Problems with teeth are quite common; caries, toothaches and many other troubles that can arise due to deterioration of teeth can occur in almost everyone. If a person eats properly and takes care of his own teeth, then the likelihood that he will develop caries is small, however, it exists in any case. What to do if you have problems with your teeth?
If you have problems with your teeth, they have begun to become loose, you have caries or severe toothache, do not hesitate to get treatment. In this case, it would be most correct to seek medical help at a dental clinic, where you can always use such a service as open sinus lifting, as well as many others, which will help you very quickly correct the situation.
Sometimes, when dental problems arise, some people try to solve them on their own, that is, self-medicate.
It should be noted that in most cases this is very dangerous, since without being a professional in this field it is extremely difficult to choose the appropriate treatment method for yourself, which can lead to a significant deterioration of the situation. For this reason, if you want to deal with this problem as quickly and efficiently as possible, you should contact a good dental clinic.
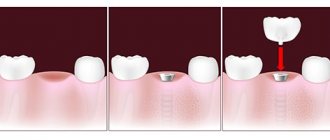
The essence of the procedure
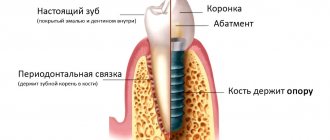
After the removal of the upper teeth, weakening and thinning of the bone tissue occurs. The lower edge of the maxillary sinuses is located next to the tooth roots, so if they are absent, the bottom descends to the bone. As a result of these two changes, it becomes impossible to secure a dental implant without damaging the soft tissue of the inside of the nose. In addition, the bone becomes fragile and cannot provide reliable fixation of the structure.
With the help of a sinus lift operation, both problems are solved - the thinned bone acquires the required volume, and the bottom of the maxillary sinus is raised due to the augmented material. This can be autologous bone (the patient’s biomaterial) or artificial bone fillers. The second option is more often performed, since it is less complex and painful. Depending on the characteristics of osteoplasty, implantation is carried out immediately or after a period of time.
Why does bone deficiency occur?
Not all patients have sufficient knowledge about their body, which sometimes leads to misunderstanding of the importance of certain procedures in dentistry. Here it is worth understanding what happens after tooth extraction. When, for some reason, a person loses a permanent tooth, the resorption of the spongy bone around the place (socket) where the roots were previously located begins almost immediately.
In the process of chewing food, the tooth received a load that extended to the jaw bone, forcing the microscopic blood vessels that penetrate the bone substance and nourish it to “work.” No roots equals no load. That is, in the “toothless” area, the bone is removed from work. The capillaries gradually atrophy, and the spongy substance left without nutrition is resorbed, because resolves, and outwardly it looks like bone subsidence. Already in the first 6 months, serious changes are noticeable, and after a year, resorption actually reaches its “peak”. As for the upper jaw, the bone substance here is more porous and light (compared to the lower jaw). It atrophies faster both from the outside and from the maxillary sinus - the latter case is often found in patients of retirement age.
Statistics show that if 70% of respondents (wearing removable or standard bridges) knew about bone atrophy and the discomfort that constantly shifting dentures bring, then dental implantation would be the preferred replacement for lost teeth. The implant uses the bone in which vital processes are restored, so atrophy practically does not occur.
What is the difference between open and closed sinus lift?
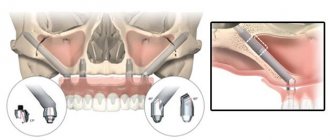
There are two main types of procedure: closed (transcrestal) or open (lateral). Their main difference is in the technique of the operation. In the first case, it is more gentle and soft, less damaging to the tissues, so they recover faster. However, the closed technique may not be used in all cases.
Open sinus lift
It is performed if the bone tissue is very thin and its height is 6 mm or lower. It allows you to increase the bone by 5 - 8 millimeters. To insert the grafting material, the surgeon makes an incision in the gum, separates the flap, and makes a hole in the bone. After gaining access to the desired area, he lifts, inserts a bone substitute, and then places sutures. The operation requires a long rehabilitation period until the wounds heal completely.
Closed sinus lift
It can be performed if the bone height is not lower than 7 millimeters. The procedure is simple: the doctor makes a hole in the gum and bone from above, lifts the maxillary sinus and injects the drug. Simultaneous implementation with implantation is possible. Usually no more than two prostheses are installed. The recovery period is easier, since the gums are minimally injured.
Materials for bone grafting
All types of materials used in sinus lifting can be divided into 3 types - autograft, xenograft and synthetic bone. Let us dwell in more detail on the features of each type.
Autograft
The best option for the procedure is the patient’s own bone – an autograft. A small piece is cut from the lower jaw or chin, then the material can be crushed and replanted while raising the floor of the maxillary sinus. The advantages of this approach are complete immune compatibility, i.e. the autograft takes root perfectly. But there are also disadvantages - sometimes a lot of material is required (which becomes traumatic for the patient, because after osteoplasty 2 operated areas will already heal). Disadvantages also include increased resorption of the autograft during the healing period; as a result, the patient sometimes requires repeated augmentation.
Previously, another type of natural material for osteoplasty was used - allograft. This substance is taken from a donor (most often cadaveric material is meant) and goes through several stages of processing and disinfection. The material is outdated due to unstable survival rate and ethical component.
Xenograft
Bone replacement materials of animal origin are obtained from bovine bone. The substance is crushed, sterilized and part of the impurities – collagen (or protein, protein) – are removed. The result is a substance that is sorted according to the diameter and shape of the particles - crumbs with a diameter of 0.25-1 mm, chips - from 1 to 2 mm, granules - from 4 to 6 mm. The crumbs can be pressed into blocks up to 3 cm long.
A large amount of proteins makes the material less dense, which reduces the fixation ability when installing an implant. It is considered optimal when the material contains at least 75-90% minerals, and the rest is collagen.
Xenografts have good survival rate and relatively low cost, so this type is often used in osteoplasty. After surgery, the material begins to interact with surrounding tissues. Gradually, your own young bone is formed, and the graft is absorbed. The following materials are widely used for augmentation: Swiss Bio-Oss from Geistlich Pharma and Russian Osteomatrix. Similar bone materials can be mixed with autografts.
Synthetic material
Synthetic bone has a complex mineral composition, presented in the form of granulate - medical two-phase calcium phosphate. It contains artificial crystalline hydroxyapatite and beta-3-calcium phosphate (an analogue of natural hydroxyapatite, which is the main building block of bone). The diameter of the granules is about 0.2-2 mm. After replanting, two-phase calcium phosphate is also gradually replaced by living young bone. Popular brands that have confirmed their high quality and biocompatibility are BoneCeramic from Straumann and Maxresorb from Botiss Dental.
Very often, along with augmentation, a PRF membrane (or PRF, PRP) is applied. This is a thick gel-like preparation obtained from the patient's own blood. The membrane contains a huge amount of fibrin protein, platelets and growth factors, which actively stimulate regeneration processes. This method will be a significant addition to osteoplasty, especially if large areas were operated on - this way the patient’s rehabilitation will be much faster and less painful.
Indications and contraindications
The main indication for sinus lifting is the implantation of lateral teeth in the area of the maxillary sinus when there is insufficient volume of the upper jaw bone.
Bone tissue augmentation is planned when:
- absence of upper teeth for a long time;
- anatomical features of the structure of this maxillofacial area (the nasal sinuses have a deep alveolar bay located close to the oral cavity);
- too thin jaw bone.
A doctor may refuse a sinus lift to a patient if there are contraindications. The list of restrictions includes malignant tumors of various locations, immunodeficiency (HIV infection, AIDS, hepatitis), blood clotting disorders, severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, chronic alcoholism, drug addiction.
The most severe contraindications include sinusitis in any form, neoplasms on the mucous membranes, anomalies of the maxillary sinuses and operations in this area, high fragility of bone tissue.
Relative restrictions are temporary, meaning they can be eliminated. The list includes acute infections, exacerbation of chronic diseases, caries, periodontitis, periodontal disease, the presence of cysts, and inflammation of the gums. It is very important to carry out sanitation of the oral cavity before bone augmentation and implantation. If this is not done, inflammatory processes and implant rejection may develop.
When is surgery effective?
The advantage of sinus lifting is the formation of the necessary bone conditions for dental implantation. The procedure restores the aesthetic and chewing function of the upper jaw teeth lost due to:
- Injuries;
- Inflammatory gum diseases;
- Diseases of bone tissue;
- Age-related changes;
- Improper oral care.
The loss of even one tooth leads to the development of atrophic processes in the upper jaw. The more teeth a patient is missing, the higher the risk of atrophy. This complicates implantation. The only correct solution is a sinus lift, especially when restoring the upper chewing teeth.
Sinus lift stages
The doctor determines the need to perform the procedure, the choice of technique and preparation for agumentation after a thorough examination of the patient:
- examination, exclusion of contraindications, identification of pathologies and sanitation of the oral cavity;
- instrumental examination of the bone (determining height);
- creation of 3D jaw and adjacent maxillary sinus using computed tomography;
- determination of the type and calculation of the amount of bone substitute.
Implantation is performed immediately or 6 months after the procedure. If it is postponed, then the instrumental examination is repeated to determine the volume of bone tissue.
Stages of an open sinus lift:
- general or local anesthesia;
- antiseptic treatment of mucous membranes;
- incision in the gum and opening access to bone tissue;
- drilling a hole in the bone using a bur;
- raising the bottom of the maxillary sinus;
- placement of an osteoplastic preparation into the cavity;
- suturing.
With the closed technique, a hole is drilled from above without cutting into the gum tissue. Through it, the dentist lifts the bottom of the sinus and introduces bone material. An implant can be installed at the same time.
After the procedure, the doctor gives the patient recommendations for better wound healing and prevention of inflammation.
Modern drugs for anesthesia in dentistry are completely safe and do not cause complications
Numbness after local anesthesia lasts only a couple of hours, and patients recover from general anesthesia immediately. The risk of an unfavorable outcome is usually not due to side effects of the drug, but to drug inconsistencies and incorrect training of the anesthesiologist, which occur very rarely.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
Possible complications
Sinus lifting of the upper jaw is safe if it is performed by a specialized dentist in a clinic with the necessary equipment. However, in some cases, negative consequences may occur both during the operation itself and during the rehabilitation period:
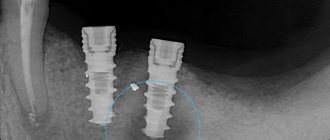
- perforation of the maxillary sinus;
- pushing the implant into the sinus;
- development of acute sinusitis, which, if left untreated, can become chronic;
- poor fastening, mobility of the structure;
- wound infection;
- bleeding from the nose or wound;
- implant rejection.
Immediately after the procedure, swelling, pain, and redness of the mucous membranes occur. Body temperature may increase. These phenomena go away on their own after a few days. To alleviate the condition, you can take analgesics, antipyretics, and rinse your mouth with antiseptics.
If infection or damage to soft tissue occurs, complications become apparent within the first 3 days. If the temperature rises, pain or swelling increases, you should consult a doctor.
The essence of the technique
First, let's look at some features of the anatomy of the upper jaw.
In its body there is the maxillary sinus, an air-filled cavity that communicates with the nasal cavity. When deciding whether to install a dental implant, the thickness of the bone material between the lower wall of the sinus and the edge of the bone is taken into account. If it is not enough in this area, then the level of the lower wall of the maxillary sinus is raised surgically. The resulting space is filled with the material necessary for further installation of the implant.
The procedure is performed by three methods - open, closed, balloon . Each of them has advantages and indications.
Recovery period
Even if the procedure was successful, complications may arise in the first few days, especially if the patient neglects the doctor's advice. Until the soft tissues heal, it is recommended to eat soft or liquid food at a comfortable temperature. Eating hard, rough foods or hot food can damage the wound.
You should not smoke, as nicotine constricts blood vessels and tissues heal worse. In the first week, you should not overheat the body, engage in sports or heavy physical labor, otherwise bleeding may occur. It is better to sleep on the side where no surgical procedures were performed.