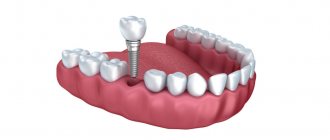
Implantation of teeth in the upper jaw has its own specifics: first of all, it is associated with the structural features of bone tissue. Its density is somewhat lower, since during the chewing process the upper jaw undergoes less stress. This leads to the fact that after tooth loss, atrophy of looser bone tissue develops faster. That is why, according to statistics, preliminary osteoplastic surgery is required precisely when installing dental implants in the upper jaw. In addition, a longer healing period is a feature - on average, it takes 1-2 months more than for lower jaw implants.
The second feature is the close location of the maxillary sinuses. If the height of the bone near the canines and lateral incisors is not enough, a sinus lift is mandatory - an operation to raise the bottom of the sinuses. The proximity of the infraorbital foramen and the nerve requires special care and requires even greater professionalism from the dentist.
And finally, an important feature is aesthetics - the front teeth of the upper jaw, with a correct bite, form the overall impression of a smile, so the appearance of the implants and gums should be as natural and attractive as possible.
Front upper teeth
The main task of installing anterior dental implants is the optimal combination of functionality and aesthetics. Therefore, the operation has the following features:
- aesthetic gum contour - creating a beautiful gum contour will not give others a chance to guess about the presence of an implant. To ensure that the gums do not lose volume, they often resort to one-stage implantation with immediate loading using a temporary crown. The latter provides some support to the gingival tissues and prevents changes in their structure;
- accuracy of installation - a computed tomography scan is required, since the implantation of an artificial root in place of the front teeth of the upper jaw must be carried out at a precise angle. Otherwise, there is a possibility of difficulties with crown installation;
- A special feature of the design of artificial roots is that the implants have a relatively small diameter and specific thread. Such designs are used to reduce trauma to surrounding tissues;
- aesthetics - unlike many other cases, instead of a metal abutment (the part on which the crown is fixed), a zirconium abutment is used. This is because the metal may be visible. Zirconium is white, which eliminates the risk of this part being visible through the gum. Crown materials - zirconium dioxide, solid ceramics - have high aesthetic characteristics and can be safely used to restore front teeth.
Choosing an implant for the smile area
The front teeth do not take part in chewing food, so special implants are installed in this area, characterized by maximum aesthetics while preserving the volume of bone tissue, minimal trauma to the gums and a shortened healing period.
Such implants are distinguished by their small diameter, as well as a special thread design and coating that stimulates the process of osteogenesis and osseointegration. To avoid the titanium structure showing through the crown or gum, zirconium structures can be used. A ceramic or zirconium prosthesis for tooth restoration replicates the properties of natural enamel, which ensures complete identity with the rest of the dentition.
Work examples
How often do you visit the dentist?
Chewing upper teeth
How a tooth is implanted in the upper jaw depends on the individual characteristics of its structure. When it comes to chewing teeth, a two-step technique is often used. In this case, the permanent crown is fixed only after the artificial root has completely taken root in the bone tissue. This method is the most reliable and predictable.
Osteoplastic surgery is a stage that often precedes the implantation of chewing upper teeth. Most experts unanimously choose classic root-shaped structures as artificial roots.
Alternatives to implantation
Depending on the number of remaining teeth in the upper jaw, the following types of dentures can be used:
- removable (with complete edentia or a large number of missing teeth) - inexpensive, but not very comfortable and aesthetic option,
- bridges (to replace one or several missing teeth in a row) - fixed on supporting living teeth, which are quite sharply ground into crowns.
The main disadvantage of these designs is that dentures do not transfer the load to the bone, since they restore only the supragingival part of the teeth. The consequence is ongoing tissue atrophy. Over time, the gums will sag, and space will appear between the mucous membrane and the prosthesis. Firstly, the prosthesis will need to be regularly repositioned, and secondly, the atrophied bone will become an obstacle to implantation. And the third reason is the increased risk of inflammatory processes, since bacteria and food debris will accumulate in the gap between the denture and the gum.
Dental implantation does not have these disadvantages, so it becomes the best option for restoring teeth in the upper jaw.
1 Perova M.D. Complications of dental implantation, their treatment and prevention. New in dentistry. 2002. 2 According to clinical studies of implant manufacturing companies (Nobel, Straumann, MIS).
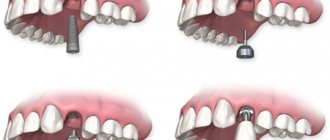
Complete absence of upper teeth
Implantation of the upper jaw in the absence of teeth can be carried out in several ways.
- Basal implantation is the main and most common method of restoring dentition. 8–12 artificial roots are used, which are installed evenly along the dentition. The advantages of this method include the fact that the doctor selects deep sections of bone tissue that are not affected by atrophy, as well as “bypassing” the sinuses. Afterwards, the prosthesis is fixed to the implants - even relatively loose bone does not act as a hindrance, since a large number of supports are used. Zygomatic implants can also be used here. A fixed prosthesis is installed within 3–4 days.
- All-on-6 technology. Numerous reviews of dental implantation in the upper jaw using this technique allow one to judge its effectiveness. It can be used even with moderate bone atrophy. Installation of a fixed prosthesis is carried out on 6 implants. 4 of them are fixed in the lateral sections on both sides, 2 - in the frontal section. Zygomatic implants can also be used here.
- All-on-4 technology. The name speaks for itself - this is implantation on 4 artificial roots. The technique is used less frequently, since in this case the requirements for bone tissue parameters are much higher, and only minor atrophy is allowed. 2 implants are installed in the frontal zone, 2 - in the lateral zone. The use of zygomatic implants is allowed. The prosthesis is installed within 3–4 days.
- Zygomatic implantation. This is not an independent method; it is used as part of the protocols described above. Zygomatic implants are up to 6 cm long. They are necessary in order to involve the zygomatic bone in the process and reliably fix a fixed prosthesis.
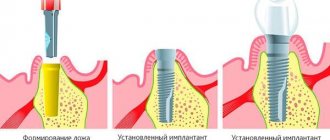
Stages of implant installation
- Preparing for treatment .
On the first visit, the doctor examines the oral cavity and talks with the patient. Possible treatment options are discussed. If there are no obvious contraindications to implantation, the patient is sent for a computed tomography (CT) scan and sometimes additionally for a blood test. - Treatment planning.
CT data is loaded into a special program that recreates a three-dimensional model of the patient's jaw. Based on this information, suitable implant models are selected and their installation locations are determined. A surgical template is then created in the laboratory using the 3D model to be used for the operation. - Implantation of upper teeth.
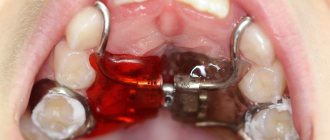
Under local anesthesia, through incisions (with the classical method and ALL ON 4/6 methods) or through small punctures (with the basal method), the implants are implanted into the jaw. - Prosthetics .
Depending on the protocol used, the dentures are fixed on the implants for 2-3 days or several months later.
Complications and possible consequences
Reversible complications after implantation of teeth in the upper jaw are possible:
- soft tissue swelling;
- numbness of the upper lip;
- nosebleeds;
- soreness.
As a rule, symptoms decrease significantly already 3–5 days after surgery. Serious consequences include rejection of implants, rejection of osteoplastic materials during preparation, mobility of the structure, allergic reactions and individual intolerance to materials. However, these risks are also present when installing an artificial root on the lower jaw. The only possible complication when working with the upper one is damage to the bottom of the nasal sinus during installation and, as a result, sinusitis and other consequences. However, in order to eliminate such a risk, a thorough diagnosis is carried out - assessing the height of the sinus floor and the structure of the bone tissue. This allows you to assess what risks of maxillary dental implantation exist and how to minimize them.
Why an implant may not take root
In the short term , the implant usually does not take root due to:
- omissions at the preparatory stage;
- violations of the surgical protocol;
- violations of sterility;
- use of uncertified design of low quality;
- incorrectly chosen implantation technique in a particular case.
The cause of rejection during the period after fixation of the crown and up to two years of use may be:
- low quality of materials from which the artificial root is made;
- improper assembly of the structure (loose fastening of the abutment);
- irrational load on the rod;
- the patient’s neglect of the rules for caring for the titanium system;
- smoking (nicotine negatively affects the condition of oral tissues).
In the later stages , you can lose an implant if:
- not maintaining dental hygiene;
- ignore annual visits to the dentist;
- The state of health changed dramatically, and serious pathologies appeared.
Recommendations
Recommendations after dental implantation of the upper jaw are as follows:
- try to avoid increased stress at first - do not blow your nose (both after bone grafting and for the first time after fixing the implant), do not chew hard foods, postpone flights;
- it is necessary to pay attention to hygiene - brush your teeth and use recommended rinses, visit a doctor according to the schedule;
- limit physical activity;
- avoid visiting the bathhouse, beach, pool;
- take medications prescribed by your doctor.
Following the doctor’s recommendations will reduce the risk of complications and ensure a long service life of the implants.
What happens in the postoperative period
Healing immediately after implantation
Implantation of a titanium rod, even with the use of new minimally invasive equipment, still remains a traumatic procedure for the jaw tissue, so after the end of the operation the following manifestations may occur:
- soreness;
- swelling of the face;
- bleeding gums in the suture area;
- increase in body temperature.
With normal healing, unpleasant symptoms disappear after 3-5 days. If your health worsens, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Reasons for visiting the clinic are::
- prolonged numbness of the jaw;
- bleeding;
- severe pain syndrome;
- redness of the operated area;
- the appearance of hematomas;
- divergence of seams.
Care instructions
In the first two weeks after surgery you must:
To avoid complications, you must stop smoking
- give up smoking, alcoholic drinks and coffee;
- exclude spicy, sour foods;
- food should have a soft consistency and not be too hot or cold;
- avoid physical activity;
- do not attend thermal procedures (bath, sauna);
- chew on the side opposite the implant;
- brush your teeth carefully, without touching the suture area;
- Carefully clean the operated area with a cotton swab soaked in saline solution;
- take medications prescribed by a doctor;
- make antiseptic mouth baths.
Which is better - a bridge or an implant?
In the absence of molars, the patient is offered to install a bridge prosthesis supported by his own teeth. The method involves turning units on both sides of the defect. The doctor takes impressions and orders a bridge. The length of the prosthesis depends on the size of the defect. The orthopedic device must have 2-3 supports to evenly distribute the load. The advantage of the method is the price; no surgery is required. Disadvantages of bridge prosthetics:
- the need to remove pulp from supporting units;
- significant turning of supports for crowns;
- accelerated destruction of anchors due to high load;
- gradual expansion of the defect;
- subsidence of tissues under the bridge;
- risk of breakdowns and injuries.
Implantation is preferable because it allows you to preserve your own units, slows down or stops atrophic changes, and allows you to evenly distribute the chewing load.
What to do to prevent complications
You can avoid complications after the process of osseointegration of the artificial root with the jaw tissue is completed by adhering to simple rules:
- Have your teeth professionally cleaned at the clinic twice a year. The procedure is performed using ultrasound and provides high-quality results. At the end of the process, the specialist applies special pastes and varnishes with a polishing effect to the teeth.
- Use a toothbrush and toothpaste that must be selected in accordance with the dentist’s recommendations.
- Use dental floss regularly. It effectively helps to get rid of food debris in the interdental spaces.
- When performing hygiene procedures, pay attention to the tongue and the inside of the cheeks. They also need to be cleaned with the back of a toothbrush.
- Use mouthwash. It kills pathogenic bacteria and freshens breath.
For a successful osseointegration process, it is necessary to adhere to the dentist’s recommendations and maintain careful oral hygiene.
Price
For your information, here are the average prices for services related to dental implantation in Moscow dental centers:
| Name of service | Cost in rub. |
| Diagnostics | |
| X-ray of one tooth | 340 |
| Orthopantomogram | 1100 |
| Specialist consultation | |
| Dentist-therapist | 600 |
| Periodontologist | 740 |
| Implantologist | 850 |
| Treatment of complications | |
| Cleaning the implant from dental plaque | 180 |
| Periodontal applications in the area of one tooth | 370 |
| Applying a periodontal bandage | 400 |
| Laser therapy of the gum mucosa | 490 |
| Implant removal | 6900 |
| Filling the gingival pocket with osteoconductive material | 10900 |
| Installing a protective membrane | 12900 |
| Professional oral hygiene | |
| Ultrasound | 2000 |
| Air Flow method | 3500 |
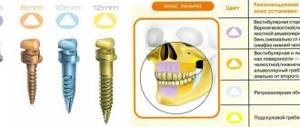
Which implants are better to place?
Requirements for implant systems for chewing teeth:
- length and diameter - classic models are preferred; rods that are too thin and short cannot withstand chewing loads;
- shape - in modern implantology, only root-shaped structures are used, as the most physiological;
- surface – for chewing areas, implants with a microporous surface are used, which speeds up the healing time;
- thread - with the help of turns of a certain pitch, the effect of compacting the bone tissue around the implant is achieved, which improves the quality of osseointegration.
At the stage of preparation for implantation, it is important to choose the brand of the system. It is better to give preference to well-known brands. The price of materials will be higher, but the advantages are extensive experience in use, confirmed by clinical trials, and a low risk of complications. The selection of implants is carried out by our implantologist personally for each patient, focusing on the anatomy of the jaw bone and health status.
Requirements for crowns on implants
Crowns are artificial teeth that are fixed to implants. The purpose of prostheses is to restore the aesthetics and functionality of a row. The artificial tooth must cover the defect, as well as withstand the loads during chewing and transfer them to the implant. Which crowns to place on implants depends on the treatment technology and the time of their use.
- Temporary. Used in one-step protocols. They are installed during the healing of the implants and removed from the bite. Made from plastic or metal-plastic. They play an aesthetic and functional role. Can be used for 3-12 months, then replacement with permanent ones is necessary.
- Permanent. Crowns for implants for the chewing part of the jaw are made of metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide. Installed after complete engraftment of the artificial root. The high strength of the dentures allows for full chewing. If excessive loads are excluded (biting nuts or hard objects), permanent crowns last for 10 years, while zirconium crowns last for more than 20 years.