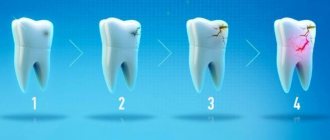
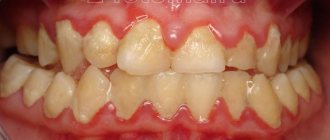
Dental demineralization is a widespread problem among both adults and children. It not only worsens the appearance of the dentition, but is also a prerequisite for the development of caries, its initial stage. Demineralization of tooth enamel is a pathological process of loss of mineral components by dental tissue, resulting in dullness, hypersensitivity, fragility of teeth, roughness, porosity of their surface, and often the presence of cracks (photo below). The main sign of pathology is the presence on the surface of the teeth of matte white, slightly grayish, or brownish spots of varying sizes, which are located in most cases in the cervical areas, but can cover the entire crown (photo below). Due to the presence of such spots, the pathology is also called focal demineralization of the enamel.
In this article we will tell you the reasons for focal demineralization of enamel, what it looks like in the photo, what features it differs in children, and we will also introduce you to treatment methods and what needs to be done for this disease.
Weakening of tooth enamel
Demineralization is a process in which enamel loses the minerals it needs - calcium and phosphorus.
Normally, they come from saliva and oral fluid through small pores on the enamel and accumulate in areas where there is not enough of them. Then mineralization occurs: mineral components are formed from calcium and phosphorus, which are attached to the protein “skeleton” of the tooth and compact it. When a deficiency of minerals occurs in hard dental tissues, the enamel softens and microdefects appear in it - narrow funnels with a diameter of up to 10 nanometers. They gradually enlarge, merge and form focal demineralization, and in severe cases inflammation of the pulp occurs.
On the website Stom-Firms.ru, read when demineralization of teeth develops, what methods of its treatment and prevention are available.
How is professional help provided?
Typically, the level of therapeutic therapy and the type of complex of measures depend on the degree of demineralization. At an early stage, it will be enough to carry out only the treatment that is performed during remineralization.
Attention! In the later stages, filling material is installed, and additional caries is removed.
But, as a rule, during demineralization, many dentists perform all the activities that are performed during remineralization. Remineralization therapy includes several stages:
- At the initial stage, professional cleaning of the oral cavity is carried out;
- Then the tooth enamel is dried;
- Next, an element with a restorative effect is applied. During this stage, products containing calcium and potassium ions are applied to the affected area;
- Finally, products with a protective and strengthening effect are applied to the surface with a restorative preparation. For this purpose, special mouth guards containing a 4% sodium fluoride solution are used.
Remineralization is the process of restoring tooth structure, which can be natural or artificial. Artificial remineralization is impossible without the participation of a professional dentist. Natural is a complete diet containing calcium, fluorine and phosphorus.
Signs of dental demineralization
The initial stages of the process are not visible - only a dentist can identify them using the following methods:
- Vital coloring. The doctor applies a special composition to the enamel, which accumulates in the area of demineralization.
- Radiation imaging. Under ultraviolet irradiation, hard dental tissues glow blue-blue. With a mineral deficiency, areas with intense luminescence are noticeable.
As the loss of minerals progresses, the enamel loses its natural shine at the site of demineralization, and dull white spots appear on the teeth. At this stage, toothache does not occur, and the loss of minerals is easy to stop. When the deficiency becomes pronounced, an enamel defect forms in the affected area - the chalky spot turns light brown, then brown or black. In this case, the tooth reacts to cold, hot, sweet or sour.
Drug Icon: treatment of caries
DMG produces a chemical for the treatment of white spot caries called Icon. The polymer substances that make up this drug penetrate deeply into the affected enamel, making it dense and shiny. Those. the affected porous enamel turns into a dense structure, the transparency of the enamel and the color of the tooth in this area are also restored.
The result of using the drug “Icon”: video
The indication for use of Icon is only initial caries in the white spot stage, and this drug has no effect on enamel spots with fluorosis and hypoplasia. The drug has a polymer composition (plastic) that impregnates the porous structure of the enamel. The price for dental treatment with Icon will be from 3,000 rubles per tooth.
Causes of tooth demineralization
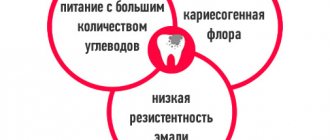
As a rule, enamel loses minerals during caries. Plaque bacteria produce acids that increase the porosity of the enamel, causing phosphorus and calcium to be washed out of it.
The demineralization of teeth is accelerated by the following factors:
- Insufficient oral hygiene. If plaque is not removed in time, bacteria form dental plaque and disrupt mineralization.
- Frequent consumption of carbohydrates. Sugary foods are a source of food for oral bacteria that destroy enamel.
- Lack of microelements. When there is little calcium and phosphorus in the body, their concentration in saliva decreases.
- Rough brushing of teeth. If the enamel is regularly mechanically injured, it does not have time to recover and gradually weakens.
- Ultrasonic cleaning. Partially damages hard dental tissues, increasing their permeability. If the enamel is thin, after cleaning with an ultrasonic scaler it loses some of its minerals.
- Fixation of bracket systems. To increase the porosity of the enamel and secure the braces tightly, before installing them, the dentist treats the surface of the teeth with phosphoric acid. It causes demineralization of the surface layers. Also, dentures and braces make oral hygiene difficult - food particles remain between the parts of the structure and bacteria accumulate.
Since the main source of microelements is saliva, when it is deficient or changes in viscosity, mineralization is disrupted. Viscous saliva does not wash teeth well, and minerals have difficulty penetrating hard dental tissues. The amount and composition of saliva is affected by diseases of internal organs, such as diabetes, hormonal disorders and cardiovascular diseases.
Caries in the spot stage: treatment
Treatment of initial caries in the form of a white spot is carried out conservatively, because There is no carious cavity, which means there is no need to drill out the tooth. We have already said above that the process of formation of white spots is associated with focal demineralization of tooth enamel (leaching of calcium and fluoride from it). Therefore, the basis of conservative treatment will be the use of dental remineralization, i.e. we will try to re-saturate the white spots with calcium and fluoride. However, this process will not be possible if oral hygiene remains at the same level.
Carrying out a remineralization course makes sense only if the patient is motivated and ready to improve oral hygiene. Treatment of foci of enamel demineralization requires the complete elimination of bacterial plaque and food debris in the oral cavity. This is possible if the patient is willing to floss after every meal and brush their teeth after every meal (while avoiding snacking between meals and drinking sugar-sweetened beverages). In fact, the patient is required to devote only 4-5 minutes to hygiene, 3 times a day.
It is also important to exclude easily digestible carbohydrates, starchy, salty, acidic foods and drinks (wine, fruits and fruit juices) from the diet. The diet should contain more protein and calcium. The patient is selected for oral hygiene products - dental floss and paste, rinses. As for toothpastes, at the beginning of treatment it is recommended to use pastes with calcium and phosphates, and at the end - anti-caries pastes with fluoride. We will talk about hygiene products in more detail below. Only after teaching the patient about oral hygiene, as well as after professional teeth cleaning, do we proceed to a course of remineralization therapy.
Course of remineralization of tooth enamel –
Remineralization of white spots is achieved through remineralization therapy with preparations containing calcium and phosphates, as well as fluorides. As we said above, at stage 1 it is especially important to use products with calcium and phosphates, or combined two-stage products such as the “Enamel-Sealing Liquid” drug (when a suspension with calcium is first applied, and a solution with fluoride is applied a few minutes later).
One of the best drugs for remineralization of enamel is Tiefenfluorid Enamel-Sealing Liquid (made in Germany), but its use can only be done at a dentist’s appointment. The course of treatment with this drug usually includes from 5 to 10 procedures.
A course of 10 electrophoresis procedures with a 10% calcium gluconate solution may be prescribed, which is done in a physiotherapy office (your dentist gives a referral there). Let's say right away that buying and rubbing calcium gluconate tablets into the necks of your teeth will be completely useless, because... Calcium gluconate dissociates into active ions only through electrophoresis. A course of calcium remineralization can also be carried out using the CPP-ACP complex, consisting of calcium and phosphates (24stoma.ru).
An example of such a product with the CPP-ACP complex is the “GC Tooth Mousse” tooth gel, which is quite available for ordering via the Internet. It can be used both at the dentist and at home (both in adults and children). After using products with calcium and phosphates, the patient is prescribed a course of dental fluoridation. Professional fluoridation is usually more effective because Usually drugs with a higher concentration of active components are used.
For example, this could be fluoride varnish "Colgate Durafat", containing 5% sodium fluoride, which corresponds to a content of 22,600 ppm of active fluorine (Fig. 9). The selection of a drug for fluoridation must be approached scrupulously, because In most dental clinics, cheaper drugs with not very high concentrations of active components are purchased for this purpose. For example, the still quite popular, but already outdated drug “Fluor-Protector” contains only 0.1% sodium fluoride.
The Colgate Durafat series of products, in addition to dental fluoride varnish for professional use, contains 2 more toothpastes with therapeutic dosages of fluorides. This is Colgate Duraphat 2800 ppm (for children from 10 to 15 years old), as well as Colgate Duraphat 5000 ppm - for adolescents over 15 years old and adults. These professional toothpastes can be purchased in pharmacies either on order or from large online pharmacies. As a dentist, I recommend them, and in Fig. 8 you can see a photo of the Colgate Duraphat 5000 ppm package that I personally purchased.
Preparations for fluoridation of enamel –
The recommended dose for a single application of Colgate Duraphat varnish in children is:
- baby teeth – up to 0.25 ml,
- changeable bite – up to 0.4 ml.
Thus, after a course of remineralization with calcium and phosphates, it is optimal to do several fluoridation sessions with professional varnish, and at the same time switch to such medicinal toothpastes. When the white spots disappear, you can continue to use one of these pastes on an ongoing basis once a day, or use other pastes with lower dosages of fluoride, but in adults - at least 1400 ppm. Other very good fluoride toothpastes, such as Elmex toothpastes (they are available for children of all ages and adults).
How is enamel demineralization treated?
If the tooth matrix is preserved, the process is reversible. The longer the focus of demineralization exists, the higher the risk that caries will destroy dental tissue. To compensate for mineral deficiency, dentists prescribe remineralizing therapy, or remotherapy.
Remineralization is indicated:
- For adults, if there are signs of demineralization - lack of shine of the enamel, white or brown carious spots.
- For children over 6 years old, both for the treatment and prevention of caries, special gels with a pleasant taste are produced for them.
- People who often experience micronutrient deficiencies - pregnant women, adolescents during puberty and the elderly.
- With a lack of saliva, a tendency to caries or chronic diseases of internal organs.
- After professional cleaning and before fixing braces.
The goal of remineralization therapy is to increase the amount of calcium and phosphorus in saliva or deliver them to hard dental tissues from the outside, using special compounds.
In the first option, accumulation occurs naturally - the dentist prescribes medications containing the necessary microelements in the form of dietary supplements. But in order for the enamel to accumulate minerals faster, the doctor often uses artificial remineralization - he applies applications and gels with a high concentration of calcium and phosphorus to the enamel, or suggests that the patient rinse with a remineralizing solution.
After remineralization, the dentist performs fluoridation - treating teeth with fluoride-containing solutions. Fluoride accelerates the filling of enamel with minerals and retains them in it. As a rule, fluoridation is combined with electrophoresis. Thanks to the electric current, the components of the solution penetrate into the deep dental tissues - dentin and pulp. Fluoridation is contraindicated for people living in areas where the soil and water are oversaturated with fluoride.
Remineralizing therapy and fluoridation are carried out in courses twice a year. One course includes 5-10 procedures.
If remotherapy and fluoridation are ineffective, the dentist will suggest the Icon technique. With this technology, he applies special materials to the teeth in layers: first he etches the enamel, then dries it and introduces a composition that seals small pores, preventing the leaching of minerals. After the procedure, the appearance of the teeth is restored and their resistance to factors that cause caries increases.
Main symptoms
Important! It is very easy to determine the presence of demineralization of teeth; this requires careful monitoring of the condition of the oral cavity. If you suddenly discover the first manifestations of this form, you should immediately contact your dentist.
But in order to identify this pathological process, it is necessary to know the main symptoms that appear during it. At the initial stage, the leaching of mineral elements manifests itself in the form of a decrease in the shine of the teeth, the surface acquires a matte structure. After this, more obvious signs appear that are worth paying special attention to:
- deformation is noted, additionally the enamel becomes rough;
- spots and stripes with a chalky structure appear on the surface;
- gradually the spots become dark with a brown tint;
- the surface of the teeth acquires a porous structure.
The causes of demineralization can be: poor nutrition, weakened immunity, disturbances in mineral metabolism and neglect of oral hygiene. The enamel becomes vulnerable to microorganisms that cause caries.
You should contact your dentist at the earliest stages. The thing is that if you delay, the demineralization process can go into a deeper stage and dark lesions with cavities will appear in place of the spots.
Prevention of dental demineralization
To maintain dental health, you should consume less sweets and carbonated drinks, which accelerate demineralization. You should not eat sweets at the end of lunch, between meals and at night - this accelerates the growth of bacteria. If you wear braces, avoid foods that stick strongly to the enamel or get stuck between the locks or ligatures, such as halva, corn sticks, and toffee.
It is important to follow the following recommendations from your doctor:
- Include vegetables or fruits in your diet - they mechanically cleanse your teeth of bacteria and food particles. When treating with braces, they should be crushed rather than bitten off.
- After eating, brush your teeth or use chewing gum after eating. A single-tuft brush or a long brush is suitable for cleaning braces.
- Consume foods that maintain the acid-base balance in the mouth, such as cheese, yogurt, cottage cheese, green tea, seafood and parsley.
- Adults and children over 2 years of age can drink fluoridated water or milk, and also take tablets containing fluoride.
To prevent bacteria from causing demineralization, you should have your teeth professionally cleaned from plaque and stones by a dentist.
Bibliography:
- Serova A.A. “Focal demineralization of enamel as a complication during orthodontic treatment” // Bulletin of medical Internet conferences - 2021.
- Dental caries. Clinical recommendations of the Russian Dental Association - 2014.
Author of the article: Mariam Arutyunovna Harutyunyan
Copywriter of the information portal Stom-Firms.ru. Specialization in translations and original articles on medicine and dentistry.
In what cases is remineralization therapy necessary?
Remineralization therapy today is included in the list of services in many dental clinics, where an integrated approach to the treatment of teeth and gums is used. Even if there are no special signs of hypersensitivity, the procedure will not be superfluous.
It makes sense to undergo the procedure if:
- teeth are susceptible to caries
- there are non-carious dental diseases (fluorosis (excess fluoride), enamel hypoplasia, enamel erosion, pathological abrasion, etc.)
- with increased tooth sensitivity, during and after orthodontic treatment
- before and after professional teeth whitening
- during pregnancy and during breastfeeding
- in case of excessive tooth sensitivity
- during the installation and wearing of orthodontic devices.
A contraindication is individual intolerance, which is determined in consultation with a doctor: you cannot undergo such procedures if you have allergic reactions to any drugs used in the procedure; allergies can cause unforeseen complications. Remineralization is not recommended if you have any diseases of the excretory system or pathologies of the thyroid gland.