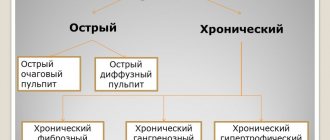
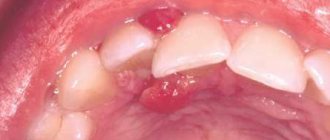
Causes of formation of salivary gland cysts
Salivary gland cysts appear as a result of blockage of the salivary ducts. Pathology of patency can be caused by various factors:
- various types of injuries;
- Poor, untimely or completely absent oral hygiene;
- unhealthy diet;
- bad habits;
- various types of infectious diseases of the oral cavity and teeth;
- difficulty or disturbance, followed by cessation of secretion outflow;
- the appearance of a plug as a result of thickening of the secretion, disrupting the patency of the excretory canal;
- the presence of various tumors that put pressure on the duct;
- the presence of scars narrowing the canal.
Symptoms
Patients with ranula complain of a tumor-like formation in the mouth or under the chin. It does not cause pain, but sometimes there may be a feeling of tightening of the mucous membrane. The contents of the ranula are transparent and colorless. During independent palpation, patients note its density and the presence of a symptom of fluctuation - a feeling of swaying with one finger, obtained with jerky movements of the other finger. This sign allows you to establish that the cyst is filled with liquid contents. If the ranula bursts, there is a risk of secondary bacterial infection.
Ranula photo
If the cyst grows excessively, it begins to cause discomfort to patients. Infants are especially susceptible to this. An overgrown cyst can fill most of the mouth, making it difficult to eat. Against the background of a raised tongue, the act of sucking is disrupted, which subsequently leads to malnutrition and developmental delays. In adults, the chewing process suffers, and it becomes difficult to pronounce words.
Classification of salivary gland cysts
Depending on the location, salivary gland cysts are divided into two types:
- Minor salivary gland cysts appear on the cheeks, lips, palate, tongue, or molars.
- Cysts of the major salivary glands: sublingual salivary gland, parotid salivary gland and submandibular salivary gland.
In addition, salivary gland cysts can be located either in the duct or in the functional part of the gland. According to the structure of the cyst, there are true (retention) and false (post-traumatic). A mucocele salivary gland cyst with mucoid mucous content is also isolated.
Classification of pathology
Cysts localized in the tissues of the upper or lower row of teeth are very common. With their development, a cavity appears, the walls of which are covered with fibrous tissue, and the inner surface consists of an epithelial layer. The capsule holds clear or cloudy liquid.
Doctors distinguish the following types of pathology:
- Primordial. This is a cyst of the lower jaw. It appears in the area of the third molar. She has very thin fibrous walls. The inside of the capsule is lined with flat epithelium. According to its structure, the tumor may contain one or several small chambers.
- Follicular. Formed before tooth eruption. It can grow in the area of the alveolar margin. Includes cells that intensively produce viscous mucus. Because of this, the internal contents of the anomalous structure are quite viscous. A follicular formation is formed from the enamel organs of the unerupted unit. One or several teeth are found inside it. These may be formed crowns or tooth buds.
- Radicular. It occurs more often than others - in eighty percent of cases. Usually grows above the upper teeth. The diameter reaches from half to two centimeters. Often inflamed. Then the cells begin to hyperplasia, network-like processes are formed that extend into the thickness of the walls. The liquid contents of the radicular structures are rich in neutrophilic leukocytes. Often with this type of pathology, the patient develops sinusitis. This is due to the peculiarities of the localization of the inflammatory site.
- Retromolar. It is formed due to a long-term inflammatory process occurring in the thickness of the soft tissues. It is a consequence of complicated teething.
- Nasoalveolar. It occurs near the nasopalatine canal (the border between the upper row and the wing of the nose).
- Aneurysmal. Very rare in dental practice. Appears only on the lower jaw. This type of neoplasm is still poorly studied. It is known that there is blood or a red-pink liquid inside it. Many scientists agree that the symptoms of an aneurysmal cavity are a consequence of hormonal imbalance.
- Traumatic. Occurs due to recent facial trauma.
- Residual. The result of mistakes made by the doctor during tooth extraction, or the consequence of the patient ignoring the surgeon’s instructions.
The doctor decides how to treat a dental cyst, taking into account the cause of its development. It is very important to understand why the tumor occurred. If the root cause is not identified, the likelihood of relapse will remain high.
Symptoms of a salivary gland cyst
A cyst of the minor salivary gland is formed in the area of the corners of the mouth inside the lip; in addition, there is a possibility of its occurrence on the mucous membrane of the cheeks. The formation of a cyst can occur as a result of mechanical damage to the minor salivary gland and areas of the oral cavity during eating or talking. Initially, the neoplasm is small and round, but gradually increases in size. A patient with such a cyst does not feel any discomfort, but in some cases he may complain of pain during talking and eating. Painful palpation of the cyst is possible. During diagnosis, it is important to distinguish a cyst of the minor salivary gland from hemangioma, fibroma and other benign tumors.
The sublingual salivary gland cyst is located at the bottom of the mouth. In its shape, the cystic formation can have the shape of an hourglass, round or oval with a characteristic bluish tint. As the disease develops, the frenulum of the tongue is disrupted and displaced, and the patient also feels discomfort while eating and talking. The cyst of the sublingual salivary gland is characterized by independent periodic emptying, followed by filling with a clear liquid. When diagnosing a sublingual gland cyst, it is necessary to distinguish it from a submandibular gland tumor, dermoid and lipoma. The possibility of sialolithiasis or viral diseases is excluded.
The submandibular salivary gland cyst is fixed in the area of the submandibular glands. A growth forms that is soft and elastic to the touch. As it grows, swelling appears in the tongue area and at the bottom of the mouth. The risk of inflammation is associated with deformation of the oval of the face. In the diagnostic process, it is necessary to distinguish a growth of the submandibular salivary gland from a gill cyst, dermoid and soft tissue sarcoma, as well as diseases associated with purulent processes in the lymph nodes and submandibular salivary canals.
A submandibular gland cyst can be localized in the salivary ducts, it is called a congenital thyroid duct cyst, located in the middle of the neck or at the bottom of the hyoid bones.
A parotid salivary gland cyst is characterized by slow growth and location near the ear; in rare cases, the cyst can be bilateral. It is smooth and elastic in appearance and has a dense consistency. This very rare form of cyst can be congenital or acquired. It is formed without causing discomfort to the patient. A parotid cyst affects the ducts of the salivary glands and can be located quite deep, which makes it difficult to determine fluctuations. If the cyst has formed in the lower part, then it is characterized by internal growth. This is due to the natural structure of the oral cavity, which complicates diagnosis and treatment. The patient begins to feel discomfort only if the purulent process progresses. When diagnosing, it is necessary to distinguish a parotid salivary gland cyst from lymphadenitis, lipomas and bronchial cysts.
Treatment of cystic formation at home
Home therapy for oral cysts only makes sense if for some reason you cannot get to a dental surgeon in the next few days. It consists of rinsing with herbal solutions and antiseptics. You can also make compresses with anti-inflammatory herbal medicines.
If the hearth breaks through, it’s too early to rejoice. Most likely, it will soon reappear in its original place. This is how cysts work - their contents expire, but the outer layer remains.
Under no circumstances should you treat a bulge on the gum or mucous membrane as a regular pimple. Any attempts to open it mechanically will not lead to anything good. But the resulting wound can become infected. Then the inflammation will spread to deeper layers in a fairly short time, and it will be much more difficult to cure.
Diagnosis of salivary gland cysts
Diagnosis of salivary gland cysts involves determining the nature of the neoplasms; they can be benign or malignant. Determining the nature of the cysts directly depends on their clinical picture. To do this, it is necessary to interview the patient, identify and evaluate complaints, examine and palpate the cyst. During these manipulations, the doctor determines the size, type, location and mobility of the cyst.
Due to the fact that all cysts have an almost identical clinical picture of the disease, for an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to carry out additional diagnostics with cytological, radiological and biochemical studies.
Cytological diagnosis of the salivary glands involves taking a puncture from the tumor mass. Thanks to this study, it becomes possible to determine the process of tumor development.
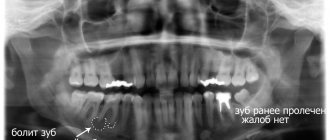
X-ray examination allows you to find out how much the salivary ducts are filled with contrast mass. The diagnostic method consists of conventional radiography and contrast radiography of the salivary ducts.
Also, for an accurate diagnosis, the method of differential diagnosis (method of exclusion) is used. This is necessary to distinguish one cyst from another.
Retention cyst on the lip: treatment
A lump on the inside of the lip is treated in the same way as a lump under the tongue.
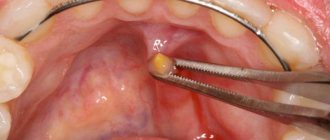
There is only one treatment option - surgery, which involves removing the entire cyst (there are no other treatment options). The surgery is very simple and usually does not take more than 15 minutes of the dental surgeon's time. It is performed under local anesthesia with lidocaine solution, and you will not feel any pain at all. It looks like this: a small incision is made on the surface of the mucous membrane next to the cyst, through which the entire cyst is removed, along with its contents. After this, 2-4 sutures are placed on the edges of the mucous membrane, which will need to be removed after about 7 days.
Removal of a retention cyst: video of the operation
During the operation, it is very important not to damage the cyst membrane, because if the walls of the cyst collapse, it is immediately lost in the tissues, and it is almost impossible to remove it entirely after this. If you leave a small fragment of the cyst shell in the tissues, the retention cyst on the lip will appear again.
What diseases have symptoms of a thyroglossal duct cyst?
Enlarged lymph nodes (inflammation, tumor lesion)
— Contrast enhancement in the center of the formation (in the absence of necrosis)
- Difficult to distinguish from an infected thyroid-lingual cyst - consider the location!
Adenoma of the isthmus or pyramidal thyroid gland
- Usually looks like a solid reinforced formation
- Hyperintense than thyroglossal cyst on T1-weighted image
Dermoid
- For example, located in the tongue
- May contain hair follicles or hair
— High signal intensity on T1-weighted image, on CT the density corresponds to adipose tissue (contains adipose tissue).
Abscess
— Inflammatory reaction of surrounding tissues
— Signal amplification from the wall
Hematoma
— No wall reinforcement
— Typical density on CT, heterogeneous signal intensity on MRI
External laryngocele
- Usually there is a connection with the larynx
— As a rule, located more laterally; contains air or liquid
Removal of the cyst with resection of the hyoid bone
Make an appointment
Foot Alexander Anatolyevich Doctor of the highest category, maxillofacial, plastic surgeon, has the highest category. More than 27 years of experience.
Doctor of the highest category, maxillofacial, plastic surgeon, has the highest category. More than 27 years of experience. Graduated from Irkutsk State Medical Institute. Repeatedly completed specializations in maxillofacial and plastic surgery in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Chelyabinsk, Irkutsk. Has the highest category. Author of a number of articles in medical periodicals. From 2013 to the present time he has been working as a medical maxillofacial and plastic surgeon. He has extensive experience in performing reconstructive surgery operations: jaw resection with immediate replacement of the defect with autologous bone, osteoplastic surgeries, implantology, post-traumatic reconstructive surgeries and congenital pathologies (bite correction using intraoral access). The doctor performs operations of a high category of complexity; reconstructive operations; operations belonging to the category of high-tech operations, including circular lifting of the skin of the face and neck (including SMAS lifting), blepharoplasty, rhinoplasty, otoplasty, elimination of wrinkles on the forehead and nasolabial folds, liposuction, removal of benign formations of the maxillofacial area , as well as scar correction and dermabrasion. Certificates and diplomas in plastic surgery, maxillofacial surgery, dental surgery are valid until 2023.
View the embedded image gallery online at: https://www.medistar24.ru/chelyustno-litsevaya-khirurgiya/478-udalenie-kisty-s-rezektsiej-pod-yazychnoj-kosti-obshchaya-anesteziya-45-000-rublej# sigProId43fcb6fc79
A midline neck cyst is a congenital pathology that occurs as a result of a violation of the intrauterine development of the baby. It is formed from the thyroid-lingual duct, which should disappear (overgrow) even before the baby is born, in the second month of the mother’s pregnancy, but in some cases this does not happen, and then the duct forms a closed cavity, which fills with fluid over time. Such a cyst often remains invisible, and can be detected not only in childhood or adolescence, but also in adulthood - either when it begins to grow and cause discomfort, or accidentally, during any medical examination of the neck for another reason. The growth of a cyst in adolescence or adulthood can be triggered by injury, infectious disease, or pathologies of the lymphatic or circulatory systems. Initially, cervical cysts are benign, but over time they can transform into malignant formations. In addition, suppuration can develop inside the cyst, and if the pus breaks out, a fistula is formed, but if the pus breaks inside the neck, then, in addition to the fistula, serious intoxication occurs in the body. If the cyst is not removed, then suppuration can be repeated many times, weakening the human body and increasingly threatening not only his health, but also his life. A cyst without inflammation can also cause discomfort - interfere with swallowing, change your voice, cause a sore throat and other unpleasant phenomena. There is no conservative treatment for cervical cysts, so the only option for eliminating them is surgery. If there is a need to carry out such an operation, it is extremely important to find a competent and experienced professional who will remove the cyst on the neck as carefully and safely as possible and completely, since if any fragments of the cyst remain unremoved, there will be a possibility of relapse.
As a rule, such an operation is planned, and before it, the doctor, as before any other operation, prescribes a detailed examination of the patient. As part of such an examination, a specialist may prescribe an ultrasound or tomography - computer or magnetic resonance imaging (CT or MRI, respectively). Urine and blood tests, puncture of the contents of the cyst, as well as other studies may be prescribed to exclude an oncological process and to obtain the maximum amount of information about both the formation and the general condition of the patient. If the patient comes with a suppurating cyst, before performing the operation, the doctor removes the pus from the cyst using a puncture method, prescribes treatment to eliminate inflammation, and only then proceeds to prepare for removal of the cyst. The operation is performed using general anesthesia in a sterile operating room. After the anesthesia is administered and begins to take effect, the doctor treats the surgical area with an aseptic agent and makes a skin incision in the projection of the cyst and up to the hyoid bone. Next, the specialist removes the tissue covering the cyst and reaches the formation itself. Since the thyroglossal duct passes through the middle part of the hyoid bone and fuses with it, when removing the cyst, it is necessary to remove a fragment of this bone to avoid the development of relapses. The doctor cuts the bone on either side of the cord of cyst formed from the duct, so as to avoid damage to the nerves leading to the tongue and located under the bone. Next, the doctor separates the bone fragment to be removed, as well as the remains of the thyroglossal duct from the remaining tissues, muscles and organs and removes the separated fragments along with the cyst as a single whole. The doctor brings the ends of the remaining fragments of the hyoid bone as close to each other as possible during suturing of the muscles. After this, the doctor stops the bleeding and sutures the wound, layer by layer connecting the tissues that were affected during the operation. A sterile bandage is applied to the wound.
After the operation, the patient remains under the supervision of specialists until his condition stabilizes, after which he can go home and only visit the doctor for observation and removal of stitches. During the rehabilitation period and until full recovery, the patient must carefully follow all medical instructions and restrictions, and then he will not be afraid of complications and will soon forget about the illness and completely return to a full, healthy life.
The multidisciplinary clinic “Medistar” brings together a galaxy of highly qualified specialists, true professionals in their field, conducting both diagnostic and advisory practice, and successfully treating ailments of any complexity. Our own laboratory, modern equipment for diagnostics and therapeutic manipulations allow us to go through all stages of the fight against the disease - from diagnosis to complete recovery, without leaving the medical center in search of the desired method of diagnosis or therapy.
Treatment of ranula with folk remedies
With a mild course and small size of the cyst, conservative treatment is allowed. For this purpose rinses are used:
- Oak bark decoction - pour 300 g of dried bark with a glass of hot water. Leave in a water bath for half an hour, strain the resulting broth and bring with boiled water to a volume of 300 ml. Rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day; the product can be stored for up to two days.
- Lemon juice rinse – leave the juice of three lemons in the refrigerator for 48 hours. Take the remaining zest and grind it along with 33 cloves of garlic. Pour the resulting mixture with two liters of boiled water and leave it in a warm place for a day. Then strain and add lemon juice. Rinse your mouth at least five times a day.