Diabetes mellitus is a contraindication for many medical procedures, as well as a disease that provokes many other health problems. Including dental ones. Dentistry and diabetes are much more closely related than many people think.
This is partly due to the fact that with diabetes mellitus all the body’s protective functions are significantly weakened, thereby increasing the risk of developing various infectious diseases. And in the oral cavity, where there is a constant nutrient medium for them, infectious bacteria multiply at a catastrophic speed, causing gingivitis
, periodontitis and
caries
.
For example, the likelihood of periodontitis
in patients with diabetes is 3-4 times higher than in other people.
In addition, with diabetes mellitus, changes occur in the very structure of the teeth: blood circulation and the supply of dental tissues with nutrients are disrupted, salivation decreases, and the enamel weakens and becomes thinner.
That is why it is especially important for patients with diabetes to visit the dentist regularly, at least once every six months, for a preventive examination.
Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2
In diabetes mellitus, an excess of sugar occurs in the body due to a lack of insulin, which processes glucose. The disease is divided into 2 types, differing in causes and severity. Implantation is possible only with the second one.
| Type 1 (insulin dependent) | Type 2 (non-insulin dependent) |
| Occurs at an early age due to predisposition and viral pathologies. | An acquired disease, it often develops in adults due to an unhealthy lifestyle and diet. |
| The pancreas does not produce insulin or not enough. | The cells of the body do not perceive insulin. |
| Severe form requiring hormonal therapy. Without treatment, the patient may fall into a diabetic coma and die. | Treatment includes nutritional correction and taking glucose-lowering medications. Without treatment, it can turn into the first type. |
| Implantation is not possible. | Implantation is possible. |
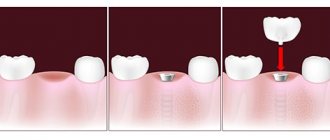
Implant installation
The procedure for implanting an artificial tooth root in a diabetic is no different from that performed on ordinary patients, except that all manipulations must be carried out as carefully as possible.
The implant must be installed as carefully as possible, without severe tissue injury. This procedure can only be entrusted to a trusted and experienced specialist.
Implant installation includes the following steps:
- Introduction of anesthesia.
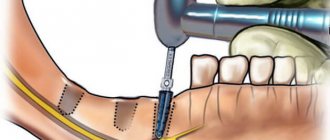
- Opening the bone tissue, preparing a bed for the implant in it by drilling.
- Installation of the structure.
Due to high patient fatigue, all stages of the procedure must be carried out quickly.
Risks of implantation
Implantation is complicated by concomitant diseases (pathology of blood vessels, heart), caries, periodontitis, xerostomia. If the patient leads an unhealthy lifestyle and does not visit doctors on a regular basis, implantation is fraught with complications.
Possible consequences:
- Allergic reaction . Occurs on materials of implants and prostheses and requires constant therapy.
- Complicated engraftment . If there are problems with the immune system, implants take longer to take root.
- Implant rejection. Failure to comply with doctor's instructions, diet, or taking glucose-lowering medications can lead to serious complications. The body will not accept the implant if the patient does not control sugar.
The longer a patient lives with diabetes, the higher the risk of implant treatment.
In what cases is implantation impossible?
The operation is not performed in the decompensated (uncompensated) stage of the disease or insulin-dependent diabetes, since in this case it is impossible to maintain the required level of health.
Installation of implants is prohibited if the medical history additionally includes:
- tuberculosis;
- bleeding disorders, blood diseases;
- mental disorders;
- arthritis or rheumatism;
- severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- oncology;
- low level of immunity;
- bruxism, pathological bite;
- chronic alcoholism;
- active smoking with the inability to give up cigarettes for a long time.
Temporary restrictions include acute infections, exacerbation of chronic diseases, dental diseases and a number of other pathologies that can be eliminated.
When an operation is possible and prohibited
Installation of implants is possible if a number of conditions are met.
Implantation possible
- Compensated type 2 diabetes mellitus - sugar not higher than 7-9 mol/l
- No concomitant diseases
- Taking hypoglycemic drugs, low-carbohydrate diet
- Careful oral hygiene
- Rejection of bad habits
- Regular doctor visits
Implantation is prohibited
- Decompensated SC of the first type
- Concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system, problems with the circulatory system
- Increased blood sugar levels, carbohydrate metabolism disorders
- Failure to maintain regular oral hygiene
- Smoking, drinking alcohol
- There is no possibility of constant monitoring by an implantologist and endocrinologist
Rehabilitation period
Upon completion of all manipulations, the doctor gives the patient detailed recommendations, which he must follow impeccably. Particular attention should be paid to controlling glucose levels, since drastic measures often provoke a rise in glucose levels. Antibiotics are prescribed for 7-10 days. The patient must strictly observe oral hygiene and visit the dentist once every 2-3 days. It is extremely important to avoid smoking. More detailed information can be found on the Implant Installation page.
The most acute period is the first 15 days. Painkillers may be prescribed at this time. Dosage and medications are selected individually. Avoiding alcoholic beverages is also non-negotiable. To ensure even sugar levels, you need a gentle diet. Avoidance of solid products will protect installed structures from damage.
Features of implantation
The risk of complications during implantation is quite high. The patient must first undergo examination by an endocrinologist and an implantologist to determine the possibility of surgery. The success of engraftment depends on the qualifications and experience of the doctor, the correct treatment tactics and the implantation system.
Preparation
- Visit to a therapist and endocrinologist, blood and urine tests, determination of sugar levels.
- Caries treatment, professional cleaning. The patient should intensify home brushing of teeth one month before surgery.
- Computer diagnostics of the jaw bone to assess its condition and determine hidden diseases.
What methods are used
- Single-stage with immediate load. The implant is implanted into the socket of the extracted tooth. The tissues are not additionally injured, healing occurs naturally. Temporary crowns can be placed immediately, permanent crowns can be placed after complete healing.
- One-stage. The implant is placed in place of the extracted tooth after the socket has healed. Using a thin instrument, a puncture is made into which the threaded implant is screwed. It does not destroy the bone and guarantees good primary stabilization. The crown is installed immediately. The method is used when there is a sufficient amount of bone tissue.
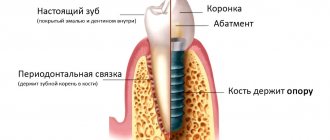
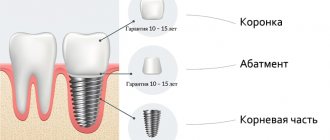
- Classic. A rod is installed in place of the missing tooth, covered with a gum flap, and sutured. After the implant has healed, prosthetics with a crown are performed - the gum is opened, a gum former is installed on the implant, and after 2 weeks an abutment with a crown is installed.
Installation of implants should be careful and minimally traumatic. Osseointegration of the implant with the bone in diabetes mellitus takes longer - on the lower jaw, implants take 6-7 months to take root, on the upper jaw - 8-9. At the same time, the percentage of rejection is higher at the top.
Requirements for implants and prostheses
Implants for diabetics are made from purified titanium. All structural elements and prosthetics must be bioinert. Metal-free zirconium crowns are recommended. The type, size, and design of implants are selected after a CT scan using 3D modeling.
When choosing a clinic, pay attention to the implantation systems and prostheses installed, as well as the experience of the specialists.
Modern technologies
For rods that are implanted in patients, alloys such as nickel with chromium and cobalt with chromium are used today. These materials are hypoallergenic and do not give a metallic taste. Such rods have increased roughness; as a rule, they are coated with silver ions. It is very important to strictly adhere to the norms and rules during their manufacture regarding the distribution of forces during chewing. Thorough sanitation plays an important role. A possible option is to prescribe antibacterial drugs before the operation.
Remember! Do not hesitate to install the structure. If the disease appeared relatively recently, the success of engraftment increases significantly.
Of course, the effectiveness of the dentist’s work depends on the quality of the pins, which should not affect the quantity and composition of the patient’s saliva. As for crowns, it is best to go with ceramics. It is ideal for diabetic patients. In addition, the material is highly aesthetic and has sufficient strength. All these requirements are complied with in our center. More detailed information can be found on the Turnkey Dental Implant page.
As you can see, advanced technologies and the latest approaches allow us to solve even complex issues these days. If 10 years ago no one allowed diabetic patients to undergo implantation, now this is already a common practice. Thanks to effective methods of maintaining sugar levels that are not dangerous for the patient, the risks of inflammation during the implantation of the structure are minimized. Low-traumatic dental technologies are used for such patients. Laser implantation has gained great popularity. True, in each individual case all taboos and possibilities are weighed, and the best option is selected.
Why is it important to monitor your sugar levels?
Due to increased sugar levels, changes occur in the oral cavity, which lead to diseases of the teeth and gums.
- Hyposalivation, lack of saliva. Dry mouth, constant feeling of thirst. Due to lack of saliva, tooth enamel is destroyed and caries occurs. Conditions for infection are created in the mouth.
- Inflammatory processes of the gums lead to tooth loss as the root system is destroyed. Healing takes longer, and purulent lesions are possible.
- Fungal infection. CS contributes to the recurrence of pathologies. The fungus attacks and destroys healthy teeth.
- Bacterial infection. Diabetics have an increased concentration of microbes in their mouths. If hygiene is insufficient, healthy teeth suffer. Accumulations of bacteria are located in dental cavities.
- Violation of regenerative processes. Diabetics have a reduced metabolism. Wounds, ulcers, and infected lesions take longer to heal.
Factors that may affect the success of the procedure
How successful implantation will be in a diabetic depends on the following factors:
- How correctly the patient was prepared for the procedure. A complete sanitation of the oral cavity and professional teeth cleaning must be carried out. This will reduce the risk of infection. Taking antibacterial drugs before implantation also reduces the risk of complications.
- Length of illness. The less the patient suffers from the disease, the more the risks after implantation are reduced.
- The presence of concomitant ailments - caries, periodontitis, xerostomia, infectious and cardiovascular diseases also affect the success of the operation.
- Type and stage of the disease. If diabetes compensation is high, implantation can be performed. Diabetics who keep the situation under control with the help of a special diet and do not use hypoglycemic drugs can also become patients of the implantologist. And for diabetics who do not cope well with increased sugar levels and who are forced to inject themselves with insulin, they are at risk of complications after surgery. Implantation is not recommended for them.
- Implant location. When implanting implants in this group of patients, doctors must take into account that the upper jaw has a greater chance of engraftment than the lower jaw.
- Implant length. As noted earlier, medium-length implants are more suitable for diabetics than those whose length exceeds 13 millimeters or does not reach 10 millimeters.
What preparation does a diabetic have to undergo before implantation?
In our clinic “AcademStom” we carry out thorough sanitation of the oral cavity:
- Professional hygienic cleaning with removal of soft and hard dental deposits (tartar).
It is known that plaque is a breeding ground for bacteria; removing it can prevent tissue infection and implant rejection. - Fighting caries.
A carious tooth is a source of infection in the body. - Gum treatment.
Before implantation, you need to make sure that the patient does not have gingivitis or other soft tissue diseases. - Bleaching.
If there are no contraindications and there is a need, before the implantation procedure it is necessary to restore the natural color of the tooth enamel.
Patients who have completed all the necessary preparation are allowed to undergo implantation.
Key Success Factors
- Enhanced hygiene throughout the entire period of preparation, treatment and rehabilitation. The oral cavity must be perfectly clean to eliminate the risk of infections.
- If you have diabetes, the entire procedure should be minimally traumatic, since healing occurs much worse. Simultaneous dental implantation for diabetes mellitus is considered the least invasive, however, in the presence of this disease, it is not always possible to immediately load. Classic two-stage implantation requires the use of laser and other minimally invasive technologies.
- Osseointegration lasts longer (6 to 7 months in the lower jaw, 8 to 9 in the upper jaw). Restoring teeth in the upper jaw is considered a more risky and unpredictable procedure in the presence of diabetes.
- Strict requirements for materials and implants. For diabetes mellitus, implants of medium length (10 - 12 millimeters) made of pure titanium or specially designed alloys are usually placed. The components of the prosthesis must be completely bioinert, the crown must be metal-free.
The cost of implantation for diabetes mellitus will be higher compared to classic clinical cases. This disease requires the use of advanced technological solutions and the most modern materials, so an attempt to save money can lead to unpleasant consequences. Many elite manufacturers produce a separate line of implants and related components for patients with diabetes, so we advise you to pay attention to such solutions.
What implants and prostheses can be placed for diabetes?
The body of a person with diabetes reacts more sharply to external influences, therefore both implants and prostheses for diabetics must be bioinert. Titanium implants without impurities and zirconium metal-free crowns have proven themselves well. When choosing dentures, preference is given to lightweight materials and their design is carefully thought out in order to achieve uniform distribution of the load when chewing.
The type of implants, prostheses and their location are planned at the stage of preparation for implantation. Based on the CT results, a three-dimensional model of the patient’s jaw is created. Next, with the help of special programs, they mark on it which implants will be implanted and how.
After approval of the operation plan, a special 3D template is created using this data. During the procedure, it is placed on the jaw and the implant is inserted at precisely marked points on it.
How the disease affects teeth - dangers
Systemic metabolic failure, which is what diabetes mellitus is, in addition to its destructive effect on the entire body, also affects the health of teeth, soft and bone tissue. That is, dangers can arise not only during implantation (complex surgical intervention), but even on previously healthy teeth. The disease affects the following processes:
New teeth in 1 day - All-ON-4 - 180,000 rub.
All inclusive!
3D modeling of the structure with a prosthesis, implantation of 4 Osstem implants, installation of a fixed prosthesis on the same day. Free consultation with an implantologist +7 (495) 215-52-31 or write to us
- mineral metabolism and absorption of calcium: their disruption leads to fragility and thinning of the enamel and the subsequent development of caries,
- change in the chemical composition of saliva: “sweet” and viscous saliva does not perform the function of cleansing teeth from bacteria, but itself serves as a medium for their development,
- blood circulation in the gums: due to vascular pathologies caused by excess glucose, blood flow is disrupted, gum nutrition is significantly deteriorated, which leads to tissue inflammation and the development of periodontitis,
- blood clotting and weakened immunity: gum inflammation in diabetics is often accompanied by candidiasis and the appearance of sores in the mouth. Poor clotting interferes with healing, and weak immunity does not fight infections that arise.
In Russia, according to WHO, the prevalence of the disease is about 10%. The connection between diabetes mellitus and the development of periodontitis as its complications has been proven. Patients with diabetes are 2 times more likely to experience periodontitis than those who do not suffer from it[1].
All this significantly increases the likelihood of complications after implant installation, and also increases the risk of rejection of structures and the development of infectious diseases.
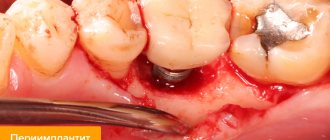
Read more about the reasons for implant rejection and the development of peri-implantitis on our website in the “Complications during implantation” section.