory. Trying to take the correct position, the wire pulls on the braces and thus corrects the position of the teeth in the jaw.
Mostly, braces are placed on patients with malocclusion over 14 years of age. Today, bite correction is performed even on adults. If eights have already erupted, the question often arises: is it worth removing wisdom teeth before installing braces? The answer will be individual for each patient, and the doctor will be able to give it only after a preliminary examination.
Is it painful to remove a wisdom tooth?
Many patients delay wisdom tooth removal due to fear of pain. Such fears in modern dentistry are absolutely groundless, since anesthetics are necessarily used for the procedure. Discomfort occurs when the effect of the drugs wears off and the analgesic effect decreases. But this is a physiological process that fades away on its own after some time. In addition, there is absolutely no need to endure pain; the doctor will prescribe medications to alleviate the postoperative condition.
When removing a wisdom tooth, some patients experience painful symptoms for a number of reasons:
- drug addiction;
- extensive purulent process;
- abuse of painkillers.
Also, the degree of pain depends on the method of removal, the condition of the wisdom tooth, and its location. For example, surgery on the upper jaw is easier. But removing a wisdom tooth from the lower jaw is more problematic due to the structural features of the jaw and large curved roots.
Myths about teeth
Myth 1. Whitening is harmful - it damages the enamel...
No. The color of a tooth is given by dentin - the main tissue of the tooth, which is located under the enamel. To reach the dentin and lighten it, a whitening gel is applied to the teeth and activated by the light of a special lamp, as a result of which the gel breaks down into water and oxygen. Oxygen penetrates dentin and discolors pigments, but does not change the structure of dentin. And calcium phosphate, which is part of whitening systems, helps improve the structure of tooth enamel. The whitening procedure ends with remineralizing therapy, which reliably protects the enamel surface. We use only advanced whitening technologies - the ZOOM2! whitening system; this technique allows you to lighten your teeth by an average of 8 shades (and sometimes 10-12) in just one visit. Remember: whitening is safe if carried out under the supervision of an experienced, certified and experienced doctor, using certified equipment using original whitening gel.
Myth 2. After whitening, cracks will appear on your teeth...
No. During professional whitening, cracks in teeth cannot appear, especially since modern systems for professional in-office whitening Zoom2 contain a special component (amorphous calcium phosphate) that can penetrate the thickness of the enamel and strengthen it.
Myth 3. Teeth can be whitened with baking soda...
Yes, but you can use baking soda no more than once a week, as it can scratch the enamel. Another thing is pastes containing bicarbonate of soda. There, the soda particles are much smaller in size and do not injure the enamel as much. Such pastes can be used daily, but not longer than a month, then you need to take a break.
Myth 4. Be sure to brush your teeth 2 times a day...
Yes. You need to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day, and maybe more. It all depends on how quickly plaque accumulates on the teeth. Ideally, you should brush your teeth after every meal.
Myth 5. In the morning you should brush your teeth after breakfast...
Yes, you need to brush your teeth after eating. But in the morning it is preferable to do this before breakfast (to remove accumulated plaque overnight and for yourself personally - to feel freshness) and always after breakfast - to cleanse the oral cavity of food debris.
Myth 6. Overbite can only be corrected in childhood...
No. You can correct your bite at almost any age. But there is a severe pathology in which changes have occurred not only in the position of the teeth, but also in the jaw bones. In this case, there are certain age limits.
Myth 7. It is necessary to treat a diseased tooth “to the last” before removing it...
Yes. Tooth extraction leads to gradual displacement of adjacent teeth, which affects the appearance and can create serious problems with chewing. Displacement will necessarily occur, because each of the teeth in the dental system has its own function and load. Therefore, it is better to treat the tooth “to the last.” But, if removal cannot be avoided, it is better to immediately place an implant. At the same time, the removal of a wisdom tooth, unlike the removal of other teeth, does not threaten a significant curvature of the bite that occurs when neighboring teeth move to the place of the removed one.
Myth 8. Healthy enamel is white enamel...
No. There are no absolutely white teeth in nature. Their color depends on dentin and is inherited. It is believed that the strongest tooth tissues are those whose color is yellowish.
Myth 9. Caries occurs from sweets...
And not only. Caries appears as a result of the activity of microbes that secrete acids that dissolve the enamel. The more remains of ANY food in your mouth, the more food for germs. We brush our teeth after every meal, but we forget that we need to do the same after eating caramel. But chocolate is even useful, because the substances contained in cocoa beans protect teeth from caries due to their antimicrobial effect. But everything must be done in moderation. Dentists recommend drinking Pepsi and Coca-Cola through a straw, because it reduces the contact of the liquid that spoils the enamel with the front teeth by almost 70%, and with the molars by 30-50%.
Myth 10. Floss and mouthwash are essential for teeth...
Almost right. Balms and rinses are additional hygiene products and are used as desired. They contain substances that prevent bacteria from attaching to the tooth surface. But dental floss is one of the BASIC hygiene products that you must use.
Myth 11. You should use chewing gum after eating...
Can. But no more than 10 minutes. After eating, the acid-base balance in the mouth changes, which contributes to the development of caries. Balance can be restored by chewing gum. But you should not chew it for a long time, since the chewing process stimulates the production of gastric juice. But since it doesn’t arrive, the stomach has to “digest” itself and its mucous membrane suffers.
Myth 12. It is not necessary to treat baby teeth - they will fall out anyway...
Wrong. You should definitely contact a pediatric dentist. Baby teeth fall out as a result of physiological resorption of their roots. Between them all this time there are permanent teeth, which erupt in place of milk teeth. If left untreated, caries of a baby tooth can lead to inflammation, delayed eruption, underdevelopment of enamel, or even complete melting of the permanent tooth germ.
Myth 13. The more expensive the toothpaste, the better it is...
Not necessary. But pastes of unknown origin can “help” you acquire new microbes that are unfamiliar to our defense systems. Therefore, it is better to buy toothpaste in pharmacies.
Myth 14. You should use a different paste in the morning and evening...
Yes. In the morning you need to use highly abrasive pastes, including bleaching ones, and in the evening – pastes containing extracts of medicinal herbs.
Myth 15. You need to change the toothpaste from time to time...
Yes. Oral microbes very quickly get used to the beneficial properties of the paste (especially if the paste contains antiseptics - triclosan, chlorhexidine) and stop reacting to them.
Myth 16. If your teeth don’t hurt, you don’t need to go to the dentist...
No. You need to visit the dentist once a year. Only a dentist can see the initial stage of caries. In addition, you need to regularly remove plaque and dental deposits (tartar). Stones can be hidden under the gum and are more dangerous than supragingival deposits.
Myth 17. Gold never causes allergies...
Wrong. Gold in the mouth can be a strong allergen. Some people experience severe inflammation in areas where gold crowns come into contact with the oral mucosa. So sometimes any ordinary alloy is better than gold.
Myth 18. Implantation is very painful...
No. Modern anesthetics, for example, ultracaine, are 6-8 times stronger in their analgesic effect than novocaine. Almost no clinic in the city no longer works with Novocaine. In the absence of contraindications or at the request of the patient, implantation can be performed under general anesthesia (anesthesia).
Myth 19. Implants do not take root well...
No. Official statistics say that out of 100 installed implants, from 2 to 4 are rejected. this is about 96-98% engraftment. By definition, there cannot be a 100% guarantee. These are not just numbers. They are backed by serious research and global experience.
Myth 20. When the nerve is removed, the tooth will definitely be destroyed...
No. After the “nerve” is removed, the tooth is fed through the suspensory ligament, therefore, the tooth does not become “dead”. And its fragility is explained by the initial tissue defect, which became the reason for the removal of the “nerve” - caries or injury. Therefore, it is important to properly restore a weakened tooth. There are international standards for dental restoration, which we follow in our Clinic: if there is a hard tissue defect of up to 1/3 of the tooth, it is possible to restore the tooth with a filling, up to 1/2 requires a ceramic inlay, and if more than 1/2 of the tooth is damaged, a crown is already necessary.
Myth 21. Wisdom teething always hurts...
Almost true. Indeed, the eruption of wisdom teeth is often accompanied by pain, because:
- the wisdom tooth does not have a milk predecessor that would prepare the conditions for its eruption;
- wisdom teeth erupt when the formation of the jaw bone tissue is completely completed, and they have to overcome significant mechanical obstacles;
- the tooth does not have enough space in the dentition, which is associated with changes in the masticatory apparatus in the process of human evolution.
Possible complications
Wisdom tooth removal is one of the most difficult operations in dentistry. Therefore, after it is carried out, various complications cannot be excluded. Thus, during the operation, neighboring “sevens” are sometimes damaged. Such severe consequences are the result of incorrectly chosen treatment tactics, as well as the low qualifications of the dentist, who was unable to understand the peculiarities of the patient’s anatomical structure.
Mature patients in some cases experience damage to the nervous system and, as a result, impaired sensitivity and numbness. Young patients encounter such disorders much less frequently.
A few hours after the removal of a wisdom tooth, bleeding may develop, which is most often provoked by intense rinsing, irritating the wound with the tongue, or eating hot food. This disorder is especially dangerous for patients suffering from hypertension and bleeding disorders.
Dry socket is the most common postoperative complication. Normally, after a wisdom tooth is removed, a blood clot forms in the socket, which promotes rapid healing of the wound. Sometimes a clot does not form, most often in smokers. After a few days, acute pain may appear, for which you should definitely consult a doctor.
The most important teeth in the mouth
Are you familiar with this situation: a chewing tooth broke or the doctor removed it. At first, you think about immediately seeing a doctor for restoration, you calculate your options, but gradually your enthusiasm fades away and the tooth remains untouched for many years.
A missing tooth is not visible – why restore it?
There are no unnecessary elements in our body and every tooth plays an important role. For example, all the front teeth are responsible for forming a smile and supporting the position of the lips; we also use them to bite food in order to then chew it with molars. The canines shape the oval of the face, force certain muscles of the temporomandibular joint to work, and support the curve of the jaw. Chewing teeth, in addition to bearing most of the load of chewing food, also support the cheeks and form the oval of the face.
Dental restoration forever!
Installation of a two-stage implant ROOTT (Switzerland) - RUB 27,000. 32,000 rub. Express implantation ROOTT immediately with a crown - 44,000 rubles. Chew and smile on day 3!
Missing teeth and aging
The absence of teeth significantly affects our external age: wrinkles appear, lips and cheeks recede. The skin becomes paler, the face becomes haggard. Let's try to understand the reasons - why even the absence of one tooth affects our age so dramatically?
- Immediately after tooth extraction, the jaw becomes deformed . Due to the absence of a tooth root, all metabolic processes in the jaw bone tissue gradually stop, the capillaries contract, and the bone partitions dissolve. A depression is created in the bone and gum - neighboring teeth begin to move towards the resulting space - the bite is bent. In addition, as the teeth change position, some of the muscles are tightened, while others, on the contrary, are weakened. New wrinkles appear, or old ones get stronger, the cheeks begin to fall inward;
- if the front teeth are missing, then the lips begin to fall inward - additional wrinkles appear in the nasolabial area;
- When we are young, our skin is elastic, but with age, its elasticity decreases. The longer teeth are missing, the more the jawbone becomes deformed and shrinks. The gums also sag noticeably, so the shape of the face changes, asymmetry appears, and the corners of the lips gradually sink down.
Let's summarize: even due to the absence of one tooth, the jawbone is deformed over time, the tone of the facial muscles is lost, which leads to the appearance of wrinkles, the cheeks sag and fall inward, the face lengthens... and this is not a complete list of what the absence of teeth affects.