580
Dental anomalies are incredibly diverse. In dental practice, sometimes there are cases that seem completely impossible.
For example, the formation in the alveolar process of several hundred follicles at once that are actively growing.
A less exotic, but also rare anomaly is the categorical refusal of the “milkman” to fall out and make way for a permanent unit.
Explanation of the term
The term “intact” (Latin Intactus means “untouched”) is used not only in dentistry, but also in other fields of science and medicine. “Intact organism”, “intact organ”, “intact cell” - all this terminology is quite correct.
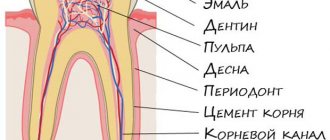
As in other cases, the word “intact” in relation to a tooth means undamaged, healthy, normal.
The case where all units in the mouth are intact can be considered ideal. So if your dentist examines your tooth and says that it is intact, this means good news for you. Every person should strive to keep their teeth intact for as long as possible.
Specialists are quite well aware of the mechanism of development of dental diseases, and preventive measures that are highly likely to avoid them. You just need to conscientiously fulfill your responsibilities to your own teeth.
Although there are still situations in which the condition of the oral cavity does not completely depend on the behavior of its owner.
Dental health
Everyone knows from childhood that there is nothing more important than your health. This is one of those things that money cannot buy. After all, they can only help a little to correct the undermined state of health. But many people take their health for granted until it is too late. This also applies to dental health.
Everyone knows that for preventive care you need to visit the dentist at least once every six months, but only a few do this. As a rule, a person does not have the desire or time for such seemingly useless trips.
What stops people from going to the doctor is usually a groundless fear of dentists. This fear is unfounded, since even the most insignificant operations are performed under anesthesia, which completely numbs the pain, even a couple of hours after the medical procedure.
Most often, a patient consults a doctor when the gums and cheeks become swollen, and the toothache becomes unbearable. And that is why many with such a negligent attitude towards their health do not know basic medical terms.
Rules for maintaining oral health
The main preventive measures against the development of dental diseases are proper oral hygiene and regular visits to the dentist.
Teeth do not become sick instantly. It takes a certain amount of time for an intact unit to become carious or pulpitic.
Regular visits to the dentist once every 3-6 months allow you to promptly notice signs of trouble and take preventive measures to stop the development of the disease.
Demineralization of enamel, the presence of soft and hard plaque, increased tooth abrasion, malocclusion creating periodontal overload - all these signs will be detected by the doctor during examination, and treatment or preventive measures will be prescribed. As a result, the development of an unfavorable situation will be stopped, and the unit will remain intact.
Good oral hygiene is considered the main condition for keeping teeth healthy. Over the past centuries of development of scientific dentistry, the causes and mechanisms of dental diseases have been studied in sufficient detail. It has been established that in most cases, poor oral hygiene is the main cause of dental disease.
Food debris that is not removed from the oral cavity becomes a breeding ground for cariogenic bacteria. Acids produced by microorganisms corrode the enamel, forming a carious cavity, which, spreading deeper and wider, destroys the tooth crown, reaches the pulp chamber and inflames the pulp, leading to the need for depulpation.
The fight against caries and tooth decay should begin with mastering proper oral care. The main goal of hygiene is to prevent the formation of plaque (plaque), which involves regular brushing of teeth with a brush and toothpaste.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnostics is carried out according to a standard scheme and includes four stages: interview, examination of the oral cavity, collection of anamnesis data, conclusion.
Allows you to identify the following factors:
- the presence of an anomaly;
- functionality;
- condition and position of the coronal part, the presence of carious lesions, fillings, the nature of the percussion sound, abrasion;
- availability of free space or, on the contrary, crowding;
- periodontal condition (by the presence or absence of mobility). In addition to the status of periodontal mobility, we can talk about the length and condition of the roots of the problem unit;
- disposition and degree of tooth displacement in all possible directions;
- periodontal condition, presence and depth of gum pockets, gingivitis, periodontitis, gum recession;
- presence of anomaly in relatives.
The cold test determines the viability of the pulp.
Radiography (orthopantomography, targeted images, teleradiography)
Gives information:
- about the condition and length of the roots of problem units, relative to the roots of neighboring elements;
- o the presence of germs or retained permanent units;
- o periodontal condition (according to the width of the periodontal fissure);
- about infraposition;
- about the loss of bone tissue of the alveolar process.
Next, the occlusion is checked using carbon paper.
Indications for removal in adults
An intact tooth is good news for any patient. However, it does not mean that such a unit should be retained in any case. It must be understood that the term “intactness” affects only the condition of the enamel and dentin, but not the position or condition of the periodontium.
That is, a tooth with healthy hard tissues not affected by destruction may be incorrectly positioned (dystopic), erupt with a delay (be impacted), stagger due to periodontal destruction, and interfere with the treatment of other units. In this case, you may need to remove it.
Clinical situations when a healthy tooth needs to be removed:
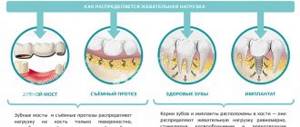
- Its presence interferes with proper orthodontic or orthopedic treatment. In the first case, the indication for removal may be the crowded position of the teeth and lack of space for them.
To free up additional space, the first premolars or canines are usually removed, often on both sides. The tooth may interfere with the installation of the prosthesis. In this case, it is also removed. - Supernumerary of intact units.
- Impacted intact teeth , which for one reason or another are impossible or impractical to “pull out”.
- Dystopic or tilted intact units, if their correction is considered undesirable.
- Tumors or cysts in the area of healthy teeth.
The intact units removed may be the third molars.
Most often, healthy teeth are removed during orthodontic treatment. But, in any case, before deleting them, all possible options are analyzed and the most appropriate decision is made.
Characteristics of compomer materials and their purpose.
Come here if you are interested in how to remove plaque.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/ispolzovanie-prokladok.html we’ll talk about medicinal dental dams.
Problems in children
In children, there is sometimes a need to remove intact milk jugs. Most often this happens with anomalies in shape and position (narrowed jaw, for example), when a healthy element prevents correction. Dystopic “milk jugs” must be removed.
Removal of intact units may require their instability before the biological change of occlusion. The most favorable time for this is the eruption of the first permanent molar.
As in adults, indications for extirpation are cysts and tumors in the alveolar region.
Violation of facial proportions and the need for their correction may also require removal of an unaffected unit.
Important. Removal of a healthy milk jug should have strong indications based on diagnostic results, including radiographic ones.
The absence of a milkman may have an adverse effect on the primordia and growth of permanent units.
Reasons for formation
Most often, the anomaly is caused by primary adentia (underdevelopment of the alveolar process) or displacement from their place (dystopia) of permanent units that were supposed to replace the persistent ones. Sometimes there is a family history of the anomaly.
The resorption of the roots of baby teeth and their loss as a result occurs under the influence of the permanent units located under them. The latter rest their tops on the roots of the “milk jugs” and start the process of their resorption. If the embryo of a permanent tooth is missing or displaced away from the roots of the “milk jug” , the resorption process does not start, and the latter remains in its place.
Prevention measures
All various preventive measures that help keep teeth healthy can be divided into 4 groups:
- Regular visits to the doctor.
- Proper oral hygiene.
- Power control. Providing the body with nutritional components that ensure the proper development of the dentofacial apparatus. Acceptance or, on the contrary, exclusion of those products that, by their physical form, are beneficial or harmful to the condition of enamel and dentin.
- Improved overall health.
Visiting a doctor for preventive purposes
As already noted, you need to visit the dentist at least 2 times a year. The optimal frequency is considered to be once every 3 months. During a preventive examination, the doctor will definitely notice the onset of the disease and take the necessary measures.
Reasons for performing dental trepanation and the specialist’s course of action.
In this publication we will discuss the importance of photodynamic therapy in dentistry.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/lidoksor-partner-stomatologa.html all the most important things about the drug Lidoxor.
Oral care
You need to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day: the first time in the morning after meals (you can rinse your mouth before breakfast), the second, mandatory time, in the evening after dinner. Pre-night cleaning is more important than the first, because if it is not done, food debris will remain in the oral cavity for a long time.
To clean the proximal space, you need to use brushes and floss.
You should begin and end brushing by rinsing your mouth with mouthwash or clean water.
The brush is changed once every 2-5 months , the paste - every 1.5-2 months. The bristles should not be very hard, suitable for enamel and gums, the brush head should not be traumatic. It is advisable to periodically use specialized pastes with fluoride, calcium, triclosan, whitening, and medicinal herbs.
To clean MVPs and orthodontic appliances, it is recommended to use superflosses - thinner threads of a special structure.
You also need to clean your tongue with a special scraper.
Do not use foreign objects, such as needles, for cleaning. Even toothpicks should be used carefully, without excessive zeal, so as not to damage the enamel or injure the gums.
Nutrition
Food must contain all the components necessary for the body. Too sweet and sour foods are considered harmful to enamel and dentin; it is advisable to reduce their intake.
The menu should contain not only soft, but also fairly hard foods that partially cleanse the teeth of soft plaque and create a healthy load for them. At the same time, too hard (nuts, crackers) and viscous (toffee) foods should be excluded from the diet.
General health
It has been established that there are cause-and-effect relationships between caries and certain diseases and conditions. Susceptibility to caries increases with Kashin-Beck disease, hypothyroidism, rheumatism, and changes in hormonal status.
Pregnancy is a predisposing factor to caries. Radiation therapy used in the treatment of tumors of the head and neck is very dangerous for the condition of enamel and dentin.
Heredity also influences a person's susceptibility to caries.
The exact mechanism by which general health affects dental health is not fully understood. However, it is assumed that the connection between them is determined by the pulp, which contains blood vessels that feed dentin and enamel, the composition of the oral fluid and the condition of the periodontium.
For all of the above cases, special preventive measures have been developed that reduce the risk and severity of mediated dental diseases. They should be used on the recommendation of a doctor.
Learn how to keep your teeth healthy from the video.