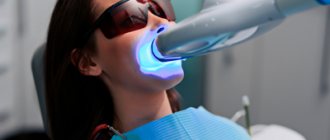
Often dental treatment in children is not complete without anesthesia. Proven ways to calm a child during painful and uncomfortable procedures include the use of nitrous oxide, also called “laughing gas.” Many parents ask questions about how it will affect the child’s health, what side effects there may be and what contraindications exist.
Nitrous oxide in dentistry for children
In this article we will talk about how nitrous oxide is used in dentistry for children.
Sedation – what is it?
Sedation involves putting the patient into a half-asleep state while using nitrous oxide. This method, actively used in modern dentistry, can relieve the patient of fear and anxiety and set him at ease.
Interesting! Qualified specialists in the USA and England have been using nitric oxide for many years. This method has virtually no contraindications and is actively used in dental treatment for children. Our doctors use sedation so that children do not worry, cry or become hysterical during their next trip to the doctor.
About sedation with nitrous oxide
Sedation does not in any way affect a person’s main reflexes:
- breathing remains the same, movements are not limited or slowed down;
- mental activity is not impaired;
- the patient can talk, see, hear, understand.
At the same time, the child feels completely relaxed, and he is not negatively disposed to what is happening around him. A child under laughing gas will not even feel the dentist injecting an anesthetic and treating his teeth. Small children cannot sit in a chair for more than 5 minutes, but the duration of treatment with sedation can increase to 1 hour, which reduces the required number of doctor visits several times.
The child feels completely relaxed, but at the same time he is conscious
Nitrous oxide sedation: new views on an effective method
A mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen (N2O/O2) is completely safe and has been successfully used for over 160 years to relieve pain and anxiety. In the early 1800s, dentist Horace Wells dedicated his life to promoting nitrous oxide in both general medical and dental practice. Because he promoted the use of nitrous oxide for pain control, he was posthumously given the title of "Discoverer of Anesthesia." Since that time, the method of sedation with nitrous oxide has become one of the most common in dental practice, in addition, it began to be used as a premedication at the beginning of the general anesthesia procedure.
Very often, dental patients seek help already with certain signs of pain or anxiety. Moreover, the feeling of anxiety can be associated directly with the visit to the dentist itself. Consequently, the doctor has to relieve these two sensations at once, since they are interrelated. The use of a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen at minimal cost allows you to effectively and safely deal with emotionally difficult clinical situations in dental practice. In this article, we will describe the main characteristics of nitrous oxide, indications for the use of the N2O / O2 mixture, and also analyze the main facts and myths associated with the long-term effects of nitrous oxide on the body, the biological effects of this gas, and approaches to minimizing the risk of contamination of the dental office space through N2O.
Advantages
Nitrous oxide/oxygen (N2O/O2) sedation offers a number of advantages over other sedation methods or alternative pharmacological agents. The properties of nitrous oxide allow this gas to not only relieve pain, but at the same time reduce anxiety. However, this effect is limited and observed over a short period of time. Nitrogen sedation can also be used in the treatment of patients with bronchial asthma, in which case the role of the gas is limited to the fact that it allows minimizing the effect of provoking stress factors. Nitrous oxide can be titrated, meaning that additional doses can be given to the patient over time until the desired level of sedation is achieved. Gas is eliminated from the body at almost the same rate as its accumulation. Most of the injected gas is eliminated through the lungs within a few minutes after stopping its supply and starting to breathe pure oxygen. You can also help remove nitrous oxide from the body by breathing regular air, but this manipulation will take a little longer. N2O/O2 mixture can be safely used among patients of all age groups. In addition to its main actions, it also allows you to somewhat suppress the gag reflex, thus creating conditions for conducting x-ray examinations and taking impressions. There are only a few contraindications to the use of nitrous oxide in dental practice, since its effect on the human body in general is neutral rather than negative.
Contraindications
In some situations, the use of N2O/O2 sedation should be delayed or avoided. When planning to undergo sedation, you should always seek the advice of your physician. The following are conditions under which it is imperative that the patient consult with a physician prior to undergoing sedation, and if consultation is not possible, the procedure should be postponed until the conditions described below have been completely relieved.
The use of medications during the first trimester of pregnancy is not recommended, therefore, exposure to nitrous oxide should be avoided. It is recommended to carry out any dental interventions in the second trimester. Similarly, with complete safety, a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen can be used in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, but, of course, after consultation with your doctor.
An upper respiratory tract infection (such as sinusitis) often causes nasal congestion, which may prevent gas from entering the respiratory system. In such cases, it is better to start sedation after the underlying disease has resolved. The use of a N2O/O2 mixture in cases of emphysema and chronic bronchitis is problematic; in these disorders, the use of sedation is prohibited due to the impossibility of ensuring proper airway patency. If you have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, the use of sedation is possible only after consulting your doctor. Given that nitrous oxide has expanding properties, its use is limited in cases of active cystic fibrosis. Likewise, it is not advisable to use nitrous oxide after ophthalmic surgery. Certain complications after sedation can develop in patients after repair of the eardrum. As a result of the gas expansion phenomenon, complications with nitrous oxide use are predicted to occur in patients with pneumothorax or constipation.
On the other hand, patients with such pathological conditions rarely seek dental care until treatment for the above-mentioned disorders is completed. Patients taking bleomycin sulfate as a drug to treat certain types of cancer have an increased risk of developing pulmonary fibrosis. This outcome is associated less with the influence of nitrous oxide than with the influence of oxygen itself (at a concentration of more than 30%). But such situations (using bleomycin and performing sedation at the same time) are rather exceptions. According to the literature, after performing pneumoencephalography, there is an increase in intracranial pressure due to the fact that nitrous oxide replaces nitrogen molecules. Therefore, after pneumoencephalography, nitrous oxide sedation should be postponed for at least a week. One should be extremely careful when using sedation for psychological illnesses, and exclude the possibility of performing this manipulation when the patient is under the influence of drugs. It is also undesirable to perform sedation among patients who do not fully understand the essence of the manipulation due to impaired consciousness (for example, with Alzheimer's disease), as well as among patients taking psychotropic drugs. But it should be remembered that in addition to nitrous oxide sedation, there are other options that can be used in the above situations.
Based on our experience, we also recommend avoiding nitrous oxide sedation in patients with whom you cannot communicate well due to a language barrier, as well as in patients who suffer from claustrophobia and who have difficulty putting on and maintaining a mask in position. It is extremely important that the physician performing sedation is familiar with all evidence-based information regarding aspects of the implementation of this manipulation.
Evidence-Based Research
An evidence base is a necessary component for the implementation of effective dental treatment. There are several reports in the literature of the effects of nitrous oxide as an occupational risk factor. Historically, nitrous oxide has been associated with many disorders, ranging from birth defects to neoplasmic lesions. However, recent research indicates that low concentrations of nitrous oxide, such as those reported in dental office settings, are completely safe for dentists to use. It is also necessary to note the effectiveness and safety of new types of devices used for nitrous oxide sedation procedures. Of the 800 dental publications discussing the effects of nitric oxide that were published before 1995, only about 25 met the required parameters for reliability and validity. Many of the above-mentioned studies were conducted using retrospective designs, which in themselves are not very statistically reliable unless all methodological criteria are adhered to to the required extent. The first study of nitrous oxide as an occupational risk factor was published in 1967: a Russian researcher pointed out reproductive problems that were noted among anesthesiologists working in direct contact with the gas. Similar publications were presented in the United States in the late 1970s and early 1980s. But since then, methods for storing, supplying, dosing and using nitrous oxide have improved significantly. Nowadays, all such systems for working with gases are also equipped with special units for intake and purification of the surrounding air from traces of nitrous oxide. In addition, completely new systems for supplying nitrous oxide as a sedative agent continue to appear on the market, which are conceptually different from older analogues.
In one influential study from 1985, Sweeney and colleagues used an extremely sensitive deoxyuridine inhibition technique to identify critical levels of nitrous oxide concentrations. So, based on the results obtained, the visible biological effect of nitrous oxide is observed only at a concentration of 1800 parts per million (ppm). To date, there has not been a single clinically confirmed case of negative biological effects of nitric oxide in dental working conditions at the low levels of gas that are observed in the air during and after the sedation procedure.
Biological effects
The most significant biological effect associated with nitrous oxide exposure is its ability to inactivate vitamin B12. This mechanism affects an enzyme called methionine synthetase. Methionine synthetase, in turn, is essential for DNA production. Impaired fetal development was found in animals that were exposed to 60% nitrous oxide 24 hours a day for 12 days. The negative chronic effect of nitrous oxide on human reproductive function was discovered only in the conditions of incorrectly conducted studies, the subjects of which were exposed to high concentrations of the gas in the complete absence of cleaning of work areas. As for DNA synthesis disorders, such a risk is associated only with women during pregnancy, or with women planning to become pregnant. However, it is best to know the exact levels of nitrous oxide in a room before doing any work in it. The toxic effect of nitric oxide on the human body is the subject of debate in modern scientific literature. Despite this, available data indicate that the gas is completely safe when used in limited therapeutic doses. Neurological symptoms associated with nitrous oxide include numbness, tingling, and in some cases paraesthesia of the extremities, clumsiness, slow gait, altered reflexes, and muscle weakness. It is logical that the severity of these disorders is associated with the duration and dose of exposure to nitrous oxide. Cases of nitric oxide overdose reported in the literature have involved exposure to the gas for several hours a day for two weeks straight. However, some people exposed to chronic nitrous oxide indicate resolution of symptoms after the gas stops, and some indicate their permanent nature.
Concentration control
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and the American Conference of Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) have been instrumental in developing recommendations regarding threshold levels of nitric oxide during human work activities during an 8-hour workday. In 1977, these organizations established nitric oxide concentration limits for health care workers. It has been determined that in operating rooms and dental offices, nitrous oxide concentrations should not exceed 25 and 50 parts per million, respectively. These levels were established based on the results of preliminary studies by Bruce, Bach, and Arbit, as well as the characteristics of the equipment used. These critical concentration levels are still relevant today. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is the organization that has the authority to enforce these recommended levels; however, because of controversy regarding their appropriateness, OSHA recognizes that it would be desirable to revalidate such concentration limits.
To address several pressing issues regarding nitrous oxide, a meeting was convened in October 1995 by the Council on Scientific Affairs of the American Dental Association. It brought together several stakeholders, including respected experts in the field, educators, manufacturers and government officials. It was concluded that the true recommended exposure limit for nitrous oxide cannot be clearly established. Sweeney et al proposed a concentration level of 400 ppm as a cutoff. In their opinion, this level is the most commonly achieved, and is much lower than the 1800 ppm level at which the biological effects of nitrous oxide were first recorded. Other countries have adopted the following nitrogen oxide exposure limits: from 25 ppm in France and Denmark to 100 ppm in Sweden and Germany.
Estimation of nitrous oxide concentration levels
To determine whether traces of nitrogen oxide are present in a room, levels must be objectively measured in parts per million. To do this, they use a device - an infrared spectrometer, which allows you to determine the concentration of not only nitrogen oxide, but also other gases in terms of parts per billion (ppb). Of course, there is no point in buying it purposefully, but you can rent it either directly from the manufacturer or at a local hospital. In addition, the spectrometer allows you to detect areas of gas leakage from containers containing it. Another approach to estimating nitric oxide concentrations is to determine the amount of nitric oxide a person is exposed to over a period of time. To do this, the measuring device is simply put on, like a dosimeter, and carried with you for several hours. Thus, the time-weighted average (TWA) of nitrous oxide absorption is determined by its amount in the collecting tank of the measuring device.
Minimizing the risk of contamination
It is extremely important to pay due attention to measures to reduce the risk of nitrous oxide contamination. Disposal of trace gases can be ensured before, during and after use for dental purposes. Leakage of small amounts of nitrous oxide can occur in the area of all equipment connections, regardless of the specific use of portable or stationary equipment. To avoid this, manufacturers recommend periodic monitoring of the equipment used. Each manufacturer provides the necessary information regarding the frequency with which control measurements should be carried out, on average twice a year. Using ordinary soap and water, you can easily identify problem areas in terms of gas leaks in the system you are using. In addition, it is extremely important to ensure the reliable functioning of systems for the extraction of gas residues that form outside the nasal tube during its supply.
It must also be remembered that nitrous oxide can enter the doctor’s body not only due to system problems, but also directly from the patient. To minimize this effect, it is extremely important to limit conversation with the patient during the manipulation, because the gas that he inhales easily exits through the oral cavity. In addition, it is necessary to ensure that the mask fits snugly, taking into account its proper size. Sometimes all that is required for a tight fit of the mask is simply to form the necessary bend in the conductive tube. Despite the fact that nitrous oxide is much heavier than air, and even when it spreads outside the mask and tube, it immediately “falls” to the floor, this gas is also extremely expansive in nature. In other words, it spreads very quickly and easily over the entire surface area. On the other hand, the partial pressure of nitrous oxide is 31 times that of air, increasing the chance of it entering the physician's airway before it reaches the floor surface in cases of leakage.
Recommendations for monitoring nitrous oxide impurities in workroom air
Below is a list of recommendations and preventive measures aimed at minimizing the level of nitrous oxide contamination in the dental office environment.
- It is necessary to first establish the baseline concentrations of nitrous oxide in the clinic and in the surrounding air using an infrared spectrophotometer.
- To assess personnel exposure to gas, it is recommended that time-weighted instruments be used.
- Every 2 years, send equipment to the manufacturer for routine maintenance and evaluation.
- Provide visual monitoring of the integrity of conductive tubes and reservoirs.
- Use the "soap suds" principle to check the tightness of connections for possible gas leaks. To do this, add a few drops of detergent to a small amount of water, and wipe the areas of connections, reservoirs and conductive pipes with this solution. If there are gas leaks, bubbles will form.
- Ensuring effective evacuation of gas traces.
- It is necessary to assess the effectiveness of room ventilation and air exchange. In certain cases, measures may be required to improve the existing ventilation system to reduce the level of gas residues in the indoor air. Some air conditioning systems do not provide air exchange at all, but operate on the principle of recirculating existing air.
- Provide full information support to operating personnel regarding the possible risks of complications associated with chronic exposure to nitrous oxide.
Summary
The sedative effect of nitrous oxide allows you to optimize the treatment process for patients with existing fear of dental interventions. The use of this gas is justified by a number of advantages and only a small number of disadvantages. Understanding the principles of reducing the effects of nitric oxide on clinical staff is also an important factor in its effective use. Dentists should be fully aware of the new facts and basic concepts of the use of laughing gas in their daily practice, while paying special attention to monitoring the concentration of this gas in the air of the working environment. If you would like to know more about local restrictions regarding critical values for nitrous oxide that are relevant for your country or region, we recommend that you contact the appropriate quality control authorities for the provision of dental and medical care for information.
Authors: Ann Brunick, RDH, MS Morris S. Clark, DDS, FACD
Sedation: What you need to know
Sedation is not a pain-relieving procedure; it can only slightly reduce pain. To completely eliminate pain, resort to anesthesia or local painkillers.
When treating a child, the doctor must take care to create a favorable atmosphere so that nitric oxide can eliminate severe anxiety.
Interesting! If the child is not too small and there are no contraindications, experts strongly recommend sedation at the first visit to the doctor.
It is better to use sedation at the first visit to the doctor - thanks to it the baby will not be nervous
Adults who are afraid of visiting the dentist may also request the use of sedation. However, an adult, unlike a child, may have more contraindications (chronic pathologies, alcohol dependence, skull trauma).
Nitric oxide is used for children who have reached a certain age, can speak and respond adequately to the doctor's actions.
During the procedure, the child will be able to talk and watch cartoons.
Anesthesia and sedation: distinctive features
Sedation and anesthesia are completely different methods used in dental treatment.
During sedation, a person remains conscious, can speak and breathe calmly. Anesthesia presupposes a complete shutdown of consciousness, immersion in sleep and lack of reaction to what is happening.
Anesthesia differs from sedation in that during it the patient is not conscious
Why is it better to entrust dental treatment to ZAX?
By contacting our clinic, you can rest assured that the health of your children’s teeth is in good hands. There is confirmation of these words. A few facts about our center:
- an X-ray machine and a device with dinitrogen oxide are at the disposal of every doctor;
- laboratory at the clinic;
- exceptional security measures;
- high speed of treatment (we do maximum work in 1 visit);
- staff anesthesiologist, etc.
If you need careful and high-quality dental treatment for your children, then call or leave a phone number for feedback. We want to become your family dentistry.
Anesthesia and painkillers
Sedation is not considered an alternative to anesthesia. Along with it, traditional methods of pain relief are used - for example, local anesthesia. Most parents worry about the child’s condition during the administration of an anesthetic.
Sedation for children is carried out before intervention in the oral cavity. In addition, nitrous oxide has a slight analgesic effect, and a real professional will give the injection so that the child will not even notice it. Also, the mask that the child puts on his face does not allow him to see the syringe and various instruments in the doctor’s hands.
Nitric oxide has a mild pain-relieving effect
How does sedation work?
Nitric oxide has been widely used for gynecological and surgical purposes for decades.
Interesting! One American company spent several years developing a system that creates a soothing solution consisting of 70% nitrous oxide and 30% oxygen. This is an electronically controlled mechanism that has a high degree of protection against failures and errors when determining the dose of the solution.
The supply of nitrous oxide is carried out thanks to a special apparatus
Gas supply is a fully automated process. Through a mask that covers the nose, the mixture enters its cavity, and a high-speed pump absorbs exhaled air. Taking into account the patient’s age and general health, the specialist uses the device to calculate the dose, which can be adjusted during the treatment process.
When the gas is inhaled, the patient becomes calm and relaxed. He remains conscious all the time, can react and carry on a conversation. Upon completion of the treatment process, the mask is removed and the laughing gas immediately ceases its effect.
Laughing gas stops working almost immediately after the patient's mask is removed.
This allows you to feel emotionally comfortable when visiting a doctor, without feelings of anxiety and fear.
Safety of the procedure for a child
Medical dinitrogen oxide does not irritate the respiratory tract and does not cause allergies due to high-quality cleaning. The inertness of the mixture excludes its reaction with other substances, changes in composition or interaction with hemoglobin. After the gas stops entering the body, it remains in it for no more than 5 minutes, after which it is completely excreted unchanged. Such features allow us to classify nitrous oxide as one of the safest medical substances. The use of gas is not prohibited during operations on pregnant women; the mixture is used during childbirth.
Without medical indications, the use of nitrous oxide is undesirable. If your child needs to have several teeth treated in a row, there are no restrictions on the amount or frequency of the drug inhaled. The technology has a limited number of contraindications.
In addition to individual intolerance, these are:
- Difficulty in nasal breathing (colds, allergies, adenoiditis);
- Dental phobia, panic fear of doctors;
- Inability to have confidential communication with a doctor (due to age or illness);
- Recent traumatic brain injury;
- Exacerbation of chronic otitis;
- Seizures, epilepsy.
To exclude complications, before using the procedure, the doctor is interested in the child’s health condition.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
| Advantages | Flaws |
| 1. Laughing gas, used in small doses and having a relaxing effect, is similar to mild intoxication. 2. The procedure is called “sedation” because the patient’s consciousness is slightly suppressed, but basic reflexes are not affected. 3. The child’s feeling of pain decreases, fear fades into the background, the stressful state appears less and less at each visit, and later goes away completely. 4. Nothing prevents the child from talking, moving and breathing. Parents will not have to use force to keep the child in the chair. 5. Thanks to thorough gas purification, the product cannot provoke an allergic reaction or cause irritation to the respiratory system. 6. Gas does not take part in the internal processes of the body. This allows us to assert that it is harmless when treating children. | 1. In some cases, children may experience headaches and dizziness. 2. Gas has a strong pungent odor, which not all children like. 3. Nitrous oxide should not be used for a runny nose or other respiratory problems. 4. You will have to pay extra for sedation. 5. Sometimes the effect of laughing gas is paradoxical. The expected relaxing effect is replaced by sharp excitement and inadequacy. Sometimes vomiting occurs. 6. Since nitrous oxide is not an anesthetic, in some cases it is necessary to additionally use local anesthesia. |
This procedure has both advantages and disadvantages
How early can N2O be used in dental treatment?
The use of a medical mixture of nitrous oxide is used for preschool children. It is problematic to force a four-year-old patient to sit in a doctor’s chair and sit there for more than a quarter of an hour without additional sedation. Whims, bad behavior and the desire to leave the office prevent the doctor from performing the necessary procedures. Nitrous oxide helps to extend the child’s time in the dentist’s chair to 40 minutes, while the child’s body does not receive any harmful effects. During this time, the dentist is able to perform even complex manipulations, significantly reducing the number of visits to the clinic.
For a child with a negative experience at the dentist, oxygen sedation is the only way to calm him down and carry out the medical procedure. The minimum age of patients for whom this method of sedation is used is 4 years. At this age, a baby can already be seated in a chair by putting on a mask, which is important during treatment.
Dental experts recommend using nitrous oxide sedation for patients at the first visit, when the examination is accompanied by full treatment. When meeting a doctor for the first time, children may experience unreasonable anxiety. Consuming the sweetish gas helps the baby relax, and his fears gradually recede. The specialist will have the opportunity to calmly conduct examination and treatment if necessary. In subsequent sessions this will no longer be necessary.
When should you use sedation?
Dental treatment for children is a rather difficult process. Sedation allows you to remove children's fear and fear. It is especially worth using it at the first visit to the doctor in order to prevent a negative experience and so that the child has a good understanding of the doctor.
Sedation should also be used for long-term treatment lasting more than 30-40 minutes.
Important! It is difficult for a child to sit in one place for so long, so it is especially important to relax and calm the baby in order to facilitate the treatment process.
Sedation is necessary because it is difficult for a child to sit in one place for a long time.
Contraindications
Sedation is not used in complex therapy, when, in addition to the child’s fear, it is necessary to eliminate the reaction to external irritating factors.
Laughing gas should not be used when:
- allergies, colds, sinusitis and if the disease complicates the natural process of breathing;
- lack of contact between the child and the doctor. Therefore, it is not recommended to use nitrous oxide for children under 3 years of age;
- recent head injury;
- seizures and epilepsy;
- excessive panic and fear.
One of the contraindications to this procedure is sinusitis.
How to order nitrous oxide?
The sale of medical “laughing gas” is carried out under a special license. You can purchase its other variety, food grade N2O, in Moscow absolutely legally without a license. To order laughing gas for a party, please contact. Our store operates 24/7, delivery by courier is carried out around the clock. There are attractive discounts and promotions for regular customers. In addition to sales, we provide cylinder replacement services. You can check all the details with the manager by phone.
How is laughing gas used?
Before using gas for children, you need to familiarize parents in detail with the upcoming procedure. It is important that the child sits in the dental chair independently and agrees to dental treatment. The baby puts a mask on his face, to which tubes from the cylinder are connected - gas flows through them.
Interesting! The cylinder is filled with nitrogen, oxygen and other components in small doses.
The effect of laughing gas will begin a few minutes after putting on the mask.
The doctor turns on special equipment, and nitrous oxide enters the patient's nose. After a couple of minutes, the doctor can examine the baby’s oral cavity and begin treatment. The child can watch cartoons during treatment. The mask does not prevent the doctor from reaching problem areas.
What is the price of sedation in dentistry?
The range of prices for sedation in Moscow dentistry is wide. The cost of sedation in one dental clinic may differ significantly from the cost of services in another dentistry. But choosing a clinic just because it is cheaper is not recommended. Remember that sedation can be a hazardous procedure if performed by an unqualified person using outdated equipment and outdated medications. The average price for treatment under sedation can reach 15,000 rubles per hour. But, at the same time, the procedure is carried out under the supervision of an experienced anesthesiologist using modern equipment and using safe drugs. In addition, the clinic should have everything necessary in case of emergency, which is very important. There are also conditions for comfortable rest for small and adult patients after treatment under sedation.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Sedation: possible consequences
Sometimes children experience a sharp rise in temperature and hyperemia. Sedation can cause temporary disruption of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
Current observations indicate a significant risk of cognitive impairment during dental treatment with sedation, which is due to deterioration in the functioning of brain neurons. Although the risk is small, it is unlikely that anyone would want these circumstances to affect them.
In rare cases, temporary complications may occur after such a procedure, for example, hyperemia
What are the advantages of the gas used?
Nitrogen, or rather its combination with oxygen, is considered the most acceptable means of sedation for a child, since the drug is used in low concentrations that can cause slight depression of consciousness while maintaining all reflexes and contact with the outside world. The doctor can talk with the small patient during the procedure. The latter is even allowed to watch cartoons.
Nitrogen does not have a very pronounced sedative effect. This means that the child will behave more compliantly during the procedure; he will not need to be restrained by force, traumatizing the psyche.
Another undeniable advantage of medical gas is that it is hypoallergenic and has no irritating effect on the respiratory tract. The compound is completely inert. It does not react with blood elements. Its effect on the body stops immediately after the supply of the gas mixture is stopped during dental treatment.
At what age can you use nitrous oxide?
Children under 7 years old are often given sedation, as it significantly increases the time the baby spends in the chair. This is due to the fact that a very young child practically does not sit still, especially if he feels fear, and after 10 minutes he will try to leave, and if that doesn’t work, he will start to have a tantrum. In such a short period of time, the doctor will not be able to completely and efficiently cure teeth. In this case, you will need 5-6 visits to the dentist for complete treatment.
This procedure can be performed on children over 4 years of age.
Often among patients there are children who already have negative experiences with dentists. In this case, nitrous oxide is what is really needed. In most cases, the child has a specific unpleasant incident in his memory, which subsequently led to fear and fear.
Since during the entire treatment the child feels and behaves quite consciously, he needs to communicate with the doctor. Therefore, it is important for a doctor to be able to invite a child into a chair in a playful format and be able to put a mask on him. The mask has a slightly sweet smell, reminiscent of children's chewing gum.
Interesting! This procedure can be done for children over 4 years old. In some cases, it is possible to establish contact with three-year-old children. In individual cases, under the guidance of a specialist, the procedure is permitted from 2.5 years.
What is sedation in dentistry?
In medical terms, sedation is a state of half-asleep in which a person retains the ability to respond to verbal commands, thereby communicating with others, primarily with a doctor. Sedation does not replace the need for local anesthesia. This is due to the fact that in a state of sedation a person retains the ability to feel pain, and this is stress for the body. Therefore, the use of anesthesia under sedation is mandatory. Sedation, at a minimum, removes the emotional coloring of what is happening, so a person simply stops paying attention to uncomfortable and disturbing phenomena.
How quickly does sedation wear off after the procedure?
The big advantage of sedation is that its effect will not take long and will begin in a couple of minutes - the child will immediately feel relaxed and will not pay much attention to the doctor’s actions.
100% of the laughing gas is released from the body within 30 minutes after the end of the procedure. Therefore, the child should not run, play or show any activity during the first two hours.
Important! Attending school or kindergarten is not a contraindication on the day of treatment.
For two hours after the procedure, it is better that the child does not run or be particularly active.
How long does the gas last?
The gas mask can be used for as long as the dentist needs to work. The process can last 10, 30, or 60 minutes. And no matter how long the child is under the influence of the drug, his condition will not be worse or better. The effect of dinitrogen oxide mixed with oxygen (ZAX) stops immediately when the supply from the cylinder is stopped. Residual effects may appear within half an hour.
Reviews
Almost all reviews from doctors regarding the use of laughing gas are positive. Dentists claim that the technology allows for better and faster dental treatment for a child, relieving him of feelings of fear or even hysterical attacks. Since the amount of gas contained is minimal and it is thoroughly purified, the child’s body is not in any danger.
Doctors speak positively about this procedure
As for parents, their opinions on the use of nitrous oxide vary. Some believe that this is a good way to calm the baby during the procedure, while others are wary of this and try to avoid this procedure. Some parents are confused by the fact that the child remains fully conscious during treatment. Because of this, many people prefer to use anesthesia instead of nitrous oxide. Another controversial issue concerns the price of using such technology. For some, the cost is quite acceptable, for others it is too high.
Reviews about the procedure
Positive aspects of using nitrous oxide in the dental office
The use of N2O in pediatric dentistry is practiced in many countries due to its many benefits:
- Creating a psychologically comfortable and calm environment for the child;
- Formation of positive experience in dental treatment;
- No complex preliminary preparation or testing is required;
- Preserving the baby’s perception and consciousness;
- Safe product;
- Preventing the gag reflex;
- Quick exit from the body.
Answers to popular questions
Is there a need to additionally use local anesthesia?
Yes, and nitrous oxide helps enhance its effect.
Is special training needed?
No special preparatory steps are required. Children should refrain from eating for two hours before treatment. After its implementation, there are no prohibitions.
There is no need to prepare for this procedure
Is there a need for additional inspections before using nitrous oxide?
As a rule, additional examinations are not carried out, but in some cases they are necessary. This issue is discussed in more detail during a consultation with a doctor, when a treatment plan and method of treatment are drawn up.
It is better to consult a doctor before the procedure.
Our prices
When using nitrous oxide in dentistry
For children, the price of the procedure increases slightly. This is explained by the fact that expensive equipment is used, plus another doctor is involved in the operation to monitor the patient’s condition. But sedation can save the child from suffering, so it’s better not to skimp on it.
Prices
Use of nitrous oxide sedation
85 rub./minute
At the children's dental clinic " Natadent"
» you can receive high-quality treatment using modern methods of sedation and anesthesia without overpayments. Despite the use of expensive advanced equipment, we strive to keep prices at an affordable level.