Glossitis is an inflammation of the tissues of the tongue. It can be superficial or deep. Most often, glossitis is a symptom of some general disease of the body, but it can also occur independently.
The main causes of glossitis are:
- carious teeth
- difficult teething
- tartar
- injuries to the mucous membrane of the tongue and oral cavity
- smoking
- alcohol abuse
- poor oral hygiene
- poisoning with heavy metal salts
- burns
- food too hot
- hot spices
- allergic reactions to toothpaste, mouth fresheners.
Superficial glossitis is often a sign of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, infectious diseases - measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria.
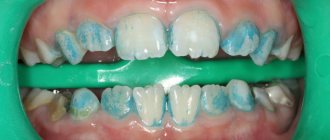
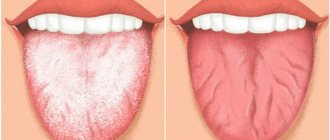
It is characterized by the presence of plaque on the tongue, its swelling, hardening, and limited mobility. The tongue becomes bright red, there is a burning sensation in the tongue, pain, loss of taste, and excessive salivation. Treatment of superficial glossitis is based on the use of local anesthetics (chloral hydrate, anesthesin in glycerin, rosehip oil, peach oil, vitamin A oil solution) and anti-inflammatory drugs. For oral administration, multivitamins, desensitizing agents (antihistamines, calcium chloride), and immunostimulants are prescribed. Oral debridement (the process of cleaning an open wound by removing foreign material and dead tissue from it so that nothing impedes its healing) is of great importance.
With deep glossitis, everything is much more complicated. The inflammatory process in this form of the disease is localized in the thickness of the tongue and manifests itself in the form of an abscess (a limited accumulation of pus that occurs during acute or chronic focal infection). Deep glossitis can spread to the floor of the mouth and cause inflammation in the chin and neck. For this form of glossitis, surgical treatment is indicated.
In addition to the above, there are also non-inflammatory forms of glossitis, namely: desquamative glossitis (geographic tongue)
This form of the disease occurs during pregnancy, damage to the gastrointestinal tract, blood diseases, metabolic disorders, some infectious diseases, helminthic infestations, lupus erythematosus, and rheumatism. Desquamative glossitis is characterized by focal destruction of the red epithelium on the back and lateral surfaces of the tongue. The alternation of lesions with restored and destroyed epithelium makes the surface of the tongue look like a geographical map. In addition to external changes, burning and pain in the tongue may occur. Therapy for desquamative glossitis is based on the treatment of the underlying disease that provoked the development of glossitis.
Reasons for the development of glossitis
As noted earlier, glossitis of the tongue can manifest itself as an independent disease caused by bacterial invasion, or be a symptom of systemic pathologies. The main cause of any form of glossitis is microorganisms, including viruses, namely:
- bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci);
- herpes virus;
- fungi.
Also, the main factors in the development of the disease include injuries to the tongue tissues from the sharp edges of broken teeth, sharp edges of dentures or the edges of fillings, prolonged and frequent exposure to chemical and mechanical irritants on the tongue, as well as thermal burns. In addition, while drinking alcohol and smoking, the risk of developing glossitis increases. In addition, the occurrence of glossitis can be triggered by the following factors:
- excessive consumption of hot drinks, food, spicy spices, caramel;
- poor oral hygiene;
- excessive use of mouth fresheners, toothpaste;
- using someone else's toothbrushes;
- tongue piercing;
- wearing braces and dentures.
Glossitis also manifests itself as symptoms of diseases and conditions of the body such as:
- lack of vitamins (A, E, B12 and folic acid);
- skin diseases;
- dry mouth;
- anemia;
- scarlet fever and measles;
- diphtheria;
- diseases of the stomach and intestines;
- helminthic infestations;
- lichen planus;
- allergy;
- stomatitis;
- rheumatism;
- taking antibiotics.
The development of a chronic form of glossitis can be triggered by dysbiosis and a decrease in general and local immunity, as well as conditions in which autoantibodies are formed in the body.
Treatment at home
Treatment of glossitis at home in adults and children should be carried out only after consultation with an experienced specialist, since independent experiments can only worsen the disease. If the disease is not severe, glossitis is treated with medications (prescribed by the doctor) at home, and the patient comes to the clinic for examinations throughout the entire period of rehabilitation. Doctors often prescribe treatment for glossitis with hydrogen peroxide, since it is an inexpensive and fairly effective antiseptic. The same can be said about chlorhexidine solution - one of the most common means of treating and preventing several types of glossitis.
Traditional medicine is actively used in the treatment of oral diseases, including glossitis. As a rule, various tinctures and decoctions are used. First of all, these are chamomile, calendula, basil and sage, which have antibacterial properties. Aloe, carrot and sea buckthorn juices help restore the supply of vitamins and also have a tonic and restorative effect.
Common manifestations of glossitis
The first symptom of glossitis is a feeling of burning, discomfort and the presence of a foreign body in the mouth. The tongue becomes bright red or burgundy and swells. In a patient with edema, salivation increases. In this case, the taste sensations are dulled, or completely lost, or the taste is distorted. With glossitis, eating causes difficulty and pain. Pronunciation becomes slurred. If the patient does not resort to treatment for a long time, then glossitis becomes chronic, which is manifested by persistent and dense swelling and changes in the structure of the tongue, sometimes mushroom-shaped growths form.
In the case when glossitis is caused by pathogenic microflora, the patient exhibits symptoms of acute inflammation, namely:
- swelling;
- hyperemia;
- painful sensations;
- temperature increase;
- bubbles that, when opened, leave pathogenic erosions.
If the patient has an immunodeficiency, the inflammatory process spreads to the oral mucosa.
Candidal glossitis manifests itself as a white coating on the tongue, which can be loose or dense and fixed; hyperplastic changes in the tongue are also noted.
If glossitis is advanced, it is complicated by abscesses. At the beginning of this stage of the disease, the patient experiences symptoms such as:
- sharp throbbing pain;
- slurred speech;
- uneven enlargement of the tongue;
- swelling;
- increased salivation.
If glossitis is complicated by phlegmon, then the resulting swelling and area of purulent tissue melting move to the bottom of the mouth and neck. During this period, the patient feels severe, pronounced pain, while the process of chewing food is disrupted. The patient has difficulty speaking and breathing, and sometimes has attacks of suffocation. The patient may also experience symptoms of intoxication, or more precisely:
- weakness;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- heat.
Features of glossitis in children
Glossitis in childhood is often a consequence of problems with bite. Other causes include: viral and bacterial infections, helminthic infestations, diabetes mellitus, genetic abnormalities. Often inflammation manifests itself due to the consumption of hot food or too cold drinks, as well as when dirt gets into the mouth.
Often children under 3 years of age suffer from herpetic stomatitis. If you consult a dentist in time, you will be able to cope with the inflammation quickly.
The main causes of glossitis in children are:
- Poor quality oral care.
- Tongue injuries that children receive due to falls.
- Allergy to dental fillings.
- Poorly installed fillings.
- Pathological inflammation of braces, plates or other structures designed to correct the bite.
- Frequent tongue biting by a child.
- Tongue injury from hot or cold foods. In this case, the likelihood of infection increases, which will further provoke an inflammatory response in the body.
- Infection with worms or other parasites.
- Diabetes mellitus in childhood often leads to candidal glossitis. Fungal glossitis can be triggered by taking antibiotics.
- Decreased immunity in a child.
Diseases that can cause glossitis in childhood:
- Diabetes.
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Any infections.
- Blood diseases.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
Sometimes children do not complain about inflammation of the tongue. Therefore, parents should regularly examine the child's oral cavity. Although in some cases children show some anxiety, become capricious, and indicate pain in the mouth.
Catarrhal glossitis can develop during teething, after an injury. Bacterial inflammation often results from diseases of internal organs. Atypical dermatitis and pathologies of the digestive organs lead to desquamative glossitis.
Differential diagnosis of glossitis
In addition, in dental practice there are several classifications of glossitis, namely:
- Desquamative glossitis has an inflammatory-dystrophic nature of damage to the mucous membranes of the tongue. It appears on the back of the tongue, which takes on a gray tint. When the epithelium is rejected, bright red areas are formed on the tissues of the tongue, the shape and size of which are constantly changing. This type of glossitis is practically asymptomatic, but sometimes the patient experiences hyperemia and slight swelling of the tongue. Since the exact causes of desquamative glossitis have not been identified, it is discovered during a medical examination;
- allergic glossitis is expressed by increased sensitivity to a particular irritant;
- Rhomboid glossitis manifests itself as an inflammatory process in which the papillae of the tongue atrophy. It occurs during the development of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. This type of glossitis can quickly take a chronic form, which is accompanied by frequent relapses;
- a black hairy tongue is accompanied by the growth and keratinization of filiform papillae in the middle and posterior region of the tongue. The reason for the development of this glossitis is also not clear. The only thing is that this disease can develop against the background of a candidal infection of the oral cavity, in which patients complain of a sore throat and a sensation of a foreign body, as well as vomiting;
- aphthous glossitis is a superficial inflammation that does not affect the deep layers of the tissue structures of the tongue. This pathology manifests itself in the form of numerous but small bleeding ulcers on the surface of the affected organ;
- folded glossitis is a consequence of developmental disorders and occurs only in children. The folded appearance of the tongue occurs due to the increase in its surface. In the longitudinal fold, which is located in the middle of the tongue, bacteria and fungal infections accumulate, which leads to catarrhal inflammation;
- candidal glossitis is an inflammatory process that occurs as a result of infection of the oral cavity. There is dryness and redness of the tongue; it itself is covered with a white or brown coating. Increased sensitivity to hot and spicy foods. The cause of infection is the patient’s reduced immunity or irrational use of antibiotics;
- superficial glossitis manifests itself as inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue. Most often it is one of the signs of stomatitis. During this period, the tongue becomes inactive and dense. The patient may experience severe pain even with the slightest movement of the tongue. In addition, he loses his sense of taste, a burning sensation appears, and salivation increases;
- atrophic glossitis is characterized by atrophy of the papillae of the tongue, as a result of which the surface of the tongue becomes smooth. The patient experiences a burning sensation, pain and increased sensitivity in the tongue area. This form of glossitis is usually one of the symptoms of B12 - folate deficiency anemia;
- interstitial glossitis is one of the symptoms of tertiary syphilis. With the development of this type of glossitis, the tongue tissues are deeply affected, the structure of the tongue is compacted and resembles a waffle towel. Due to the appearance of pathological changes, the motor activity of the speech organ becomes difficult. If the patient does not undergo timely treatment, this leads to irreversible processes. Muscle tissue is replaced by connective structures, which degenerate into malignant neoplasms. After which the patient is diagnosed with tongue cancer.
Causes and symptoms
Doctors are not yet able to determine the exact cause of glossitis. Research shows that the source of glossitis is both hereditary and infectious diseases.
It is still impossible to predict which of them will be important in each individual case and how it will work. Of course, the hereditary factor also plays an important role here, however, its actions have not yet been unraveled.
The appearance of glossitis can be caused by:
- chemical and thermal burns;
- allergic reaction;
- alcohol and smoking;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- infection with a viral infection;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- taking certain medications.
However, the main reason for the development of Gunter's glossitis is the presence of percynic anemia. It is associated with a malfunction in the metabolic process, which interferes with the absorption of vitamin B12.
The vitamin can be supplied with food, but is not absorbed in the intestines due to a lack of enzymes; as a result, the liver and red blood brain do not receive vitamin B12 in the required amount and the patient’s hematopoietic function is impaired.
R
The disease can develop in both adults and children, who are no less susceptible to the disease.
The risk factors for them are the same, important in this case is personal hygiene, which parents should monitor.
Children rarely complain about the appearance of a problem, especially at the beginning of the disease; later they may say that their tongue hurts.
Symptoms of Gunter's glossitis are observed primarily on the tongue and oral mucosa:
- redness and smoothing of the surface of the tongue;
- bright crimson color of the mucous membrane;
- slight burning sensation.
In addition, there are symptoms of percynic anemia:
- weakness and fatigue;
- rapid heartbeat, angina pectoris;
- the appearance of shortness of breath with minor physical exertion;
- the skin turns pale, acquiring a lemon-yellow tint, the mucous membranes become bluish;
- gaining excess weight;
- asthenia;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- possible disruption of the central nervous system with spinal paralysis and decreased reflex function, psychosis.
At first, the disease practically does not manifest itself in anything; the patient often learns about the presence of Gunter's glossitis at an appointment with a dentist, who pays attention to the changes occurring in the mucous membrane of the tongue and gums. A therapist can also identify the problem, but he sees it as a manifestation of anemia.
With further development, discomfort in the oral cavity allows the patient to notice problems and seek help from specialists. Gunter's glossitis appears during the period of remission of anemia, and is accompanied by an improvement in the general condition of the body. But as it worsens, it does not disappear, gradually becoming more prominent and noticeable.
With further deterioration of the patient's condition, the following may occur:
- edema;
- pain in the tongue and other affected mucous membranes;
- bleeding;
- the burning sensation will increase, accompanied by tickling and the sensation of a foreign body in the mouth;
- active salivation;
- speech impairment due to a decrease in the motor capabilities of the tongue.
Lack of treatment will lead to more serious lesions and the formation of phlegmon of the tongue, characterized by purulent melting of the tissues of the tongue, the development of swelling and pain. As a result, not only speech is disrupted, but also the process of eating and breathing. Death is extremely rare, but possible.
Other methods for diagnosing glossitis
In the case when glossitis is accompanied by specific and pronounced symptoms, then, based on a visual examination, the dentist is able to make correct assumptions about the nature and form of the disease, as well as suggest the source of pathological changes. To determine the depth and nature of the lesion and to identify the disease that caused glossitis, diagnostic methods are used such as:
- general and biochemical blood test to confirm or refute the presence of an inflammatory process in the patient’s body;
- analysis of saliva for the presence of infection and recognition of its causative agent;
- Ultrasound examination of the digestive tract.
If a specialist has difficulty establishing a diagnosis, the patient is recommended to undergo additional examination, namely:
- RPR test to detect antibodies to cardiolipin antigen;
- microscopy of a scraping on the surface of the tongue for Treponema pallidum;
- cytology;
- serological tests for syphilis;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect antigens;
- analysis to determine the content of vitamin B12.
Only after establishing the correct diagnosis can a specialist prescribe the appropriate treatment and necessary therapy to the patient.
Types of inflammation of the tongue
Glossitis of the tongue, photos of which can be viewed on various Internet resources, has the following forms (varieties):
- Folded glossitis.
- Desquamative glossitis.
- Candidiasis glossitis.
- Gunter's form.
- Diamond shape.
- Hairy black form.
- Interstitial.
In addition, there are also two forms of glossitis: acute and chronic.
The acute form of inflammation is accompanied by a change in color, as well as the general structure of the tongue. Due to the fact that the disease in this form has pronounced symptoms, it will not be difficult to diagnose it even without clinical studies. To make a diagnosis, the doctor will only need to collect an anamnesis and examine the patient.
Chronic glossitis, the symptoms and treatment of which directly depend on the specific form of the disease, has a less pronounced course. To identify it, sometimes the patient needs to undergo a full list of tests, as well as undergo a comprehensive examination of the body.
It is important to know that despite the fact that chronic inflammation of the tongue is not so acute, this form of the disease is considered the most dangerous, since it has a negative effect on the body for a long time. Chronic glossitis is also much longer and more difficult to treat with medications.
Treatment method for glossitis
If a patient is concerned about the appearance of his tongue and pathological symptoms associated with the oral cavity, then he needs to urgently consult a doctor. In the case when the main above-mentioned diseases (syphilis, anemia, neurosis and others) provoke glossitis of the tongue, then treatment should be aimed at their correction. At the time of therapy, the patient is recommended to exclude hot and very spicy foods from his diet. During this period, the patient is prescribed soups, slimy porridges and purees. Before and after meals throughout the day, the patient has to rinse his mouth with various sanitizing preparations. If the patient has a pronounced type of glossitis, then treatment is carried out using applications with anesthetics. If there are signs of tongue dryness, to reduce pain, the surface of the tongue is lubricated with a mixture of anesthesin and glycerin. To restore the integrity of the mucosa, vinylin, peach oil or rosehip oil are used. If necrotic plaque occurs during glossitis, the tongue is wiped with a cotton swab moistened with proteolytic enzymes. If erosions and ulcers cause pain, then it is better to use applications with iruksol to remove plaque. To prevent secondary infection and complications of glossitis, the patient is recommended to treat the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions after the procedures. When a patient exhibits pronounced symptoms of hyperkeratosis due to glossitis, surgical intervention is resorted to. Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antifungal drugs are prescribed according to indications. Patients are also recommended to take immunomodulators and restoratives.
With effective treatment of the underlying disease, glossitis responds well to treatment. Prevention of glossitis involves maintaining oral hygiene, regular dental examinations, and eliminating spicy foods from the diet.
Comments
At what age do people usually get Günther Müller's glossitis?
Vladimir (01/30/2021 at 11:57 pm) Reply to comment
- This type of glossitis, in fact, like all others, can develop in patients of any age, but people who have chronic diseases, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, and smokers are always at risk.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (02/05/2021 at 09:16) Reply to comment
It turns out that our tongue can say a lot about the body, it’s not for nothing that doctors always ask to see it, even if they just came for a medical examination. Can any age have these diseases or older people?
Maria (02/05/2021 at 07:32) Reply to comment
I wonder what is better to eat to avoid such serious problems? It seems to me that a lot depends on food. Against the backdrop of abundance, you begin to not understand what is useful and what is not.
Marina (02/05/2021 at 08:20) Reply to comment
I once had glossitis, about five years ago. Although I don’t smoke, don’t drink, I lead a healthy lifestyle. Before this I had a sore throat. What folk remedies do you recommend that are the most effective?
Irina Frolova (02/05/2021 at 09:40) Reply to comment
Hello. I developed glossitis due to candidiasis. The tastes are very dull. Everything seems to have been cured, but I don’t feel the same brightness from food. Please tell me, can something be done about this or is it forever?
Vera (03/04/2021 at 10:56 am) Reply to comment
Since childhood, all doctors have told me “geographical language.” It has some stains and a yellow-green coating. Is this a disease or not? It just doesn't bother me the way it feels. But it's not very easy to clean.
Vladimir (03/04/2021 at 11:38 am) Reply to comment