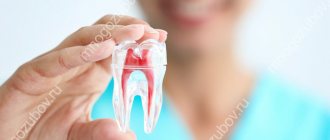
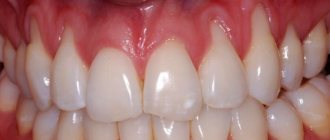
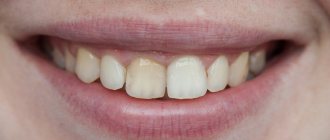
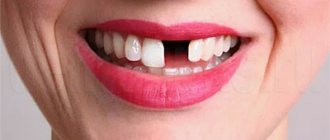
recession is a condition in which the gingival margin shifts and the necks and roots of the teeth
Exposure of the necks of teeth may be accompanied by increased sensitivity to “hot and cold” and the development of cervical caries.
Gum diseases can lead to tooth loss, since when the gingival margin shifts, the tissues holding the tooth (periodontal)
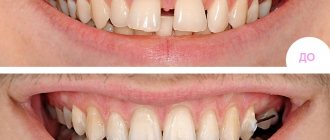
See how it happens:
Recession (recession) of the gums: why do the roots of the teeth become exposed and what to do about it?
If you notice that one or several teeth at once have exposed roots, you need to urgently consult a dentist. With age, gums inevitably recede, weaken, and lose their former strength and elasticity. But if the case has nothing to do with age-related changes, it is important to determine the exact cause of the pathological phenomenon. Be that as it may, you cannot ignore the situation, but you also need to approach solving the problem wisely. Further in this article we will analyze in detail the possible preconditions for gum recession, that is, its receding, and also consider modern methods of treating diseases of the mucous membrane and ways to eliminate aesthetic defects.
What causes gum recession?
Doctors include the following as the main causes of gum recession after dental implantation:
- incorrectly selected implant,
- incomplete coverage of the prosthesis with soft tissue,
- overpressure of the structure,
- eating rough food during the rehabilitation period,
- using a brush with stiff bristles,
- insufficient oral hygiene,
- progressive gingivitis or periodontitis.
To determine the exact cause of the problem, it is necessary to undergo a dental diagnosis. This should be done when the first alarming symptoms appear.
How does tooth root exposure occur?
The structure of any tooth involves the visible part, that is, the crown, neck and root system. In some pathological processes and phenomena, the soft tissues of the oral cavity weaken, become thinner and droop, exposing the necks and roots of the teeth. This situation is typical for various inflammatory diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, degenerative changes in the mucosa, systemic pathologies and hormonal imbalances. In addition, recession often develops against the background of an incorrect bite, a frenulum that is too short, or after poor-quality dental treatment.
Exposure of tooth roots almost always occurs simultaneously with the formation of periodontal pockets. The gums lag slightly at the base of the crown, and bacteria begin to accumulate in the resulting space, which leads to tissue inflammation. This phenomenon accompanies the development of periodontal diseases, therefore complex treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease involves regular deep cleaning of periodontal pockets from hardened deposits.
The recession goes through several stages of its development, and at the last stage there is a real risk of complete loss of teeth. It is better not to let the situation get to the point where the teeth begin to become loose, and when the first signs of a problem appear, immediately seek advice from a dentist.
Associated symptoms
We can say that a tooth consists of three main parts: crown, neck and root. Only the crown remains visible to the eye, while the neck should be covered by the gum, and the root should be located in the alveolus, a specially designated recess. When gum recession begins, the cervix is exposed, but that's not all. Along with this defect, other accompanying symptoms appear:
- acute pain upon contact with cold, hot, too sweet or acidic foods, because the teeth are exposed - and they are very sensitive in the root area, since there is almost no enamel here,
- darkening of the enamel, which only worsens the yellow color of the tooth neck,
- the visible part, that is, the crown, becomes visually longer,
- the gums seem to rise up (or fall down - depending on the jaw) above the tooth, move away from it, resulting in the formation of voluminous periodontal pockets,
- during hygiene procedures, the gums hurt and swell, become red,
- Large interdental gaps appear at the base - that is, in the area of the roots, which are much thinner than the crown parts.
The teeth near the roots become darker.
It is worth noting that the above-described signs cause a lot of trouble for young and middle-aged patients, while older people experience virtually no discomfort, which is a serious danger. As a result, older patients often seek help only when it is simply impossible to save the tooth.
The main symptoms that accompany gum recession
When gums recede due to natural processes associated with aging, the first signs of recession usually appear in the area of the front teeth of the lower jaw. If this phenomenon has a pathological basis, it is most often accompanied by the following accompanying symptoms:
- tooth pain in the root area,
- swelling of the mucous membrane,
- redness of the soft tissues near the diseased tooth,
- bleeding, which increases with mechanical stress.
In later stages, more serious symptoms arise: from bad breath to basal inflammation, pathological mobility, and even complete loss of teeth. It is better to start treatment at an early stage than to have to spend your entire life treating the chronic form.
Why roots may become exposed - common causes
This symptom occurs in a wide variety of clinical cases, which indicates a large number of potential causes of recession. The most common prerequisites can be divided into several independent categories - a little more about each below.
1. Insufficient or, on the contrary, excessive hygiene
Irregular brushing of teeth leads to the appearance of a dense yellow coating on the enamel, as well as hard deposits above and below the gums - it is no longer possible to remove them on your own. Gradually, tartar will grow, which will inevitably lead to the formation of periodontal pockets and a lowering of the mucosal level. To avoid this, it is enough to maintain hygiene and regularly visit a dental hygienist for a professional cleaning procedure.
The same result can be caused by too intense brushing and using an unsuitable brush; it is better to consult your dentist about the choice of hygiene products.
Malocclusions
Malocclusion often leads to irrational distribution of chewing load, which over time negatively affects the condition of periodontal tissues. In this case, the patient may initially be prone to inflammatory or dystrophic processes. With such a clinical picture, even a child will be diagnosed with the initial stage of recession, and to eliminate this defect will have to undergo a course of orthodontic treatment.
This category of prerequisites also includes a frenulum that is too short, which literally pulls back the gums and leads to gradual exposure of the roots. Sometimes recession is only a consequence of too thin mucosal tissues or roots close to it - and this will only be an anatomical feature of a particular patient.
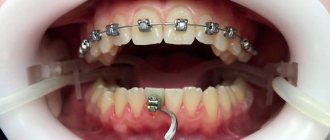
Recession can also be caused by orthodontic treatment, for example due to increased pressure on the teeth when wearing braces or as a result of poor hygiene.
Inflammatory diseases of periodontal tissues – gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease
Usually it all starts with superficial inflammation of the gums - gingivitis. If you do not pay due attention to this problem in time, the pathological process will very quickly spread to deeper layers, which will lead to the development of periodontitis. Periodontal disease in its true meaning involves dystrophic destruction of mucosal tissue, that is, without obvious signs of inflammation. But such a clinical picture is very rare, so this disease today is more often considered as a complication of advanced periodontitis or its long-term treatment.
It must be recognized that it is impossible to completely eliminate inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues once and for life. However, it is always possible to achieve a stable condition and further maintain it with regular care and systematic prof. examinations at the dentist. Only the treatment must be comprehensive, and you should not expect a quick result. The treatment regimen must be developed individually and necessarily taking into account the stage of the pathological process. A good course of treatment lasts about a year, during which the patient must systematically visit a specialist, undergo therapeutic and restorative procedures, and conscientiously follow all the instructions of his attending physician. Only such an integrated approach can guarantee a positive prognosis.
Iatrogenic causes - medical errors
Sometimes the roots of teeth become exposed due to poor quality dental treatment. The reason may be unsuccessful administration of anesthesia, violation of tooth preparation technique, or incorrectly fixed crown or bridge. In some cases, the initial stage of recession is diagnosed after orthodontic treatment with braces, when the doctor incorrectly calculated the force of pressure on the dentition or wanted to speed up the course.
Abundant subgingival calculus
Large accumulations of hardened deposits in the cervical and root areas can be the result of severely neglected hygiene or an aggressive course of inflammatory periodontal diseases. As mentioned above, this leads to the fact that the gums begin to move slightly away from the surface of the teeth and their roots, forming periodontal pockets. As a result of pathological processes, the nutrition of the mucous membrane sharply deteriorates, the tissues weaken and begin to decrease in volume - a recession occurs.
These are just some of the potential causes - the most common. Often, the roots of teeth become exposed due to sudden hormonal changes, for example, during pregnancy or menopause. The symptom can also be triggered by a malfunction of the thyroid gland, for example, with the development of diabetes mellitus. When a defect is observed in the area of one tooth, it may be the result of trauma.
For what reasons can tooth roots become exposed?
Many people are interested in the name of the disease in which the roots of the teeth are exposed. This phenomenon in dentistry is called “gum recession,” but it is more of a symptom than an independent disease. It is most often found in the area of the lower front teeth.
Most often, the cause of this phenomenon is periodontitis - inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues that are chronic in nature. Such pathological processes are usually the result of poor oral hygiene. Thus, plaque and food debris that accumulate on the surface of the teeth and in their spaces gradually affect the soft tissues and provoke the development of inflammation. This explains why the gums become weak and loose and begin to recede, exposing the necks of the teeth and leading to their loosening.
Periodontitis can cause pathology
Periodontitis is an infection of the soft and also bone tissues that support the tooth. If periodontitis starts, it can lead to tooth loss. In addition, it can have a negative impact on the body as a whole. For example, your blood sugar levels may increase.
Another cause is periodontal disease - unlike periodontitis, it is not an inflammatory disease, but a systemic one. But at the same time, the gums still shrink in size, only not because of the accumulation of a large amount of plaque, but because of the atrophy of this tissue and metabolic disorders.
“My husband was diagnosed with periodontal disease, but he is a heavy smoker, the doctor said that this could be the main reason. If you look closely, you will notice that the gums at the junction with the teeth are very thin and weak. It seems to me that if she has sunk like that, she should immediately see a periodontist, or at least just a dental therapist.”
Alya, Krasnodar, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
Other common factors leading to receding gum margins include the following:
- violation of teeth brushing technique, too much pressure with a brush, including on the gums,
- carious destruction in the area where the gums adhere to the neck of the tooth,
- malocclusions, short frenulum and other pathologies of the oral cavity,
- disorders of the thyroid gland, stomach and intestines1.
Cervical caries can cause the gums to separate from the tooth
. To correct the defect, you first need to find out the specific reason for its appearance. If it is not corrected, the gums will continue to recede and may ultimately lead to the loss of your teeth.
What diagnostics are required?
Treatment can begin only after a thorough diagnosis. During a visual examination, the doctor assesses the degree of exposure of the roots and records the depth and width of the recession. If the loss of soft tissue is significant, the patient must be sent for an x-ray examination, because often with severe periodontal inflammation, the pathological process spreads to the bone tissue and leads to its atrophy.
Types of dental root exposure
In addition, it is x-rays that make it possible to determine the class of recession:
- 1st class: the gums recede slightly, exposing the yellowish necks of the teeth,
- 2nd class: there is a displacement of the edge of the mucosa within 2-4 mm towards the root, the tissues in the area of the interdental septa turn pale,
- 3rd class: the mucous membrane completely exposes the necks of the teeth,
- 4th grade: there is a pronounced loss of mucous and bone tissue, x-rays show its atrophy. The neck along with the root protrudes from under the gum, and the spaces between the teeth become wider and more noticeable.
It is important to determine what exactly caused the recession, and symptomatic therapy can already be prescribed based on the diagnosis. For this reason, independent attempts to cope with the problem do not produce results, and sometimes even provoke complications.
Methods for treating recession
Treatment tactics are chosen based on the stage of the pathology and the characteristics of the clinical picture. When diagnosing class 1 and 2 recession, it is usually sufficient to remove plaque and hardened deposits, teach the patient the correct technique for brushing teeth and select appropriate hygiene products. Antiseptic rinses and vitamins are prescribed as conservative therapy. As part of a comprehensive prof. hygiene, soothing and regenerating hydrogels should be used, fixing a collagen resorbable membrane, which will strengthen and saturate the mucosal tissue with natural nutritional components.
In advanced cases, treatment with the Vector device, gum curettage, patch surgery and a course of plasma lifting may be required. If the neck of a tooth under an artificial crown is exposed, re-prosthetics is most often required. Read on to learn more about how to properly treat recession.
1. Conservative therapy in the early stages
As part of the conservative treatment of class 1 and 2 recession, a comprehensive prof. hygiene: cleaning from soft plaque and hardened deposits, including in the root area, remineralization and fluoridation of enamel, strengthening and saturation of gum tissue with the help of special hydrogels and collagen membranes to stimulate cell growth and renewal.
For better cleaning of shallow pockets, the Vector device is used - under the influence of ultrasonic waves, tartar is destroyed more easily and quickly, which makes the procedure more effective. If the pockets are deep enough, closed or open curettage is performed. The latter is a full-fledged operation, and this technique can hardly be classified as conservative therapy. However, curettage is an integral step in the complex treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease.
As part of the procedure, the doctor peels off a flap of the mucous membrane and gains unhindered access to the cervical and root areas, performs thorough cleaning of hardened deposits and antiseptic treatment of the tissues. Curettage is often performed in conjunction with cleaning with the Vector apparatus and flap surgery. Sometimes in such cases it is necessary to additionally splint loose teeth using fiberglass thread.
For self-rinsing, patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory and antibacterial solutions: Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Furacilin or, for example, Rotokan. If purulent discharge occurs, antibiotics are prescribed: Amoxicillin, Lincomycin, Ciprofloxacin, etc. - only as prescribed by a doctor. In addition, the specialist must give recommendations on following a certain diet, using a special paste and a brush with soft bristles.
Flap operations
When diagnosing class 3 and 4 recession with a noticeable lowering of the mucosal level, surgical intervention is required. Let's start with the fact that if the cause of the symptom is a shortened frenulum, appropriate plastic surgery is performed. In other cases, vestibuloplasty is performed to hide a visible defect: the doctor dissects the gum and base, after which the mucosal flap is slightly pulled to a new location.
As part of the operation, donor material can be used - a flap of tissue taken from the patient from other areas of the oral cavity, including from the palatal area. After such an intervention, a rather long rehabilitation period inevitably follows, during which the patient may experience some discomfort. The doctor will definitely prescribe appropriate medications, including antibiotics, rinses and applications with antiseptic and wound-healing effects.
Plasmolifting – resorbable membranes
The technique involves the targeted injection of the patient’s own blood plasma into problem areas of the mucous membrane - a substance rich in platelets, which effectively stimulate the regenerative functions of soft tissues. First, the patient needs to undergo a general clinical blood test to identify possible contraindications - 1-2 days before the procedure. At the next appointment, the specialist takes venous blood from the patient, places it in a test tube, and then in a centrifuge. The device literally separates the blood into separate fractions in 15-30 minutes. After this, the doctor injects the resulting autoplasma into the patient’s gums through an injection or using a resorbable, that is, self-resorbable APFR membrane. The course usually includes from 2 to 3-5 procedures.
Solution
If the neck or root of a tooth located next to the implant is exposed, gum plastic surgery may be required. Flap operations are common in dental surgery. To cover exposed areas, soft tissue flaps taken from the hard palate are used. This is a fairly simple operation, the contraindications for which may include:
- allergy to anesthetics,
- malignant tumors of the jaw,
- poor blood clotting,
- uncompensated diabetes mellitus.
What does traditional medicine offer?
Thoughtless use of traditional medicine will not only not help solve the problem, but will also speed up the pathological process or even lead to complications. Therefore, all kinds of rinsing with decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs must be agreed upon with the attending physician. Such prescriptions are used as maintenance therapy, but not as primary treatment. The tips described below are considered the most effective.
Gargling with decoctions
A decoction of St. John's wort is an excellent remedy that not only has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, but also promotes rapid healing of wound surfaces, strengthens mucosal tissue and increases its regenerative capabilities. To prepare a decoction, just add 2-3 tablespoons of dry herb to 300 ml of boiled water. The mixture should sit for some time, after which it can be filtered and used for rinsing.
Compresses with the addition of medicinal herbs
Excellent natural antiseptics are chamomile, calendula and sage. They not only destroy pathogenic microorganisms, but also effectively soothe inflamed tissues, relieve pain, and help improve trophism in the mucous membrane. To prepare a compress, you need to pour boiling water over the mixture of the above listed herbs and leave for a couple of hours until it cools completely. The resulting herbal mixture should be wrapped in a small piece of gauze and applied to the sore spot.
Gum massage
A light massage effectively stimulates blood circulation in soft tissues, improves their nutrition, strengthens and helps speed up recovery. It is enough to use light pressure to walk along the entire length of the alveolar ridge on the upper and lower jaws. In this case, you should not put too much pressure on the mucous membrane, so as not to accidentally injure it. You can increase the effectiveness of the massage using eucalyptus or mint oil.
If periodontitis or periodontal disease is to blame - only comprehensive treatment
The development of periodontitis is accompanied by the spread of inflammatory processes to periodontal tissue. Periodontal disease leads to a decrease in gum volume and rapid atrophy of the oral mucosa due to degenerative processes rather than inflammatory ones. In its “pure” form, this pathology is extremely rare - in 3-5% of cases. Today, it is more often considered as a complication of an advanced form of periodontitis or a consequence of its long-term treatment against the background of the aggressive course of the pathology itself. In both cases, an integrated approach to treatment is required, and it is better for the patient to immediately prepare for long-term therapy.
The treatment regimen for each patient should be worked out taking into account the individual characteristics of his clinical picture and the stage of development of the disease. Typically, such a course lasts about a year, during which some procedures are carried out once, others in a course of up to 10 visits. The complex may include the following therapeutic and preventive measures:
- diagnostics - computed tomography, tests, microflora culture, etc. diagnostic measures,
- comprehensive hygiene – removal of plaque and hard deposits, polishing and fluoridation of enamel, strengthening of mucosal tissues through the application of special hydrogels and a collagen membrane with extracts of medicinal herbs,
- splinting in case of mobility of some teeth,
- closed curettage (for pocket depths up to 4 mm) and open (for greater depths) in combination with treatment and polishing of the root surface,
- application of periodontal dressings with a pronounced healing effect,
- plasmolifting,
- injection vitamin therapy,
- laser therapy to stimulate the restoration of soft tissue cells,
- the use of medications based on hyaluronic acid to nourish the mucous membrane and stimulate its natural restoration (Revident and Revident+),
- fixation of collagen membranes (Creos from Nobel) and APRF membranes based on the patient’s own blood (an alternative to injection plasma lifting),
- the use of drugs to stimulate the growth of soft tissue (Straumann Emdogain),
- use of bone volume replenishment products (BoneCeramic from Straumann, Bio-Oss)
- training in the correct cleaning technique, selection of individual hygiene products, regular visits to the periodontist for preventive examinations.
Periodontitis is a chronic pathology, which is virtually impossible to cure completely. However, within a year of comprehensive treatment and restoration of gums, acute symptoms can be reliably relieved and stable remission can be achieved. However, you will have to continue to maintain the achieved effect, and for this you need to visit your specialist once every six months and carry out maintenance therapy according to his indications.
Prices for Prevention
| Name of service | Price |
| Professional oral hygiene Along with daily home hygiene, professional teeth cleaning is a mandatory procedure for the prevention of dental diseases. Find out what procedures professional oral hygiene includes | 6800 ₽ |
| Ultrasound removal of tartar (one tooth) Hard plaque is removed with an ultrasonic scaler. See how teeth are cleaned with ultrasound | 240 ₽ |
| Removal of soft dental plaque using the Air Flow device Soft pigmented dental plaque is removed by air-abrasive cleaning. See how plaque is removed with the AirFlow device | 3100 ₽ |
| Coating one tooth with fluoride varnish Bifluorid, Multifluorid After applying the varnish, a protective film is formed on the teeth, and the enamel is saturated with useful minerals. The procedure is effective for the prevention of caries and the treatment of dental hypersensitivity. | 280 ₽ |
| Coating one arch with fluoride varnish Bifluorid, Multifluorid | 2500 ₽ |
| Deep fluoridation (remotherapy) This procedure restores the natural structure of the enamel. Once saturated with essential minerals, the enamel regains its strength. Find out how remotherapy reduces tooth sensitivity and protects against caries | 3500 ₽ |
| Hygiene lesson with manual skills training During the lesson, the doctor will teach you how to properly care for your mouth to keep your teeth and gums healthy. See what poor oral hygiene can lead to and how to properly care for your teeth | 550 ₽ |
| Preventive examination once every 6 months If you regularly attend preventive examinations, the dentist-therapist will promptly recognize the first signs of caries and treat it at the initial stage, preventing the development of pulpitis and periodontitis. Sign up for a preventive examination | free for regular customers |
Share the link:
- Click here to share content on Facebook. (Opens in a new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
orthodontics, orthopedics, periodontology, prevention, articles, therapy, surgery topics: gingival margin, home dental hygiene, closed curettage, exposed roots, exposed cervixes, open curettage, professional teeth cleaning, remotherapy, gum recession, fluoridation
How to strengthen gums - prevention
To prevent root exposure, it is important to ensure proper prevention of soft tissue recession. To do this, you need to carefully monitor your oral health, brush your teeth twice a day, and do it correctly and with the help of an individually selected brush and paste. Twice a year you need to visit the dentist for prophylaxis and prof. hygiene, treat pathological processes in a timely manner, correct bite defects or the consequences of poor-quality treatment.
Proper comprehensive hygiene involves not only removing plaque and deposits, but also fluoridation and necessarily strengthening the gums. After cleaning, the mucous membrane is treated with a special disinfecting solution, as well as a soothing hydrogel with regenerating properties. The final chord is a special collagen membrane - impregnated with extracts of natural medicinal plants. It nourishes and saturates the soft tissues, and after some time it dissolves on its own, without causing any discomfort to the patient.
If you seek help in time when you detect the first signs of recession, the prognosis for treatment will be very favorable. Elimination of the primary cause of the symptom leads to recovery in 95% of cases. Unfortunately, in the remaining 5%, relapses can occur even after surgery, which indicates the need to change treatment tactics1. In any case, exposure of tooth roots is a serious problem, and under no circumstances should it be ignored.
Preventive actions
It is unlikely that anything can guarantee absolute protection against the gradual exposure of tooth roots, however, experts in the field of dentistry and periodontology, in particular, have identified a number of preventive recommendations, the observance of which will minimize any risks of recession. Here are some basic rules:
- systematically visit the dentist for preventive examinations,
- try to get rid of bad habits, eat less sweets and other foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates - the main enemy of healthy teeth,
- enrich the diet with fresh fruits and vegetables - when biting and chewing hard fruits, natural cleaning of the enamel occurs,
- brush your teeth at least twice a day, rinse your mouth after each meal, use dental floss,
- If any suspicious processes appear in the oral cavity, immediately consult a doctor.
Preventive examinations at the dentist will help avoid problems
. Important! If your gums are your weak point, be sure to consult your dentist before purchasing a toothbrush and toothpaste. With increased sensitivity of soft tissues, too hard bristles can cause pain, microtrauma and other problems.
Gum recession is not only an aesthetic problem. In fact, this phenomenon directly signals the presence of serious pathological processes in the soft tissues of the oral cavity. Such changes should alert you and be a reason to visit your doctor.
- Barer, G.M. Periodontal diseases. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment, 2003.