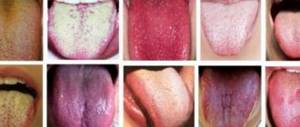
Chronic hyperplasia of filiform papillae (black hairy tongue) - a change in the tongue, expressed in the growth and keratinization of the filiform papillae of the middle and posterior thirds of the tongue.
The etiology is not clear. It was not possible to find a specific pathogen; in scrapings from the tongue, bacteriological examination in most cases reveals a banal flora - saprophytes.
Predisposing factors: trophic (impaired metabolic processes of the tongue epithelium); physical and chemical (alcohol, tobacco, drugs, changes in the acidity of oral fluid); diseases of the gastrointestinal tract; infectious diseases; hypo- and vitamin deficiencies.
It occurs predominantly in men, more often in middle and old age. There may not be any subjective sensations. Sometimes the unusual appearance of the tongue, the sensation of a foreign body on the back of the tongue, the appearance of a gag reflex when speaking and swallowing, sometimes a feeling of itching, awkwardness in the tongue, or a feeling of a foreign body on the palate are disturbing.
“Hairy” tongue – what does it mean, how does the pathology manifest itself and how to treat it
Dental problems can affect not only the teeth and gums, but also other elements of the oral cavity, and the tongue is no exception.
Some pathological processes affect the condition of this particular organ, which is why the patient begins to experience severe discomfort while talking and chewing. In some cases, pain and swelling occur; a dense coating on the surface of the epithelium can become a signal of the presence of an obvious problem. But one of the most frightening phenomena can be considered the appearance of so-called hair on the tongue and its severe darkening. Read further in this article about what it means when they talk about “hair” in the mouth, what the organ looks like with this pathology, why it develops and how to deal with the problem.
How is hairy leukoplakia of the tongue treated?
Prevention of the disease of hairy leukoplakia of the tongue can be a general strengthening of the patient’s immunity, proper nutrition, light physical activity, exercise, daily routine, regular sleep, as well as prevention of HIV infection.
Direct treatment of tongue disease in patients begins with identifying the leading cause of oral leukoplakia. If a particular virus is present in the patient's DNA, intensive antiviral drugs, such as zidovudine, acyclovir or ganciclovir, are prescribed. However, the prescribed medications will only help remove the visible characteristics of hairy leukoplakia of the tongue in the patient - the disease itself and the oral cavity as a whole cannot be completely eradicated. Therefore, as always, there remain risks of virus outbreaks where there is a likelihood of severe immune dysfunction. In case of relapse, signs of the disease return. Although sometimes patients' symptoms of oral disease can disappear spontaneously without exposure to medications.
It also happens that if a patient has hairy leukoplakia of the tongue, medical examinations and test results may not reveal infection as such. In this case, the doctor is obliged to ensure that the reason for the constant irritation of the infected lesions of the patient’s oral cavity is eliminated. Such reasons for the patient may include sharp edges of the tooth or teeth and an incorrectly installed filling. The dentist will eliminate the object of concern by grinding down the tooth or reinstalling the problematic filling. If the disease manifests itself as a result of smoking, then clearly the only correct advice for the patient would be an unconditional renunciation of such a habit. Since among the total number of patients with hairy leukoplakia of the tongue there are also children, the causes of infection in them may be: lip biting, teething, and such a bad habit as biting nails.
As for healthy people, they have nothing to fear; the risks of getting sick are excluded. Foci of infection will go away on their own in about a month when the irritant is eradicated. But there is an important point: if the patient observes visible symptoms after eliminating the causative agent of the tongue disease (whitish spots on the tissues of the mouth, oral cavity, tongue or mucous membranes), especially when the surface of the mucous membrane is severely deformed, then the medical recommendation in this case would be surgical removal problem areas. To do this, the dentist or maxillofacial surgeon uses local anesthesia and cuts off these affected areas.
Definition - what a “hairy” tongue actually is
If the tongue is noticeably blackened and processes resembling small hairs appear on its surface, we can talk about chronic hyperplasia of the filiform papillae. The development of this pathology is accompanied by severe deformation of the structure of the surface of the tongue. It all starts with the hardening of mucosal cells, which ultimately leads to an increase in the length of the taste buds.
"Hair" can reach a length of up to 2 cm
On a note! The disease occurs in both adult patients and children. At the same time, males are more likely to encounter it in adulthood.
Black hairs “grow” from the root of the tongue, gradually increasing in diameter, usually up to 2 mm. The length of one such process can reach 2 cm or more1. In this case, the surface of the papillae becomes hard, and over time acquires a brown or even black color - the saturation of the shade can say a lot about the degree of neglect of the problem. Typically, the pathology proceeds slowly, and pronounced manifestations make themselves felt only in the active stage of development of the disease.
Language structure
To understand what is happening and why the papillae of the tongue hypertrophy, let us consider its structure. It is a muscular organ that is covered with a mucous membrane. The body of the tongue is covered with papillae of four types:
- leaf-shaped, they are located on the lateral surface of the tongue and contain taste buds and glands that produce a secretion resembling viscous saliva;
- grooved, they are located at the root of the tongue, the largest and fewest papillae of the tongue, contain taste buds;
- mushroom-shaped, they are randomly located over the entire surface of the tongue, also containing taste buds;
- thread-like, the most numerous, located on the back of the tongue, their function is to retain food and touch, they do not contain taste buds.
Thus, the anatomy of the tongue lacks hair follicles from which hair grows. Therefore, the name “hairy tongue” is conditional. The overgrown filiform papillae are very reminiscent of hair.
Description of associated symptoms
The pathology in question is also characterized by other accompanying symptoms. It is these signs that distinguish it from other diseases that affect the condition and appearance of the tongue. These symptoms include the following phenomena and processes:
- The patient has an irritating feeling that there is a foreign body on the surface of the tongue. This feeling appears already in the first stages of the development of the disease. At the same time, a person cannot yet visually see the changes taking place, but he feels them perfectly. Gradually, the discomfort becomes more pronounced and over time can lead to constant vomiting,
- an increase in the length of the papillae, a change in their color,
- the formation of affected areas with clearly defined boundaries - usually shaped like an oval or diamond,
- the formation of a dense gray or black coating,
- the appearance of itching on the palate.
It is obvious that as the disease progresses, a person gradually loses taste sensitivity, and therefore the ability to fully enjoy his favorite food. Patients also note dryness of the oral mucosa.
Clinical picture of black hairy tongue
Patients with a black hairy tongue complain of:
- foreign body sensation;
- increased gag reflex, due to the increased mass of filiform papillae at the root of the tongue;
- decreased taste sensitivity;
- halitosis (bad breath);
- burning sensation in the tongue due to the addition of candidal infection.
Hypertrophied filiform papillae are located in the middle and posterior thirds of the dorsum of the tongue. In this case, the affected area is round, oval or triangular. The length of the enlarged papillae can reach two to three centimeters, and the diameter can reach two millimeters. At the base, the filiform papillae are wider, more dense upon palpation, and colored in various tones of brown: from light to almost black. The tip and lateral surfaces of the surface of the tongue, however, are not changed. Regional lymph nodes are not enlarged. In patients with black hairy tongue, the general condition does not suffer.
The diagnosis of black hairy tongue is made on the basis of complaints, the development of the disease and objective data. On examination, an area of pigmented, hyperplastic filiform papillae is observed on the tongue. At the base their color is less intense than at the periphery. When the doctor runs the instrument along the tongue from root to tip, the papillae are raised. The hygiene index in patients with black hairy tongue is unsatisfactory. Upon examination, it is discovered: multiple caries and extensive dental plaque.
In smears taken from the affected area, yeast-like fungi with budding cells are often found, as well as normal microflora of the oral cavity.
Differential diagnosis of black hairy tongue is carried out with Addison's disease, as well as with leukoplakia (hairy form). In some cases, to exclude concomitant pathology, consultations with a therapist and gastroenterologist are necessary.
What causes pathology to develop?
The appearance of hair on the surface of the tongue is always a consequence of some phenomena and processes occurring in the patient’s body. In fact, this is a symptom that acts as a complication against the background of a certain pathological disorder in the functioning of internal organs and systems. Most often, the cause of “hairy” tongue is one of the following factors:
- fungal infection, such as stomatitis,
- disruptions in metabolic processes,
- problems in the digestive system,
- long-term use of a particular group of medications,
- imbalance of oral microflora.
This is what a fungal infection on the tongue looks like
“I also encountered the same problem at one time. Thank God, I noticed it at the initial stage, when the tongue was just beginning to become covered with something like stubble. I was, of course, stunned. I immediately went to my dentist, he cleaned me, healed caries in one tooth, and prescribed applications to the tongue. Judging by the tests, the whole problem is due to the course of antibiotics that I took shortly before. Now everything seems to have passed, but I was in a very early stage, I don’t know if this can be treated in advanced cases...”
Kir!85, Ekaterinburg, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
A “hairy” tongue is a phenomenon that requires a professional approach to treatment. Therefore, you should not make independent attempts to cleanse the organ, since in this case the situation can only get worse. It’s better not to take risks and entrust the solution to the problem to professionals.
Diagnostics
It is necessary to distinguish hypoplasia of filiform papillae from diseases where a change in the appearance of the tongue is a symptom - cirrhosis and dysfunction of the liver, Addison's disease, problems in the thyroid gland, myocardial infarction, erosive gastritis, leukoplakia due to HIV infection and some others, as well as from pigmentation caused by the consumption of food pigments.
What does diagnostics include?
Recognizing a “hairy” tongue is not difficult. All changes can be easily seen with the naked eye. Clearly elongated, dark-colored filiform papillae directly indicate the development of pathology. However, it should be noted here that in medical practice there is also such a concept as “false hairy tongue,” and in this case we will be dealing with simple pigmentation of its surface.
Usually the cause of the so-called false phenomenon is a malfunction of the intestines or, for example, a lack of proper hygiene and acute inflammatory processes in the oral mucosa. As part of the diagnostic examination, the doctor will conduct a thorough visual examination and may also suggest a bacterioscopic examination for the presence of leptotrichium bacteria.
Only a dentist can diagnose the disease
How to prevent development?
It is difficult to completely exclude the development of this disease, since all the factors that cause it are not clear. However, doctors recommend high-quality oral hygiene, including its professional variety.
In addition, it is necessary to promptly treat gastrointestinal diseases and other general pathologies that can provoke the disease. It is also important to give up bad habits (smoking, drugs).
If you notice any signs of this disease or simply unusual changes in the appearance of the tongue, it is better to immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can diagnose the disease and offer the best solution to the problem.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags hyperplasia tongue
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
ROCS cream for fixing dentures: what problems does it solve?
Next article
Oral cancer: how effective is treatment and when?
How to treat pathology
Since the appearance of dark hair-like growths on the tongue is not a full-fledged independent disease, the help of a therapist or gastroenterologist may well be needed to treat the root cause of this symptom. As for symptomatic therapy, the patient can be offered tissue restoration using the following methods:
- application therapy: applications soaked in a keratolytic agent are applied to the darkened area - it has a mild effect on dead cells and stimulates metabolic processes in tissues. This method is good because its use does not damage the mucous membrane, but at the same time it gives only a short-term effect,
- injection: the patient is given an injection of 2% novocaine and calcium chloride directly into the source of the lesion. The procedure is usually carried out twice a week. This method is considered less traumatic and the most effective,
One of the treatment methods is injection - cryodestruction: in this case, the keratinized areas are irrigated with liquid nitrogen, which leads to the gradual death of the deformed papillae. This procedure makes it possible to quickly get rid of the defect, but it is not carried out in all clinics.
As part of the treatment, the patient is also prescribed medications. Otherwise, the main emphasis is on eliminating the original source of the problem, which is dealt with by highly specialized specialists.
Treatment
Effective treatment can only be carried out by a specialist after research and diagnosis.
Which doctors should I contact?
The disease is classified as dental, but can be caused by various factors .
That is why, first of all, you should contact a dentist. After examination and initial diagnosis, the intervention of other specialists - a dental surgeon, psychotherapist, infectious disease specialist or gastroenterologist - may also be required, depending on the presence of general problems and diseases.
There is also a need to visit a dental hygienist.
Methods
Treatment of black hairy tongue can be carried out in two different directions - general and local.
General treatment is aimed mainly at eliminating provoking factors , as well as general strengthening of the body and normalization of the patient’s psychological state.
- Treatment of somatic general diseases - gastritis, infections of various kinds, and much more.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity and professional hygiene.
- The use of sedatives (motherwort, valerian, tranquilizers), psychotherapy sessions.
- Multivitamin complexes that also contain microelements.
- Vitamin B5 (calcium pantothenate) is used to normalize metabolism. The course lasts about a month (from 0.3 to 0.6 g daily in three doses).
- Desensitizing agents are prescribed in cases where the disease occurs against the background of general sensitization. They allow you to reduce specific reactions to irritating factors.
- Antifungal therapy in the diagnosis of fungal stomatitis.
If the root of the tongue is enlarged, what does this mean?
In the next review we will talk about further actions after cutting the child’s frenulum.
Follow the link to talk about the reasons for the appearance of a green coating on the tongue.
Local treatment involves eliminating the external manifestations of the disease . Depending on the body’s reactions and various indicators, different techniques can be used.
- The use of keratolytic agents to eliminate keratinization (resoruin, salicylic alcohol).
- Cryodestruction (liquid nitrogen) to remove altered papillae.
- Keratoplasty applications for healing and restoration.
- Daily tongue cleansing.
Sequence
First of all, it is necessary to carry out sanitation of the oral cavity, since this measure is mandatory for any cause of the disease.
Simultaneously with local therapy, general therapy is carried out, which can last much longer than simply eliminating the symptoms and changes that have occurred in the tissues of the tongue.
What could be the consequences?
If you ignore the obvious signs of the development of pathology for too long, after a while it can lead to complications that will negatively affect the condition of the oral cavity as a whole. Experts consider the following phenomena to be possible problems in the future:
- inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues,
- deep caries,
- partial loss of sensitivity of the tongue,
- microflora imbalance,
- decreased intensity of salivary fluid secretion,
- dryness of the mucous membrane.
Pathology can also negatively affect the condition of other internal organs and systems. For example, enlarged papillae inevitably lead to rapid proliferation of bacteria, and hence problems with the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system.
What factors provoke it?
The disease was first described back in 1835. However, its etiology has not yet been clarified, and scientists cannot come to a consensus about the causes of this problem.
At the same time, there are a number of factors that can provoke its development. These factors were determined by collecting and systematizing data from clinical analyzes of patients and anamnesis.
Recently, doctors and researchers increasingly share the same point of view. It lies in the assumption of organ sensitization that occurs under the influence of certain factors.
Sensitization is a sharp increase in tissue sensitivity, which provokes the development of an allergic reaction. In this case, it manifests itself exactly like this - specific tissue swelling with subsequent enlargement and keratinization of the papillae.
There are three groups of predisposing factors : trophic and physicochemical, as well as various general diseases.
- Trophic factors are a disruption of metabolic processes normal for the epithelium of the tongue.
- Physico-chemical factors mean the effects of tobacco, alcohol, medicinal and narcotic substances, and a significant change in the acidity of saliva.
Sometimes even the consumption of certain foods can lead to the appearance of this disease. A similar phenomenon was observed mainly in children.
Some researchers assign an important place among predisposing factors to the development of fungi of the genus Candida, since the majority of patients with hairy black tongue are also diagnosed with candidal stomatitis. However, this may be a consequence rather than a cause of the disease.
The occurrence of the disease in question is also very often associated with various disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and liver dysfunction. A fairly large number of patients had chronic colitis and gastritis.
To summarize, we can identify certain factors that can serve as an impetus for the development of hypoplasia and keratinization of the papillae.
- Poor or lack of oral hygiene.
- Smoking.
- Drug use.
- Taking (long-term) antibiotics and some other medications.
- Too little saliva production.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Radiation to the face and neck, for example during chemotherapy.
- Infectious diseases.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Metabolic disease.
- Too frequent and active rinsing of the mouth with special liquids (balm-rinses), which can affect the change in acidity.
Preventive measures
To minimize the likelihood of coming face to face with such an unpleasant problem, it is important to ensure competent and high-quality prevention. To do this, experts in the field of hygiene and dentistry strongly recommend adhering to the following rules:
- daily brushing of the tongue: twice a day you need to brush not only your teeth, but also your tongue, because no less bacteria accumulate on it than on the surface of the enamel. To do this, you can use the rear ribbed surface of the brush, if it has one, or, for example, purchase a special device in the form of a tongue scraper,
Cleaning your tongue daily will help avoid the problem. - use of rinses: an excellent option can be a pharmaceutical product that not only fights bacteria, but also helps reduce inflammatory processes, helps remove food debris not only from the surface of the organ, but also under the tongue,
- systematic visits to the dentist: it is advisable to undergo preventive examinations at least once every six months. Regular visits to the dentist’s office will allow you to quickly detect the problem in its very beginning, and therefore quickly eliminate it,
- floss and irrigator: to maintain general oral hygiene, do not forget about such important devices as dental floss and irrigator - a portable device that removes plaque and dental deposits through a jet of water and air supplied under high pressure.
Any dental problem can be solved if you respond in time to suspicious changes in the condition of the teeth and oral cavity. The appearance of any neoplasms on the mucous membrane, the occurrence of pain and the formation of plaque on the tongue - all this is a serious cause for concern and an obvious signal that you need to see a doctor.
- Borovsky E.V. Therapeutic dentistry, 2003.