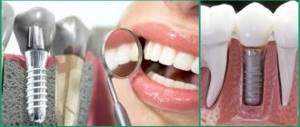
When you can and cannot do an MRI of the brain with dental implants and metal crowns
Article navigation
- How does MRI work?
- When and who should not undergo the study
- MRI in the presence of an implant
- Do metal dental implants move?
- MRI of the head, brain and neck with implants
- Risks of MRI diagnostics with titanium dentures
- Should I tell my doctor about implants?
- Admission to tomography in the presence of crowns
- MRI of the brain in the presence of braces
- Myths for patients with implants
question to a specialist
In the age of modern technology, only the lazy have not heard of such a wonderful diagnostic device called a tomograph. There are several types, but the most accurate is the magnetic resonance machine. Doctors of various specialties refer for MRI. But a number of patients have a question: is it possible to do an MRI with implants and metal crowns on teeth? The answer to this question will surprise many - read further in our article about diagnostic methods for people with metal dentures and contraindications.
What could be the real reason for refusing an MRI?
- Claustrophobia. The patient is placed in a closed apparatus for a short time, which can provoke a panic attack. But here it all depends on the degree of claustrophobia and the type of examination. In addition, each device has an “alarm” button, when pressed, the procedure immediately stops and medical personnel approach the patient.
- An installed pacemaker may come into dangerous resonance with magnetic waves and stop working.
- Before starting the examination, the hearing aid must be removed, since the magnet in the hearing aid may be damaged under the influence of a magnetic field. And the presence of middle and inner ear implants is an absolute contraindication, since they often contain metal alloys with strong magnetic properties.
- An insulin pump is an absolute contraindication for MRI.
Before the procedure, you must tell your doctor
about everything that may affect your health and the diagnostic result. You can’t hush something up for fear that an MRI won’t be done. As a rule, any problem can be solved, and in the case of metal prostheses and implants in the patient’s body, the doctor will simply adjust the tomograph so that, taking into account the location and composition of the prosthesis, the device will produce the highest quality clear image. If there are absolute contraindications to MRI, the doctor will select the most informative and permitted type of examination in your case.
If the patient “forgets” about the fake ideal smile, the pictures will turn out blurry, and he will have to undergo an MRI again, having honestly admitted all the interventions in the body.
If you are planning to undergo MRI diagnostics from qualified specialists, using modern expert-class equipment in comfortable conditions and in the shortest possible time, call the phone number listed on the website, or leave a request in the feedback form. Medical specialists will answer your questions and conduct all necessary examinations within one business day. Let's take care of your health together!
How does MRI work?
Let's figure out what a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is and how it works. This device is designed for targeted examination of tissues and blood vessels of the body. Modern devices with a power of 1.5-3 Tesla are capable of identifying problem areas smaller than 0.2 mm. The principle of operation is based on radio waves and the magnetization properties of the nuclei of hydrogen atoms, which are located everywhere in the body (and we remember that a person is 70% water).
The nuclei of hydrogen atoms “respond” to a powerful magnet (enter into resonance), and a special program records a picture and displays it on a computer. The diagnostic result consists of many virtual sections or sections of the desired organ - the brain or spinal cord, liver, vascular system, etc. And the radiologist makes a written report on the data obtained.
New teeth in 1 day - All-ON-4 - 180,000 rub.
All inclusive!
3D modeling of the structure with a prosthesis, implantation of 4 Osstem implants, installation of a fixed prosthesis on the same day. Free consultation with an implantologist +7 (495) 215-52-31 or write to us
In general, there are two types of tomographs that are installed in specialized institutions - a cone-beam tomograph (CT) and an MRI machine itself. The first, even with implants, does not distort the image, but is also not suitable for studying small areas (for example, brain tumors). During an MRI, a magnet may cause some image distortion in the area of metal products in the body - but whether implants are included in this list will be discussed later.
On a note! Tomographs are also available in dentistry - they are less powerful and give a much worse picture (however, for the needs of the clinic this is enough). Neither the presence of implants nor the presence of metal crowns is a contraindication to this study. However, such devices are cone-beam and do not contain magnets.
Why do you need a CT scan during implantation?
When undergoing dental implantation, a CT scan is considered desirable. Thanks to this innovative technology, implantation operations have become more predictable, carried out much faster and safer, ultimately reducing the patient’s rehabilitation period. After all, the process of osseointegration directly depends on the quality of their installation, and this can only be achieved after a thorough examination.
It is CT that allows the dentist to:
- preliminary study of the patient’s bone density;
- analyze existing defects and identify inflammatory processes;
- determine the location of the maxillary sinuses, the location of nerves and blood vessels;
- calculate the exact dimensions of the future product and the depth of its penetration into the bone;
- install the implant at the desired angle of inclination, in accordance with the dentition;
- plan the permissible physiological load on the implant.
That's why all of this is so important. After all, dental implantation involves the implantation of an artificial root into the gums and bone tissue, and if all the features of the jaw are not taken into account and it ends up in the wrong place, then the person will constantly experience discomfort or pain.
When installing prostheses on implants, it is also necessary to do a CT scan (other examination methods are allowed). This will help the dentist perform all the necessary manipulations with millimeter precision, and will save the patient time and money.
Application in individual cases
For a dental implant to last for many years, it must be completely surrounded by the jawbone. But its structure differs from person to person: in anatomical shape, height and width, density, presence of depressions and defects, etc. Therefore, for a dentist, the task of introducing an artificial root is not an easy one, and requires an individual approach:
- The implant must be placed where the bone is strong and thick.
- It should be positioned at such an angle that the tooth on it does not protrude from the natural row (aesthetic effect).
- It is important to correctly determine the depth of penetration into the bone so as not to touch the nerve or damage important anatomical structures.
Only computed tomography and preliminary 3D modeling will help you take into account all the nuances.
When implanting upper teeth
The most dangerous is the installation of implants in the lateral sections of the upper jaw. In these zones, deep in the bone, there is a maxillary sinus, which usually increases in size when teeth are lost. This situation will significantly complicate the operation if a CT scan is not performed in advance.
Before implanting teeth in the upper jaw, preliminary preparation and diagnosis of the maxillary sinus and nasal cavity are required. The fact is that this zone can complicate the procedure for a number of reasons:
- the presence of acute or chronic inflammation in the maxillary sinuses;
- tumors, polyps, cysts;
- increased size of sinuses due to tooth loss.
Chronic inflammation of the maxillary sinus will inevitably cause swelling of the mucous membrane. In addition, there may be exudate underneath, which will negate the dentist’s work and will not allow the implant to take root. The normal condition of the sinus is a rounded thickening of the mucosa in the alveolar bay, known as a mucocele.
To avoid complications after surgery or complete rejection of the implant, it is first necessary to cure all diseases that may become an obstacle to its installation (including sinusitis). Proper installation of an artificial root in the upper jaw should be carried out after joint consultations of two specialists: an ENT specialist (otolaryngologist) and a dentist. This will help predict the results of treatment and implantation in advance.
When and who should not undergo the study
In response to the question: “Is it possible to perform MRI with dental implants?”, doctors answer in the affirmative. But a number of conditions must be observed - they do not relate to the implants themselves, but are of a general nature. First, let's systematize the contraindications to this study. They are divided into 2 groups – relative and absolute. The following are considered absolute contraindications:
- any large ferromagnets in the human body: large metal implants on bones, middle ear prostheses, metal fragments in soft tissues. But dental implants are not included here,
- electronic stimulators: on the heart, middle ear prosthesis.
Ferromagnets are substances and alloys containing nickel, chromium, steel, cobalt, and any compounds with a large percentage of iron. Highly susceptible to magnetism. In a powerful magnetic field, ferromagnets can move if they are located in soft tissues. The consequences of such a movement are almost always unpredictable and can cause harm.
Relative contraindications - this term hides restrictions on MRI that can be circumvented. For example, undergo diagnostics later or on a different device. Let's consider the relative contraindications to MRI:
- inability to lie still during the examination: this may include small children and patients with nervous disorders. They are put into a short medicated sleep,
- early pregnancy: due to the lack of confirmed data on the harmful effects of the magnetic field on the fetus,
- hemostatic clamps in blood vessels,
- tattoos: if metal is present among the components of the pigment, then it will heat up in the device, even causing burns,
- braces, crowns or other prosthetic devices that contain ferromagnetic metals - primarily steel. But there are some peculiarities - if the prosthesis is in the mouth, and you do an MRI of the leg, then there are no risks.
Contraindications mainly relate specifically to MRI, and the closed type - when the patient is completely placed in the machine. There are also open-type tomographs - they have fewer restrictions for diagnosis, but their accuracy is lower.
Contraindications to CT with contrast
Contraindications to CT with contrast include:
- presence of a confirmed allergy to iodine;
- acute or chronic renal failure due to the possibility of complications due to the administration of a contrast agent;
- blood creatinine level above 100 µmol/l;
- severe diabetes mellitus (risk of complications from contrast enhancement while the patient is taking medications containing metformin);
- some thyroid diseases.
It is possible to do a computed tomography scan with contrast during breastfeeding. You just need to exclude lactation within 48 hours after the study.
Questions
Is it possible to do a CT scan during pregnancy?
Any form of X-ray diagnostics is contraindicated at any stage of pregnancy. Computed tomography uses well-known x-rays, which have a negative effect on the fetus. Therefore, CT scanning for pregnant women is performed only in exceptional cases when it comes to saving the life of the mother. If there is a threat to the life of a pregnant woman, they will try to carry out a tomography using a low-dose program, covering the tummy as much as possible with a special lead blanket that reflects X-rays. But even these precautions cannot exclude the possibility of the development of abnormalities in the fetus. The likelihood of this threat depends on the stage of pregnancy. The use of computed tomography in the early stages of pregnancy is strictly undesirable, since this may be fatal to the embryo, and the woman will have to terminate the pregnancy. According to the observations of expert radiologists:
- in pregnant patients who were irradiated at 1-2 weeks due to radiation from CT scans, in 98% the fetus died or stopped developing;
- in women irradiated at 2-5 weeks of pregnancy, in 70% of cases there was a miscarriage or frozen pregnancy, and in 20% the fetus had malformations of the liver, heart, and thyroid gland;
- In pregnant women who underwent computed tomography at 6-12 weeks, in 80% of cases the child developed multiple pathologies of organ development.
Is it possible to do a CT scan after x-rays and fluorography?
In case of medical necessity, an X-ray or fluorography examination can be combined with a computed tomography session on the same day. The main thing is to ensure that the total radiation dose does not exceed 15-20 mSv. On average, X-rays provide 0.2 mSv of radiation exposure per scanning session. The level of radiation exposure on MSCT is significantly higher and depends on the scanning area. It can range from 1 mSv to 15 mSv per examination.
Is it possible to do CT scans for children?
Computed tomography is a radiological form of diagnosis. It is not recommended for children under 14 years of age unless absolutely necessary. X-rays have a negative impact on the formation of the central nervous system in a child and increase the chances of cancer in children under 5 years of age. The dose of radiation that a child receives during a tomography session leads to an increase in the number of cells with mutations in the P53 gene, which is responsible for the development of cancer, and increases the chance of developing leukemia and brain cancer by 35%. Therefore, a child’s CT scan is performed only as prescribed by a doctor and in the presence of compelling medical reasons, when the benefits of the examination outweigh the health risks associated with it. Doctors strive, whenever possible, to replace computer scans with safer forms of diagnostics - ultrasound or MRI.
Is it possible to do a CT scan at a temperature?
Temperature is not a contraindication to native tomography, but it may be a limitation for contrast-enhanced CT. Changes in a person's temperature may indicate an inflammatory process in the body, and in such a state, the introduction of iodine-containing contrast can provoke a crisis.
Can I do a CT scan with dental implants and braces?
The short answer is yes. X-rays do not in any way affect dental implants, crowns and braces, no matter what material they are made of. Dental implants also cannot affect the quality of the tomograms obtained. They do not produce any artifacts on CT images.
Is it possible to do CT with titanium and metal plates?
Metal in the body is not a contraindication to CT, regardless of the alloy composition of your metal inclusion. Therefore, computed tomography can be used as an alternative form of diagnosis when, due to the metal in the patient’s body, magnetic resonance imaging cannot be performed on the patient.
Is it possible to do a CT scan with a pacemaker?
If you have a pacemaker of any model, you can do a CT scan. CT scans use X-rays and they do not have any negative effect on any artificial pacemakers. Therefore, CT is used as an alternative to MRI if the patient has a pacemaker, neurostimulator, or insulin pump, which can fail in the magnetic field of the magnetic resonance imaging scanner. But it is safe for such patients to undergo examination with a CT scanner.
Is it possible to do a CT scan after chemotherapy?
A CT scan may be ordered after a series of chemotherapy treatments to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. The decision about when control images need to be taken is made by the attending physician. Chemicals used in oncological treatment are not a contraindication to CT. The only thing you should always remember is that X-rays tend to accumulate in the human body, so the recommended interval between CT examinations for an oncological diagnosis should be 2-3 months. For diagnostics, you should also choose spiral low-dose units.
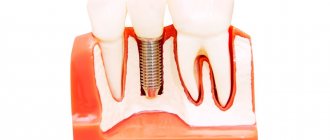
Magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of a dental implant
So why wouldn't a dental implant be an absolute limitation to MRI? Here you need to understand that implants are made from metals endowed with diamagnetic and paramagnetic properties. What it is? The operation of an MRI scanner is based on the magnetizing properties of certain substances. So, para- and diamagnets react weakly to powerful magnets, such as those installed in the tomograph.
Paramagnetic materials are almost not subject to the action of a magnetic field and do not shift in it. These are the following materials:
- titanium: the main metal from which modern implants are made,
- aluminum: medical gurneys made of this metal can be brought into the room where MRI is performed,
- platinum: softer and more expensive than titanium.
Diamagnets - magnetization is not significant, it occurs in the direction of the applied field:
- hydrogen: it was the presence of this element in the human body that made magnetic resonance imaging possible,
- copper: oxidizes quickly, not suitable for implantation into the body,
- gold and silver: very soft metals.
Magnetic resonance imaging can be performed on any part of the body. If the organ being studied is located in the lower half of the body, then the implant will not affect the result in any way. And if the upper part is examined, then there may be some distortions - however, the implant itself will not move, that is, it will not be magnetized and will not break out of the body.
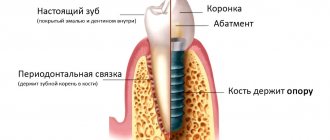
Do metal dental implants move during examination?
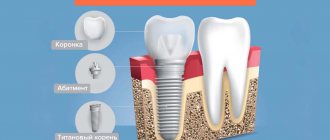
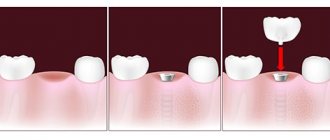
To understand whether an implant can move under the influence of a magnet, you need to know what it consists of. Dental implants are a modern replacement for your own lost teeth. It consists of a metal implant (reliably fixed in the jaw bone and replaces the tooth root), an abutment (connecting part) and a crown - an analogue of the upper part of the tooth. If the prosthesis is installed efficiently, then it is not at all perceived as a foreign body. It looks like it's your own tooth. These sensations are achieved thanks to the special structure of the implant - it contains micropores, and bone grows into them over time. Thus, it fully replaces the tooth root and does not wobble.
Why the implant does not move during MRI:
- rigid fixation in the jaw: the bone securely holds the tooth root prosthesis in place,
- consists of titanium: i.e. does not magnetize and does not heat up.
MRI of the head, brain and neck for patients with dental implants – can it be done or not?
The brain is the control center for all organs of the body, and its proper functioning is vital. And nature could not leave such a necessary organ without protection, i.e. skulls But it is precisely this that creates a serious obstacle in the study of diseases of the brain and its blood vessels. X-rays and ultrasound cannot “enlighten” the skull, and computed tomography is low-power and will not be able to show pathological areas smaller than 1 mm in size. For this reason, MRI is prescribed to study the soft tissues of the head - the brain and blood vessels - as the most informative method.
MRI of the head with titanium dental implants has no contraindications and can be done. Just first you need to check with your dentist what material the implant is made of (although you should also have this information on hand), but the prosthesis. If you have metal-ceramic crowns installed, they may contain steel impurities - then it is better to refuse magnetic resonance imaging and undergo PET (positron emission tomography) or CT (computed tomography).
On a note! If one center refuses to give you an MRI, go to another - modern devices can muffle the “noise” from metal implants. But, naturally, these are the latest generation devices and you need to look for them.
Before undergoing an MRI, you must indicate in the questionnaire that you have a dental implant. Tell the specialist about this immediately before diagnosis.
MRI for dental implants
Is it possible to do MRI in patients with dental implants or is their presence a contraindication to the procedure? The answer to this question depends on what materials the different parts of the artificial teeth are made from.
Dental implants are a metal rod screwed into the jaw onto which a prosthetic tooth covered with a crown is attached. In modern dentistry, titanium pins are implanted into the jaw. Titanium is a paramagnetic material compatible with the human body that has anti-corrosion properties.
The material currently used to make implant crowns varies:
- metal ceramics;
- metal-plastic;
- aluminum;
- porcelain;
- zirconium dioxide;
- ceramics on gold;
- composite materials.
These substances are considered inert with respect to the magnetic field of MRI, but not everything is so clear. For example, metal-ceramics and metal-plastic are composite materials consisting of metallic and non-metallic phases. The composition of the metal phase may include chromium, nickel, cobalt, aluminum, iron, titanium, precious metals, that is, metals with different magnetic properties. At the same time, the content of metals in the composition of metal-ceramics and metal-plastic ranges from 15 to 85%.
Zirconium implants are a relatively new orthodontic development. Dental prostheses are made from a hypoallergenic and inert compound in relation to living tissues - zirconium dioxide. Compared to metal-ceramic implants, zirconium implants do not contain metals, so it is believed that they will not be affected by a magnetic field. The presence of zirconium prostheses must be reported to the MRI doctor.
Handicraft manufacturers use structures made of ferromagnets (nickel or iron) to make dental implants. These metals are short-lived and susceptible to corrosion in the human body. However, they somewhat reduce the cost of prostheses, which is why they are still popular among the population. The danger of the presence of ferromagnetic materials in implants is that they react to the influence of a magnetic field: they can heat up and move in the mouth.
How can people get an MRI if they have this kind of fixed dentures in their mouth? People with fixed metal dentures in their mouth should definitely check with their dentist what material they are made of. Before the procedure itself, this information must be brought to the attention of the MR diagnostic physician. If a patient has implants with ferromagnetic metals, magnetic resonance examinations should be avoided so as not to cause harm to health.
Risks of MRI diagnostics with titanium dentures
Due to the fact that prostheses implanted into the jaw bone are mostly made of paramagnetic titanium, magnetic resonance imaging with dental implants is a completely feasible and completely safe procedure. Titanium is a biologically inert material, i.e. it is not able to oxidize and release harmful substances during contact with bones, muscles and blood vessels of the human body. Of course, in medicine it is not pure titanium that is used, but its alloys with a small amount of other elements. This is done to make the material durable and light. But they also do not have any negative impact when undergoing an MRI.
By the way, titanium is comparable in strength to steel, and in lightness - to aluminum. Therefore, this metal has received recognition not only from dentists, but also from traumatologists and orthopedic surgeons.
Titanium is also used to produce abutments, gum formers, and metal arches (bases) for dentures.
Effect of MRI procedure on implants
Since the examination is based on the use of magnetic waves, many patients have a logical question: is it possible to do MRI with dental implants? These concerns are understandable, but not always justified.
In dentistry, as in any other area of medicine, prosthetic technology is constantly evolving, new materials and techniques are appearing. So, if previously dental crowns were made of an alloy of copper and gold, today you will be offered metal ceramics or titanium alloy.
What is the difference? Old copper-gold technology produced distortions in MRI images
, but did not affect the health or condition of the patient during the procedure. Today in dentistry, titanium with small admixtures of other elements is widely used, which makes the prosthesis lighter and more durable. By its nature, titanium is chemically inert, therefore it does not oxidize, does not emit harmful substances and does not react to magnetic waves, which means it does not distort images. All this applies not only to teeth, but also to prosthetic bones and joints.
Metal-ceramics during MRI also does not affect either the state of health or the diagnostic result.
But, in addition to the implant itself, there are also pins, plates and screws on which it is attached. They may be the problem. Implant fastening parts are made from various ferromagnets and special iron alloys
, which have positive magnetic susceptibility. Exposure to a magnetic field can produce distorted results and affect the patient’s well-being during the procedure.
Should you tell your doctor that you have dental implants?
A patient with installed dental implants must notify the doctor about this. Then the specialist makes the necessary adjustments, taking into account the location and composition of the prostheses. These settings eliminate the appearance of blurred distortions (also called field artifacts). And then the results of the examination will be clear and precise.
But if a person decides to keep silent about “non-native” teeth, then the picture will turn out blurry, because implants, although slightly, do affect the quality of the pictures. And such a careless patient will have to pay for the procedure and undergo diagnostics again. Why does the blame in this case fall on the patient? Because before the MRI, he will definitely be asked about the presence of implants and what kind of metal they are made of.
“Mom 2 years ago had an MRI of the head and blood vessels, using a high-field tomograph. And she’s had implants installed in her upper jaw for about 5 years now. And nothing, everything went fine. There are no special sensations during the procedure. Just be sure to tell the girls at the reception that there are implants before starting the procedure. They warn the doctor themselves, and then the device is reconfigured.”
Vitalina, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum.
How do iron parts of implants affect different areas during MRI?
Regardless of the area of examination, before the procedure it is necessary to remove all metal objects:
- buttons,
- rivets,
- hooks,
- lightning,
- buckles,
- keys,
- coins,
- keychains,
- decorations,
- watch,
- Cell phones,
- magnetic media (cassettes, floppy disks),
- credit cards.
In addition, it is necessary to warn medical personnel about the presence of implants or prostheses in the body.
, especially those containing metals. During an MRI of the head and cervical spine, the iron alloys in the denture fixtures can heat up and move. This can lead not only to distorted diagnostic results, but also to discomfort or possible injury to the subject. However, such an outcome is only possible if there are large fragments of metal in the body, and the mass of the pin or plate is negligible. Therefore, even with a large number of implants, the occurrence of such a situation is almost impossible. And certainly, the presence of an implant in the body is not a reason to refuse an MRI.
The presence of metal fasteners in dental implants does not have any effect on other types of MRI - bones, joints, thoracic and lumbar spine. Direct MRI diagnostics of teeth is rarely prescribed; it is difficult to “get close” to the jaw using this tomograph.
And MRIs of the limbs, lower back and spine are without consequences. Dental diagnostics using this method is rarely prescribed - it is difficult to “get close” to the jaw using MRI.
Is it possible to have access to tomography if I have crowns?
Are there any special features in MRI diagnostics for patients with dental crowns? This question also worries many. Some people worry that under the influence of magnets, metal, metal-ceramic crowns and pins can fly out of their places and damage something in the mouth. Experts note that metal crowns and pins have absolutely no effect on MRI results, but only if they are made of pure ceramics, zirconium dioxide or high-quality alloys. If the crown is made of metal-ceramics, then it is worth clarifying the metal content in the base - it is likely that you will not be allowed to conduct research.
3D tomography after implant installation
The question often arises: is it possible to perform 3D tomography after installing implants, crowns, and pins?
Unlike MRI, in which artificial bodies “sound” and mislead the dentist, computed tomography after implant installation is allowed, and even recommended. It will be needed in cases where it is required:
- determine the engraftment of the artificial root;
- establish the reason for the instability of the structure or the shortening of its service life;
- check the quality of implant installation if the operation was performed without preliminary computer modeling;
- promptly detect possible complications invisible to the naked eye.
As for metal crowns, there is no need to rush to get a CT scan. First you need to consult a specialist. Conventional metal structures can complicate the examination, as they create optical effects on 3D images, which can lead to incorrect diagnosis.
A separate case is the presence of a pin in the oral cavity. If it is made of fiberglass or ceramic, then CT is acceptable. And if it is made of metal, then the choice of examination method is made based on the criteria:
- level of technical equipment of the clinic;
- qualification of an implantologist;
- the possibility of using alternative diagnostic methods.
Remember that only a specialist with many years of experience can correctly decipher the results of a tomogram that contains titanium or metal pins.
MRI of the brain in the presence of braces
At the beginning of the article, we talked about relative contraindications to undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. These include various bracket systems. Such structures rarely contain titanium (the structure is still bulky, and titanium is not a cheap metal), so they are made from inexpensive ferromagnetic materials (mostly medical steel). These materials, in turn, are magnetized in an MRI scanner. Therefore, braces, retainers and clasp dentures are prohibited from MRI scanning of the head and neck.
But you can undergo diagnostics of the lower part of the body or in an open-type apparatus.
But if the clasp prosthesis is easy to remove and undergo diagnostics without problems, then difficulties may arise with braces. There are 3 ways here:
- Braces and retainers can be removed: if urgent examination is required,
- undergo PET or computed tomography: there are no contraindications for them,
- undergo an examination after the end of the period of wearing braces or retainers: if the diagnosis is not urgent.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS WITH 4 OSSTEM IMPLANTS FOR 1 JAW - RUB 130,000.
Implantation even with bone tissue atrophy. Work guarantee! Save RUR 20,000.
on promotion >> Free consultation with an implantologist +7 (495) 215-52-31 or write to us
Myths for patients with implants
The most common myth about magnetic resonance imaging scares most patients. An incompetent interlocutor - a work colleague or a neighbor next door - may say in horror: “What, you can’t do a tomography with implants - the prosthesis will be pulled out of the jaw by a magnet and it will stick somewhere, or the device will be damaged.” And the person will believe and refuse MRI in favor of a less informative, but more harmful examination (for example, computed tomography).
Every patient referred for magnetic resonance imaging should remember that dental implants are not a contraindication. And if you are denied such an examination, then you need to look for a clinic with modern equipment and a qualified radiologist.
Author: Vasiliev A. A. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
Advantages of the “gold standard” diagnostics
Thanks to computed tomography, the doctor can examine all pathologies at the initial stage of their development, make a diagnosis and promptly prescribe the necessary treatment. When implanting teeth, three-dimensional images are indispensable; they allow you to choose the most suitable option. According to studies, osseointegration is successful in 98% of cases if a preliminary examination is carried out using a tomograph, and in 65% of cases the implants do not take root in the bone tissue due to the lack of CT images from doctors.
The main advantages of computed tomography include:
- Safety of the process - the patient receives a much lower radiation dose than with a regular X-ray (CT is allowed even for young children).
- The procedure is carried out very quickly (the session lasts from 8 seconds to 5 minutes).
- High accuracy of reproduction of the final result, which eliminates the need for the dentist to decipher images.
- Detailed information - the image shows both soft tissue and the smallest foci of inflammation.
- Clarity and contrast of the picture, allowing you to detect even the smallest nuances.
- The ability to study the surveyed area in three planes at once.
- Scaling of images, which allows you to repeatedly enlarge the desired area and view the desired area from all sides.
- Possibility to identify the location of dental nerves in relation to implants.
- Pictures can be copied or printed so that the client can review them.
3D tomography allows you to assess the condition of the dentition, the width of the bone and even hidden complications.
Tomography is carried out absolutely painlessly and comfortably for the patient. Depending on the modification of the equipment, during the examination he may be in a lying, sitting or standing position. The procedure does not require preliminary preparation - it can be completed at the first appointment, for example, when a person comes for an implantation consultation. You don't have to wait for your photos - they will be ready almost immediately.
For a dentist, CT also provides additional advantages: he can determine the treatment method and surgical plan on a 3D model, test its effectiveness, and eliminate possible errors. This will make it possible to see how the dentition will look after correcting the problem.