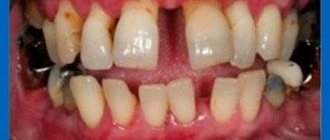
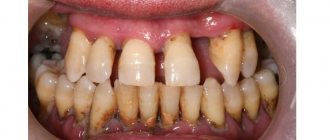
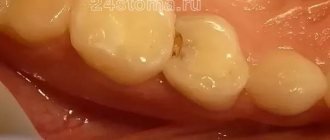
One of the common dental pathologies is periodontitis (periodontal disease). It implies damage to the alveolar bone, due to which the neck of the tooth is exposed, and then its root. As a result, teeth appear visually longer, and they also become mobile over time. With the development of periodontal disease, the alveolar bone gradually becomes thinner. This can lead to complete loss of your teeth. To preserve the aesthetics of a smile, dental prosthetics can be performed in case of periodontitis. In addition to restoring the external attractiveness of the smile, this procedure allows you to relieve the overload on the remaining units of the row.
What are the dangers of periodontitis and periodontal disease for a patient?
- inflammation of the ligaments of the teeth and nearby bone tissue,
- formation of voluminous gum pockets,
- loss or contraction of the gums, as a result - exposure of the roots of the teeth, which is fraught with increased sensitivity and an increased risk of developing caries,
- accumulation of a large amount of dental plaque,
- bad breath due to rotting food debris and plaque deep in the pockets,
- gum recession and root exposure,
- development of periodontitis - formation of cysts and granulomas on the roots of teeth,
- violation of the aesthetics of the dentition - due to the absence of teeth, changes in their shade and the appearance of gaps in the root area,
- mobility and loss of teeth.
But, unfortunately, inflammation is not limited to just one oral cavity. Periodontitis leads to many problems throughout the body - disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (which is logical, since along with food we swallow pathological microorganisms that are in the oral cavity), pathologies of the cardiovascular system and even kidneys! Read more in the article “The nature and dangers of periodontitis”
Just 10 years ago, periodontitis was an incurable disease. Medicine was unaware of methods for relieving inflammation and restoring periodontal ligaments to reduce the depth of periodontal pockets. All measures were aimed only at improving hygiene to stop the inflammatory process and slow down the progression of periodontitis. At the same time, the depth of the periodontal pocket did not decrease and, with poor hygiene, the disease took hold.
Preparation for prosthetics
To install a prosthesis, certain conditions are required:
- no bleeding gums;
- elimination of acute diseases of the oral cavity;
- absence of periodontal pockets;
- healthy gums on which the structure will rest;
- absence of caries;
- healthy bite;
- no plaque or stones.
Initially, during preparation, temporary dentures are placed, so removable, fixed dentures or splinting products are used, respectively, the main task: stabilization of teeth against the background of acute inflammatory phenomena.
Installation of permanent dentures requires certain conditions. The procedures are carried out if there are no: bleeding gums, acute diseases of the oral cavity have been eliminated, no plaque or caries. The type of permanent structure is chosen taking into account the structure of the patient’s jaw, the degree of pathology and the duration of the disease.
The vicious circle of periodontitis with tooth loss
Natural teeth require periodontal ligaments and a sufficient amount of bone tissue to be attached to the dentition. The habitat of the pathogenic flora of periodontitis is located around the tooth and leads to the destruction of these ligaments, bone and, as a result, to tooth loss. But if there is no tooth, then there is no environment for the development of the disease.
At the same time, a violation of the integrity of the dentition contributes to the development of periodontitis, since without chewing load the bone in the area of the missing tooth atrophies (decreases in volume), the neighboring teeth, under pressure and due to excessive load, “working for two”, gradually shift into the area of empty space. Thus, gaps form between the teeth, periodontal ligaments stretch and weaken, periodontal pockets increase and the disease becomes aggressive.
Restoring lost teeth using traditional methods - bridges supported by your teeth or removable dentures - only aggravates the situation. Removable dentures do not transfer the load to the bone, but compact it even more. They are attached with clasps to adjacent teeth and, against the background of developing atrophy, lose their fixation and damage (rub) soft tissues when chewing.
Dental bridges require grinding of your own teeth to secure them - this is already harmful and a long-term death sentence. Bone atrophy in the area of the missing tooth, which is camouflaged by the bridge crown, continues, the gums sag, microbes and food debris accumulate under the intermediate crown - the habitat of periodontitis. The supporting teeth shift and eventually the structure of the entire bridge breaks, and along with it the patient loses the supporting teeth.
In advanced stages, treatment of periodontitis, even using the latest treatment methods, is ineffective and sometimes the only way to stop the inflammatory process is to remove the affected mobile teeth, as the disease begins to seriously harm the entire body. Therefore, it is very important, when identifying a diagnosis, not to abandon the situation, but to begin to fight the disease immediately.
What types of prosthetics are possible for periodontal disease?
Before installing dentures, dentists must carry out comprehensive treatment of the disease in order to achieve its remission. If bone loss is not stopped, any prosthesis will quickly become unusable.
Zirconium dioxide crowns
fixed onto ground natural teeth.
Metal ceramics and porcelain are not used for periodontal disease. Dentists prefer to install zirconium crowns - they prevent the accumulation of bacteria and inhibit the development of the disease. Zirconium dioxide crowns are quite expensive, so they are most often installed in the smile area.
Bridges
fixed to abutment teeth or crowns.
Such dentures create excessive pressure on the “support teeth” and jawbone. Therefore, such prosthetics for periodontal disease are a rare occurrence. In addition, bridges can be installed only if the teeth are not loose and the bone tissue is completely preserved or its atrophy is minimal. That is, a bridge is a possible solution only for the initial stages of periodontal disease. When the disease begins to progress again - and this, unfortunately, is inevitable, the supporting teeth will begin to move due to excessive load and the bridge will either have to be changed or a new solution to the problem must be sought.
Removable dentures
fixed with clasps and occlusal pads.
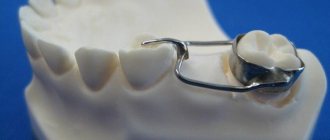
A removable denture for periodontal disease should have minimal impact on soft tissues and mucous membranes. Therefore, dentists often install a splinting clasp prosthesis for patients with periodontal disease, which restores lost teeth, tightly fixes natural teeth and evenly distributes the chewing load. This design can be used even if all the teeth are loose - in this case, the doctor connects them and secures all the elements of the row together. The clasp splinting prosthesis is fixed on the supports with clasps - ring-shaped and claw-shaped hooks.
Implantation is the only effective way
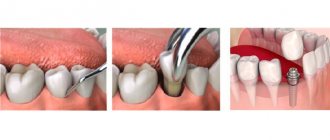
Implants are screwed into the bone and do not require periodontal ligaments to secure them. The surface of the necks of special implants is resistant to the accumulation of microbes. Thus, dental implantation is the only effective way to restore teeth in conditions of periodontitis , but only if the disease is stopped . The patient gets rid of chronic periodontitis, the periodontal ligaments are restored, and the soft tissues are strengthened, remodeled and, with good hygiene, serve as a natural barrier to the penetration of infection into the bone.
The integrity of the dentition and proper distribution of the chewing load contributes to:
- stimulating blood circulation and normalizing nutrition of bone and gum cells,
- stops uneven distribution of chewing load and overload of teeth,
- prevents changes in bite and tooth mobility.
Implants should not be installed near teeth affected by periodontitis. If the remaining teeth, as the main source of “infection,” are left without complex therapy, then the development of infection will lead to an attack by pathogenic microflora on nearby implants and the soft tissue around them, and this will lead to complications and even rejection. Therefore, first of all, before implantation, you need to undergo a comprehensive course of periodontitis treatment and reduce the risks.
BE CAREFUL! Some unscrupulous and inexperienced doctors convince patients to place implants next to adjacent teeth affected by periodontitis, without informing them of the danger and essentially hoping for a “miracle.” Under no circumstances do this without simultaneous treatment and bringing periodontitis into a state of stable remission. Plus the realization that careful hygiene with this approach is very important in the future.
ON A NOTE! According to the American Association of Periodontists www.perio.org, the average age of a patient with periodontitis is 40+, 70% have implants in the oral cavity with developing complications.
With the development of microbiology and nanomaterials, drugs have been developed that not only stably stop the disease for many years, but also make it possible to restore the consequences of complex forms of periodontitis up to 80% in 1 year. Today, advanced dentistry has effective tools for preserving teeth. Smile recovery periodontal complexes are aimed initially at eliminating the environment for the development of the disease, and then enriching the affected areas with active growth factors to create a favorable environment for the natural regeneration of the patient’s cells and tissues.
Deep cleaning of periodontal pockets and 1-2 procedures will not stop the progression of the disease. Periodontitis is a multifaceted disease with an individual pathogenic flora for each patient and it must be treated accordingly, using a set of antibacterial and restorative measures, selected individually after a thorough study of microflora culture from periodontal pockets, drawing up a periodontogram, analyzing the state of bone tissue using computed tomography and additional blood tests.
Do you want to save your teeth and stop the disease? Smile recovery periodontal complexes that really work.
find your solution
Implant installation - stages
Treatment of periodontal diseases
The main task of implantation in conditions of periodontitis or periodontal disease is to stop the disease, otherwise there is a high probability of rejection. Here it will not be possible to get by with cleaning periodontal pockets; this will not stop the course of the pathological process. Drugs can help achieve remission. They are selected individually after examination:
- examination of the contents of periodontal pockets;
- periodontogram;
- blood tests;
- CT scan of the dentofacial apparatus.
The medication course takes up to 1 year. At the same time, measures are taken to preserve the remaining teeth, if possible. Periodontal complexes are used aimed at creating favorable conditions for the natural regeneration of jaw structures.
Bone tissue augmentation
Osteoplasty is a surgical operation aimed at increasing the height and volume of the jaw bone to create reliable support for dental implants. Performed before implantation. If you place titanium rods in atrophied tissues, this is fraught with their exposure, overload and rejection. The use of single-stage rods is risky due to the risk of damage to blood vessels and nerve fibers.
The method of extension is selected based on the clinical picture. Our Center uses the following methods:
- Sinus lifting is prescribed for the upper jaw when there is a risk of injury to the maxillary sinus with classic implants. It involves creating access in the bone to the bottom of the sinus for subsequent lifting and filling the resulting space with a graft. It is performed in an open or closed manner, depending on how many millimeters it is necessary to increase the height of the alveolar process.
- The technique of directed regeneration, the use of barrier membranes are indicated for increasing the bone of the upper or lower jaw horizontally and vertically. To protect the graft from external factors, protective membranes are fixed: resorbable (absorbable) or non-resorbable (non-absorbable).
Installation of implants
We perform dental implantation for periodontitis and periodontal disease according to the classic protocol:
- The mucous membrane of the gums is dissected.
- Using cutters, holes are formed in the bone for titanium rods.
- Implants are placed.
- Cover screws are secured.
- Stitches are applied.
- The sutures are removed after 7-10 days (if non-resorbable threads were used).
- After 4-5 months, an examination is carried out to determine whether prosthetics are possible. If the rods have taken root, the cover screws are replaced with gum formers to create the correct gingival contour.
- Impressions are taken and sent to a dental laboratory.
- After 2 weeks, the formers are replaced by abutments, onto which dental crowns or prostheses are attached.
Features of dental implantation for periodontitis
First of all, in order to save the remaining teeth, the patient must accept the fact that he needs to undergo a fairly long course of treatment, usually 1 year. After all, the periodontal and bone ligaments need to recover, and this is not a quick process. Simply placing implants for periodontitis is a bad idea, since the conditions are unfavorable:
- there is atrophy and loosening of bone tissue,
- implants are poorly fixed in the inflamed bone,
- after installation, implants are surrounded by inflamed tissue, which can lead to disruption of their fixation and subsequent rejection,
- bone growth is difficult - in the presence of inflammation, the grafted material may not take root.
The good news is that thanks to periodontal complexes under the supervision of a periodontist, it is possible to put early and moderate periodontitis (stages I and II) into a state of stable long-term remission while simultaneously restoring missing teeth. The bad news is for those who have been diagnosed with acute forms and advanced stages, when there is tooth loss or mobility - removing all teeth and replacing them with implants is the most effective option. If the initial situation allows you to combine the procedures, the implants will be installed simultaneously - in the sockets of the extracted teeth.
What patients say about treatment
Nadezhda Aleksandrovna Selfie and review after implantation of all teeth, including the use of zygomatic implants
Mikhail Evgenievich With words of gratitude for the new smile! One year after basal implantation
Natalya Vladimirovna 1.5 years after all-on-4 implantation: re-prosthetics
Larisa Valentinovna Selfie with doctors after complex all-on-4 implantation
Olga Vyacheslavovna 10 months after all-on-6 implantation – examination, correction and hygiene
— Selfie and review after implantation of all teeth, including the use of zygomatic implants
With words of gratitude to the attending physicians - a review and photo after prosthetics using the all-on-4 technology: “Many thanks to Evgeniy Aleksandrovich for the excellent job done! Yuri Alexandrovich for his beautiful smile! May God bless you with health and prosperity. Happy New Year!"
Nadezhda Alexandrovna
Selfie and review after implantation of all teeth, including the use of zygomatic implants
Doctor: Specialization: Experience:
3 days
View all reviews
— With words of gratitude for the new smile! One year after basal implantation
After basal dental implantation in the upper and lower jaws, as well as after subsequent re-prosthetics (changing the denture to a permanent structure). In the photo - with the attending physicians: orthopedic dentist Stanislav Chorny, as well as implant surgeon Nikolai Namdakov.
Mikhail Evgenievich
With words of gratitude for a new smile! One year after basal implantation
Doctor: Specialization: Experience:
3 days
View all reviews
— 1.5 years after all-on-4 implantation: re-prosthetics
With orthopedic dentist Zhargal Dulgarov after changing the adaptive prosthesis to a permanent one. The patient began treatment in our clinic back in May 2021. During this time, all-on-4 implantation was performed on original Nobel Biocare implants with immediate and delayed loading. A permanent prosthesis was installed on one jaw in November, now it’s time to re-prosthetize the second jaw. The patient chose a comfortable option made of ceramic composite – a durable and very aesthetic material.
Natalya Vladimirovna
1.5 years after all-on-4 implantation: re-prosthetics
Doctor: Specialization: Experience:
3 days
View all reviews
— Selfie with doctors after complex all-on-4 implantation
With the attending physicians who performed dental prosthetics as part of complex all-on-4 implantation. With the installation of a fixed prosthesis immediately. As part of the implantation, implants original to this protocol were used - from Nobel Biocare.
Larisa Valentinovna
Selfie with doctors after complex all-on-4 implantation
Doctor: Specialization: Experience:
3 days
View all reviews
— 10 months after all-on-6 implantation – examination, correction and hygiene
With words of gratitude for a new smile and a new life! After implantation of the upper jaw according to the all-on-6 protocol with immediate installation of a fixed denture within up to 3 days. With the attending doctors: maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist Nikolai Namdakov, orthopedic dentist Stanislav Chorny, as well as hygienist Sona Bakarian after a comprehensive cleaning of the oral cavity as part of a free service.
Olga Vyacheslavovna
10 months after all-on-6 implantation – examination, correction and hygiene
Doctor: Specialization: Experience:
3 days
View all reviews
Dental care
Regardless of whether the patient has chosen a removable denture or received implants with a firmly fixed structure, it is important to ensure the highest quality oral hygiene and not to forget about regular visits to the periodontist. It is not difficult to keep the situation under control - take a course of medication twice a year, take vitamins, and use ultrasound techniques. In this case, artificial teeth will last you longer, and your remaining relatives will not suffer from this insidious disease.
Dental prosthetics in case of complete absence of teeth
Prosthetics or dental implants - which is better?
Not all implants can be installed for periodontitis
In addition to therapy against periodontitis, it is important to choose the right implants. They must have high primary stability in the current unfavorable conditions and have a special coating to improve integration, both with the soft tissue of the gums and with various types of bone tissue. The surfaces of these implants at the level of contact with the gums have properties of resistance to the accumulation of microbes.
In the world, there are only 3 implantation systems, Nobel Biocare, Straumann, Oneway Biomed, which have been studied for more than 40 years, the implants of which take root and are not rejected in conditions of periodontitis. Naturally, provided that foci of infection are eliminated, complex treatment and rehabilitation of the affected tissues are completed.
Nobel Biocare® - Xeal® and TiUltra® Surfaces The intimate contact between the soft tissue and the abutment creates a barrier that protects the underlying bone and ensures long-term stability and healthy gum tissue.
It is a smooth, non-porous, nanostructured anodized surface with a chemical composition and topography designed specifically to enhance soft tissue attachment.
When developing these surfaces, scientists relied on 20 years of research into the effectiveness of anodized implants and laboratory results.
The single orthopedic surface of On1 eliminates the need for surgical manipulation of soft tissues during subsequent prosthetics.
The main objectives of these surfaces are to ensure a favorable outcome of implantation in the long term and reduce the incidence of re-implantitis.
More details
Straumann® Roxolid SlActive - Tissue Level Straumann® Tissue Levels have a smooth milled neck, which simplifies the manipulation of soft tissues and eliminates the need for the use of healing abutments during subsequent prosthetics. In the event of a slight recession of the soft tissue, the polished neck of the implant will protect the surface of the implant from the accumulation of microbes.
Nanostructures on the implant surface promote early osseointegration and a larger area of bone penetration.
The SLActive® surface is characterized by an increased anti-inflammatory response during the early healing stage. The results of world studies have confirmed the exceptional survival rate of implants in difficult clinical situations and when using aggressive treatment protocols: in patients with diabetes mellitus, after chemotherapy and radiation therapy, in heavy smokers, in patients with chronic periodontitis.
More details
OneWay Biomed® - antimicrobial coating BCS MU and Zygomatic implants are one-piece structures designed for osteofixation in the deep parts of the maxillofacial bone and cranial buttresses. For example, the bicortical plate, basal bone, zygomatic region, jaw tubercles, hyoid and mental bones, pterygoid process, etc.
Such implants do not require integration with the alveolar bone of the jaw, since they are securely fixed in other, non-resorbable areas. Over time, the newly formed alveolar bone compacts around the implants, providing additional support.
The surface of the implants has an antimicrobial coating, which prevents plaque and bacteria from accumulating.
The implant and abutment are a single whole; after implantation, soft tissues are not subjected to additional surgical interventions at the prosthetic stage.
More details
In addition, it is important to minimize the number of surgical manipulations on soft tissues after implantation, therefore implants with a single orthopedic surface On1 installed at the soft tissue level are preferable. During subsequent prosthetics, the orthopedist does not injure the gums and does not create additional mechanical stress on the implant, essentially working “above the gum.” In addition, all components of the prosthesis must be bioinert, that is, not cause inflammatory reactions from surrounding tissues.
Post-operative care
Upon returning home after implantation, the patient is required to strictly adhere to medical instructions. The success of the process of osseointegration of structures with jaw tissue directly depends on the quality of hygiene, taking prescribed medications, and following recommendations. The list of appointments includes:
- undergoing anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy in the first two weeks;
- Thorough brushing of teeth in the morning and evening with an electric brush;
- using an irrigator and floss to treat hard-to-reach places and interdental spaces;
- Regular visits to the dentist according to the schedule;
- exclusion of solid foods from the diet;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- reduction in the level of physical activity.
Scenarios for tooth restoration against the background of periodontitis
Remember that affected teeth are a source of infection. It is on them, on their porous surface, that a huge number of pathogenic microorganisms accumulate. If implants with an active surface are placed next to such teeth, even the most resistant ones, which contain chemical elements that contribute to the healing of bone cells (such as SLA-Active from Straumann and Ti-Ultra from Nobel Biocare), they still will not are able to cope with a massive attack from all sides and bone tissue atrophy.
PARTIAL IMPLANTATION WITH REMAINING TEETH
- the depth of periodontal pockets is less than 8 millimeters,
- local foci of inflammation, swelling and itching are observed,
- mobility of teeth I and II degrees,
- bone quality type II and III,
- no suppuration and periodontal abscesses,
- teeth are in satisfactory condition,
- healing potential is medium to high.
EXTRACTION OF ALL TEETH AND COMPLEX IMPLANTATION
- teeth in the oral cavity are affected by diseases,
- there is degree III mobility of the remaining teeth,
- formation of deep periodontal pockets of more than 8 millimeters,
- purulent discharge from periodontal pockets,
- exposure of the neck of the teeth,
- abundant hard dental deposits,
- healing potential is low,
- severe atrophy of bone tissue.
Vladimir Ivanovich, 62 years old
“I had a difficult situation - there were almost no teeth left, it was painful, it was difficult to eat, there was constant psychological discomfort from these problems. I went to the clinic and everything was done quickly, professionally and competently! Incredible work and stunning results that are hard to believe. But he's real! Thanks to the doctors for my new life!”
- forget about bad breath
- communicate without hesitation
- refuse complex, lengthy and expensive treatment of periodontitis
- start living without constant visits to the dentist WITHOUT LIMITATIONS
watch a video with the patient
On day 2-3, a fixed prosthesis with an elastic acrylic base is installed. It gently envelops the gums and does not cause pain at all, even in the presence of an inflammatory process. There remains a functional space between the base of the prosthesis and the gums, which allows for hygienic care, which is especially important in the presence of gum inflammation. In addition, a number of companies (for example, Oneway Biomed) are developing implants with a smooth polished neck and an antimicrobial coating, which prevents plaque accumulation in the presence of inflammatory processes in periodontal tissue2.
In addition to the presence of inflammation of periodontal tissues, women should also pay attention to the state of hormonal levels, and, if necessary, undergo additional examination by an endocrinologist. Read more about the features of dental implantation in women >>>
earlier
Now
Patient history
“I arrived on Thursday, and on Tuesday I was already able to talk, eat, drink and smile with MY OWN teeth. I was pleasantly surprised by the work. Honestly, I didn't expect this. Here I saw what real work is: just installing the prosthesis took at least 2 hours, the fit was perfect, down to the millimeter! Many thanks to the doctors!”
watch a video with the patient
Implantation options depending on the severity of the disease
| Partial implantation (remaining teeth are retained ) | Full implantation (all teeth are removed) | |
| Depth of periodontal pockets | up to 8 mm | more than 8 mm |
| Nature of inflammation | localized | generalized (affects the entire jaw) |
| Mobility of dental row units | I-II degrees | III degree remaining units |
| Bone quality | Type II-III (cortical layer thickness 3-5 mm, spongy layer with a developed network of thin trabeculae) | severe atrophy of the jaw bone |
| Condition of remaining teeth | satisfactory | accumulation of dental plaque |
| Tissue healing ability | high or medium | low |
Implantation options for periodontitis
Basal implantation – BASAL COMPLEX
Complex basal implantation is the main and most optimal method, which is used in the presence of acute or chronic inflammation of periodontal tissue.
To restore all teeth, 8 to 12 implants are used, which are evenly distributed along the row. A large number of supports in the form of implants allows you to more reliably fix the prosthesis and significantly extend its service life, even in the presence of bone tissue atrophy, as well as inflammatory processes of periodontal tissue. A fixed prosthesis is installed on the 3rd day. Read more about basal implantation technology >>>
All-on-6 technology
Prosthetics on six implants for periodontitis and periodontal disease, along with basal implantation, is used quite often, since 6 supports to support the prosthesis are quite sufficient even in the presence of tissue inflammation and bone tissue atrophy (but of moderate degree). The denture is installed immediately (within up to 3 days), which allows the patient to return to a full life.
Learn more about the all-on-6 protocol >>>
All-on-4 technology
This protocol involves the use of only four implants for full dental prosthetics. Its use is justified in the presence of inflammation of the initial or middle stage, that is, with slight atrophy of bone tissue. For prosthetics of the upper jaw, it is possible to use elongated zygomatic implants. The prosthesis is installed on the 3rd day.
Learn more about the all-on-4 protocol >>>
Zygomatic implantation
Included in all comprehensive solutions for complete edentulism. This approach uses zygomatic implants, the length of which reaches 6 cm. They are installed only on the upper jaw and use the zygomatic bone, which is not subject to inflammatory processes, for fixation. The fixed prosthesis is fixed for 1-3 days.
Read more about zygomatic implantation >>>
earlier
Now
Patient history
“I am very pleased with the result of the work. The amazing thing is that in 4 days, and not in 2 years, I got my full life and confidence back. And most importantly, I was given back the opportunity to smile, which I had long forgotten about. If they say that this is impossible, read, call, ask - here you will get any information!”
watch a video with the patient
Content
- Features of prosthetics
- Proper dental care
Periodontal disease is a non-inflammatory disease of the dental spectrum, difficult to treat and with an unclear etiology. It is believed that the prerequisites for the disease are heredity, low immunity, endocrine disorders, and serious diseases of the internal organs. If possible, the provoking factor should be eliminated. If not, it is important to constantly keep the situation under control, preventing atrophy of the alveolar processes and tooth loss.
Tooth loss is accompanied by the fourth stage of periodontal disease. However, even at earlier stages, any untreated tooth may require removal, which means the question of prosthetics for periodontal disease will arise.
PROMOTION
Removable dentures - inexpensive
from 10,000 rub.
Disadvantages of implantation for periodontitis and periodontal disease
Dental implantation involves surgical intervention, which, against the background of the inflammatory process of periodontal tissues, can cause certain difficulties. In addition, even when using one-stage implantation methods, the risk of rejection of structures is still noticeably higher than when installing implants into healthy tissue. After the installation of implants, the patient himself must not only strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions, but also carefully carry out hygiene procedures: not only in the morning and evening, but also after each meal. This is extremely important to ensure that as little harmful bacteria as possible remain in the oral cavity, which will cause inflammation of periodontal tissue.
“Inflammatory processes of periodontal tissues, as a rule, spread throughout the entire dentition, so a comprehensive solution to the problem is required. For periodontitis and periodontal disease, the only possible solution is one-stage implantation with immediate loading. The method uses one-piece implants that are fixed in the deep layers of bone tissue. Such sections are not subject to either atrophy or inflammatory processes. That is why the installation of implants is possible when periodontal tissue is destroyed.”
Bespalov Roman Dmitrievich, maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist, more than 25 years of experience make an appointment
Doctor's advice - it will take a lot of time to prepare for implantation
The patient should be prepared for the fact that treatment and preparation for implantation will take a long time - on average 1 year. These are necessary measures, since regardless of the causes of the disease, when installing implants, the doctor is faced with resorption of the jaw bone and unsatisfactory condition of the gums. Osteoplasty in conditions of inflammation is also not performed. First, the source of infection is stopped, and then bone tissue is augmented.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
Are alternatives possible?
In case of inflammation of periodontal tissue, two-stage implantation is not recommended due to the fact that implants with this approach are installed in the central part of the bone tissue, which is most susceptible to inflammatory processes. This means there is a high risk of developing complications and rejection of structures. It will also not be possible to install a dental bridge - there is a high probability that the teeth remaining in the oral cavity will begin to loosen after some time. This will lead to mobility of the bridge and breakdown of the entire system.
In case of partial edentia and at the same time mobile teeth that are in a relatively healthy condition, the problem can be solved by installing a clasp denture. It has a metal base, which will allow you to secure the position of loose teeth and at the same time provide prosthetics for lost ones.
If there is acute inflammation that extends to most or all of the dentition, you may consider installing a removable soft plastic denture. At least for the duration of the acute stage of inflammation.
1 According to the World Health Organization (WHO). 2 According to official clinical trial data from Oneway Biomed.
What is periodontal disease and periodontitis?
These diseases have significant differences. Periodontal disease is characterized by degenerative changes in the hard and soft tissues of the jaw. There is no inflammation, but with grade 3 tooth mobility it is possible due to trauma, as with periodontitis. The gums become pale, the roots of the teeth become exposed, and the gingival papillae become smaller or atrophy.
With periodontitis, an inflammatory process in the gums, bone pockets, hard deposits and bleeding are detected. Unlike periodontal disease, the pain is constant, and when exposed to food irritants, it increases sharply. Tooth mobility is observed already at the 1st degree of severity of periodontitis, which complicates prosthetics.