What are caries and pulpitis?
Caries is a disease in which the hard tissues of the tooth are destroyed due to the loss of minerals from the tooth enamel.
How and why caries forms, read our article on the treatment of caries. The carious process, progressing, gradually reaches the pulp chamber, in which there is a neurovascular bundle of fibers that nourishes the tooth - the pulp, and destroys it. Bacteria from the carious cavity penetrate inside, infect the pulp, it becomes inflamed and pulpitis begins.
Both adults and children suffer from caries and pulpitis, but the course of the disease at different ages and its treatment differ.
Read about the treatment of caries and pulpitis in adults and pulpitis in baby teeth in the sections dedicated to these topics. In this article we will tell you about the treatment of caries and, especially, pulpitis of permanent teeth in adolescents, as well as about its features.
Reasons for the development of caries on baby teeth at 3 years of age
At 3 years of age, baby teeth are more susceptible to caries than molars. Carious lesions are a serious pathology that makes itself felt after the eruption of teeth. Demineralization occurs, hard tissues gradually soften, resulting in the formation of holes.
Below we consider the main reasons for the development of disease on baby teeth:
- If in the first trimester of pregnancy a woman suffered from serious illnesses and took certain types of medications, there is a high probability that the development of the baby’s tooth buds will be disrupted. The result of this in the future may be progressive caries.
- Caries is infectious in nature. Therefore, it can be transmitted to the baby from parents while eating from the same dishes.
- Poor oral hygiene is the main reason for the development of pathology. Children should be taught to brush their teeth correctly as early as possible. When the baby's first tooth erupts, hygiene can begin. You can find special silicone brushes on sale that will gently and carefully clean your teeth of plaque.
- Excessive consumption of sweets can also lead to the formation of holes in the teeth.
- Bad habits in childhood. For example, drinking sweet drinks from a bottle at night can provoke so-called “bottle” caries, which by the age of three will take on a deep form. The disease first affects the incisors. After dinner and brushing teeth, children should not be given sweets, including candy and chocolate.
- If a child was seriously ill before the age of two and was treated with medications, there is also a high probability of developing caries.
- Lack of fluoride and calcium in the diet. It is necessary to reconsider the baby's diet. You can start taking vitamins only after preliminary consultation with your pediatrician.
Immediately after eruption, a tooth affected by caries begins to decay. Most dentists believe that the development of caries is associated with damage to the rudiments during the period of intrauterine development. Therefore, pregnant women should remember an important rule - to take care of their health, since many drugs can negatively affect the health of the child’s teeth. The second global reason for the development of carious processes is poor oral hygiene. Therefore, it is better to immediately accustom your child to proper brushing of teeth.
Why do children under 14 years of age have an increased risk of caries and pulpitis?
During the period of formation of a permanent dentition, when the child’s permanent teeth begin to erupt, there are 2 factors that increase the likelihood of developing dental diseases and parents need to take them into account.
- The anatomical features of “freshly erupted” permanent teeth contribute to the development of caries and its complications. The incompletely formed, delicate enamel of young permanent teeth, especially in the area of numerous fissures (grooves) on the chewing teeth, is very vulnerable.
- A psychological feature of the “difficult” transitional age, when it is not easy to persuade a child to brush his teeth correctly and thoroughly, and, even more so, to go to the doctor and cure caries in a timely manner, especially if the child is afraid of the dentist.
What to do in the first minutes if a child has a broken tooth?
First, calm down yourself and calm your child. If you have something cold on hand, it is good to immediately apply a compress to the injury site to relieve pain and prevent severe swelling (if the injury is not open).
For an open wound, clean it of large contaminants and cover it with a sterile gauze pad. Time is very important! The most important thing is to get to the dentist as quickly as possible! The doctor will conduct an examination, take an x-ray to see all damage to the hard and soft tissues surrounding the tooth and rule out a fracture of the jaw bones, as well as carry out the necessary treatment.
In the future, such teeth require dynamic observation at a time determined by the dentist. With timely treatment and regular monitoring, the prognosis is favorable.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of caries of permanent teeth in adolescents.
To maintain the health of your teeth for a long time, you need to start carefully monitoring their health as soon as they erupt.
To do this, just follow a few simple rules.
- Provide quality hygiene, including professional dental hygiene for the child.
- Try to regularly attend preventive dental examinations at your clinic every 6 months, because... The development of caries in children in mixed dentition occurs very quickly.
- As a preventive measure at this age, it is recommended to do fissure sealing - this is “sealing” the recesses on the chewing surfaces of the lateral teeth
special filling material containing fluoride. This procedure mechanically closes the “weak” spots of the tooth and, at the same time, strengthens its enamel, releasing fluoride into the tissue.
- Teenagers often develop whitish spots on their teeth. It is necessary to find out what type of lesion such a defect belongs to - carious or not. This can be done by undergoing caries diagnostics with the Diagnocam apparatus in our clinic - this type of examination is digital and does not expose the child to radiation, therefore it is suitable for regular use. If a carious lesion is detected at an early stage, it can be cured without resorting to preparation using the modern ICON infiltration method
- If a child has crooked teeth and crowded teeth prevent them from being properly cleaned, then it is necessary to consult a pediatric orthodontist and begin orthodontic treatment.
- Treat caries in a timely manner in the early stages of the disease - this will allow you to save permanent teeth as much as possible from preparation, because the earlier caries is detected, the less affected tooth tissue the dentist will have to remove.
This approach to the child’s dental health, if not eliminates it, will significantly reduce the risk of serious carious lesions. If time was lost at the first symptoms of the disease, then a complication of caries – pulpitis – will have to be treated.
Why do you need to treat baby teeth?
Dentists say that baby teeth should be preserved until they are replaced by permanent teeth. Typically, teeth begin to change at 6-7 years of age, and this process is completed by 13-14 years of age.
Here are the reasons for the need for treatment of baby teeth in children:
- The permanent tooth germ is located next to the baby tooth germ. Therefore, an infection from a baby tooth can affect the germ of a permanent one. As a result, there is a risk of a diseased tooth appearing or it may not appear at all.
- If a baby tooth is not treated in time, it has to be removed. When a baby tooth is removed early, the teeth that surrounded it may begin to shift. Due to this, the permanent tooth will erupt out of place, the dentition will be uneven and an incorrect bite will form.
- Untreated caries is a constant source of infection in the oral cavity and the entire body. It leads to the development of chronic diseases of the ENT organs, digestive system, and decreased immunity. In addition, a child with dental caries is more likely to suffer from colds and acute respiratory infections.
- Dental problems often lead to a deterioration in the process of grinding food. This, in turn, contributes to the development of many gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Lack of teeth, as a rule, leads to deterioration of diction. The fact is that during the pronunciation of many consonant sounds, the tongue rests on the teeth. In their absence, the tongue may rest on the roof of the mouth. Then, when a permanent tooth appears, the child has to relearn how to pronounce sounds. And this process is quite complex and long.
- For a child, no less than for an adult, the beauty of a smile is important. Bad teeth or their absence spoil the baby’s appearance, which leads to unnecessary worries about his appearance.
How is the progression of pulpitis in permanent teeth different in children?
Pulpitis is a serious disease, it must be treated, otherwise you can actually lose a tooth, get gumboil and even blood poisoning.
As in other age groups, pulpitis in adolescents under 14 years of age occurs in 2 main forms:
- Acute, with severe pain at night and in the evening, a painful reaction to temperature and chemical stimuli, an increase in temperature in case of general intoxication and the development of purulent complications.
In the absence of timely adequate treatment, the acute form becomes chronic.
- Chronic. This form of pulpitis can pass painlessly with the appearance of periodic pain reactions to cold, hot, sour, sweet. The acute inflammatory process in the pulp subsides, and the sluggish course of the disease contributes to the development of complications from periodontal tissues. Exacerbations occur periodically.
Attention parents! During adolescence, children may hide the disease and take painkillers uncontrollably.
Is it possible to cure caries in a child without drilling? What methods are there?
It is possible if the carious cavity is at the initial stage.
- Remineralizing therapy.
- Treatment method with the Icon system.
- In some cases, we replace the drill with a RONDOflex device - this is an air-abrasive handpiece. Preparation occurs using a mixture of water jet and aluminum oxide powder. The treatment proceeds in a gentle manner and is not accompanied by noise, vibration, or unpleasant sensations.
Unfortunately, most often parents bring their child to the clinic when a tooth is already bothering him and the baby complains of discomfort or pain. Usually this is already the stage of pulpitis. In these cases, treatment without a drill is impossible.
IMPORTANT! I always recommend my patients to come for a preventive examination 2 times a year, even if there are no complaints. Often pathological processes in the tooth are asymptomatic.
Features of the structure of newly erupted permanent teeth in children.
As we have already said, newly erupted permanent teeth in a child have a number of anatomical features and differ from the teeth of an adult, namely:
- They have fragile, not fully formed and mineralized enamel.
- They have unformed roots that connect to the growth zone.
- The root canals of such teeth are wide, with a funnel-shaped expansion towards the root apex.
- The thin and fragile walls of the dental canals do not have secondary dentin; they are easily injured and destroyed.
- There is insufficient mineralization of dentin in the roots of the tooth.
Therefore, when treating pulpitis of permanent teeth in children, there are a number of limitations and features that the pediatric dentist knows and must follow. Endodontic treatment (root canal treatment) of permanent teeth in children is complex and requires great care.
By the way, for this reason, it is better for adolescent patients to contact a pediatric specialist rather than an adult dentist-therapist.
Symptoms of teething in babies
It happens that the eruption of the first unit in a child is asymptomatic. Parents in such a situation completely unexpectedly make a discovery when they find a white stripe in their child’s mouth.
However, most cases are characterized by the presence of characteristic teething symptoms:
- saliva is produced profusely;
- a rash and red spots appear on the chin due to constantly flowing saliva;
- gums become inflamed and swollen;
- the child is worried, cries and is capricious;
- appetite decreases;
- severe itching forces the baby to put toys and other objects into his mouth;
- body temperature rises sharply (more often occurs when two or more teeth erupt at the same time);
- sleep is disturbed;
- A runny nose and cough may appear, which intensify when the baby is in a horizontal position;
- the voice is hoarse;
- general weakness is noted;
- sometimes there is loose stool or diarrhea;
- Vomiting rarely occurs (due to saliva flowing into the stomach).
Methods for treating pulpitis in adolescents under 14 years of age, and how do they differ from treatment for adults?
Before starting treatment, the dentist’s main task is to determine whether the patient’s permanent tooth has roots, what stage of formation they are in, and also to find out the condition of the tooth, the location of the source of inflammation, the shape and length of the root canals. To do this, the patient must undergo an x-ray.
Treatment will be different for teeth with formed and unformed canals.
There are 3 main methods of treating pulpitis.
- A conservative method of treating pulpitis is without removing the pulp; during the treatment, the canal is washed with an antiseptic, a calcium-containing paste is applied to the pulp chamber and filled.
- Partial pulp removal
This method involves removing the infected coronal part of the pulp, cleaning and rinsing the cavity, which is then filled with a drug. After the inflammation subsides, the tooth is filled.
- Surgical method with complete removal of the pulp (depulpation). In this case, the pulp is removed, the canals are expanded and washed, and then filled.
We do not use arsenic pastes to treat pulpitis - the same popularly known “arsenic” to “kill” the pulp. Modern technologies and materials make it possible to treat pulpitis using more humane methods for patients of all ages.
Read more about these techniques in our articles:
Treatment of pulpitis of baby teeth
Treatment of pulpitis (in adults)
When and what methods of treating pulpitis of a permanent tooth in a child can be used?
- A child’s diseased permanent tooth has unformed roots.
In this case, during treatment ONLY gentle methods of treating pulpitis are used - a conservative method of treatment or partial removal of the pulp while preserving its living root part.
Depulping – i.e. Complete removal of the pulp is not applicable for such teeth, because their pulp connects to the tissues of the growth zone, which will be injured, and this is not allowed. It is necessary to preserve the living growth zone until the formation of the tooth and periodontal tissues is completed.
In the process of treating permanent teeth with developing roots, all manipulations are aimed at relieving inflammation and preserving the growth zone of the tooth. Subsequently, to avoid relapses, it is recommended to regularly monitor the patient using radiography until the tooth root is completely formed, and then carry out high-quality endodontic canal treatment.
- A child’s diseased permanent tooth has already formed roots.
When treating such a tooth, any of the above methods can be used, including complete removal of the pulp (depulpation). The latter is preferable, but the dentist chooses a technique based on the specific situation.
- Conservative treatment is carried out in case of “early” stage of the disease and in case of injuries.
- Partial pulp removal is effective in treating chronic and onset acute forms of pulpitis.
- The indication for depulpation is any form of pulpitis with severe pain and if other methods do not produce results.
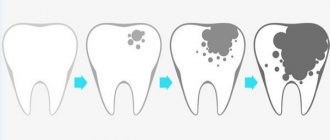
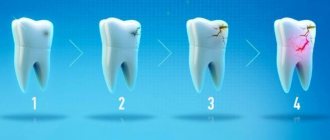
Stages of caries
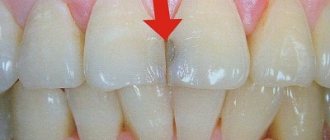
- At the initial stage, white spots appear on the enamel. They can be completely different in shape and size. The process of destruction of enamel can be prevented if the child is shown to the doctor in a timely manner.
- Surface. The disease develops within the enamel layer. The cavity may be light or darkened. The child reacts painfully to sweet, sour, and hot foods. The main method of treatment at this stage is filling.
- Average. The dentin tissue is affected, and the pain becomes stronger. In this case, the cavity needs to be cleaned and filled.
- Deep. Most of the dentin is affected by caries. The baby may experience severe pain.
If you do not show your child to the dentist in a timely manner, possible complications may include serious diseases such as pulpitis and periodontitis. In addition, a diseased permanent tooth may grow in place of an untreated fallen tooth.
Other important features of the treatment of pulpitis in permanent teeth for children under 14 years of age:
In order for the treatment of pulpitis to be successful and the patient to have no relapses or complications, it is necessary to:
- Strictly maintain sterility to avoid infection during treatment.
- Use a rubber dam to isolate the patient’s oral cavity from the manipulation field.
- Carry out a thorough filling of the canals - the voids left in them will provoke the re-development of inflammation.
- Monitor the quality of canal filling after treatment using repeated x-ray diagnostics.
- Do not forget that not only adults, but also children need high-quality fillings and dental restoration, and, sometimes, even prosthetics with ceramic inlays.
How to prevent caries on baby teeth at 3 years old
Parents should pay close attention to the growth of baby teeth.
What rules should not be forgotten:
- Accustom your baby to oral hygiene as early as possible. For young children, the rules of brushing their teeth can be taught in a playful way.
- Use only an age-appropriate toothbrush and toothpaste. For children, it is necessary to choose toothpastes that are safe to swallow. Children under three years of age are not recommended to brush their teeth with fluoride toothpastes. This is because fluoride is an active substance and can cause problems if swallowed.
- At first, parents should supervise the teeth brushing process. The baby can swallow a large amount of paste.
- Watch your diet. A child of three years old should eat well. Choose healthy foods enriched with microelements and vitamins.
- Visit the pediatric dentist with your child twice a year.
Remember that a child’s baby teeth need the same competent care and timely treatment as their molars.
How is pain relief performed when treating pulpitis in adolescents under 14 years of age?
Pulpitis is often accompanied by severe pain, so high-quality and safe pain relief is especially important for effective treatment and comfortable well-being of the patient.
Treatment of pulpitis in children is carried out completely without pain, for this purpose local conduction anesthesia is used. For severe pain, it is combined with intrapulpal anesthesia.
To prevent a child from having a negative reaction to an injection of an anesthetic drug, in our clinic we use local application gel anesthesia (freezing).
If there is increased anxiety, preliminary sedation is recommended; before visiting the dentist, the child can be given light sedatives - valerian, Novopassit, motherwort tincture, according to the instructions and in the dosage indicated for his age/weight.
Holes in baby teeth at 3 years of age: treatment of the superficial and middle stages
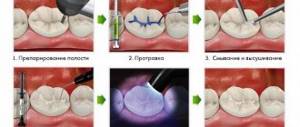
These types of lesions can be eliminated by cleaning the cavity with an instrument or using a drill. An anesthetic is administered before the procedure. In most cases, children are afraid of such procedures, which complicates the treatment process. Composites of different colors are used as filling materials. The child can independently choose the shade he likes; this often helps relieve fear and arouse interest in the procedure.
Modern clinics also use other methods for treating caries in three-year-old children:
- Chemical-mechanical. The area affected by caries is treated with a special solution, then the softened dead tissue is removed with an instrument.
- Air abrasive. The cavity is treated using a stream of water, air and abrasives.
- Ultrasonic. Ultrasonic waves affect the cavity. As a result of such manipulations, the affected tissue easily comes off.
- Laser. The laser beam ideally disinfects the affected area.
Such techniques allow pediatric dentists to quickly and painlessly eliminate caries at various stages of development.
A child has knocked out permanent teeth, what to do?
With dairy everything is easy and simple. But with permanent teeth it is much more difficult. This is primarily due to the fact that the wrong approach can have a very bad effect on aesthetics.
In principle, the algorithm of actions is the same, but there are several fundamental differences in the actions of parents. You need to understand that if a child knocks out one of the side teeth, then this matter can easily be corrected over time, because the resulting cavity will be filled with displaced neighbors.
But if a child knocks out a permanent front tooth, what should be done? In this situation, you cannot do without consulting a specialist, since the absence of an incisor will significantly spoil your child’s smile. Modern technologies make it possible to replace it with a prosthesis, or build it up from scratch. Of course, this is worth the financial investment, but the baby’s happiness is much more expensive. The main thing is that in our time, any problem can be solved, and your child will grow up happy and healthy.