Treatment of baby teeth in children, bad breath When you enter the pediatric dentistry department, you see a sad picture. Mothers and grandmothers try to console babies crying from toothache. This can be avoided by systematically showing children to dentists.
You need to learn correctly and take care of your teeth from early childhood. We, adults, often turn to specialists when toothache can no longer be tolerated. And we are surprised that the treatment process becomes endless.
Bad breath in a child
Bad breath from a baby can occur for a variety of reasons, from stress to diseases of the digestive system. Most often, halitosis in children occurs due to untimely brushing of teeth, excessive dryness in the mouth and nose; it goes away after cleansing and moisturizing. If your child constantly has bad breath, you should immediately consult a doctor. Osostomia (as doctors call halitosis) may be the first sign of a serious illness; parents should not take this symptom lightly. It is advisable to consult a dentist to check the condition of the baby’s teeth and gums. If the unpleasant symptom does not disappear, consult a pediatrician, do a general blood test, and depending on its results, consult a specialist.
Bad breath in a child can indicate many diseases.
Your baby is teething, do you need help?
After the birth of your baby, your life gradually stabilizes and you get used to your new role as a mother. And suddenly, a few months after returning from the maternity hospital, the baby begins to cry often, his temperature rises and his appetite worsens, his gums become red and inflamed. But there is no reason to worry! What happens to a baby is a natural condition called teething. How to help a child in such a difficult time for him?
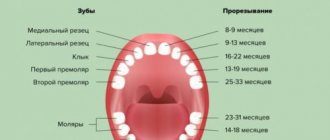
On average, teething continues from 6 months to 3 years, although, according to statistics, most children do not have their first tooth until 8 months. Very early (before 3 months) or late (after a year) eruption of the first teeth indicates the presence of serious diseases. Then you need to see a doctor. It is also necessary to show him the child if it is discovered: a change in the sequence of teething, teething outside the dentition (that is, sideways from the gums, etc.), incorrect formation of teeth, birth already with teeth.
The first sign of the onset of teething is redness and swelling of the gums, which, after 7-10 days, again acquire a normal appearance, but with only one change. A thin white stripe appears at the top of the gum - an emerging tooth. Other frequent, but not constant, symptoms of teething are: an increase in body temperature to approximately 37.5 -38.0 degrees, loose stools or a decrease in the baby’s appetite. The most accurate and constant sign of this process is considered to be increased salivation and itching of the gums. The child’s behavior at this time is reminiscent of the reactions of a pet hamster or other rodent - he puts everything into his mouth and chews everything: toys, wooden bars of the crib, pacifiers, even his own fingers. When teething, a sour (metallic) odor may occur from the baby's mouth, as antibacterial substances are produced in the saliva at this time. They change the smell of saliva.
Pediatricians agree that teething in children is, as a rule, a normal physiological process that does not require complex medical procedures. At the same time, it has been proven that during teething, even if it occurs without complications, the child feels physiological discomfort, which puts a strong strain on the nervous system. Moreover, unlike older children, in children during the first years of life, fatigue and depletion of brain functions occur much faster. Inflammatory processes of the gums cause pain and fever, cause diarrhea, prevent the child from sleeping and lead to the appearance of other disorders that we have listed.
There are many drugs available in pharmacies that are specially designed to relieve the symptoms of teething in children, which ultimately reduce the load on the child’s nervous system and prevent its exhaustion. Pediatricians have developed a simple test for parents, including only 5 questions, by answering which they can understand in what cases drug assistance is required during teething. If positive answers are received to at least 2 questions out of 5, then it is necessary to use medications to alleviate the baby’s condition when side effects of teething occur.
Question 1: Does the child have a fever?
Question 2: Has one of the main symptoms of teething appeared - itching of the gums, due to which the child pulls various objects into his mouth and chews on them?
Question 3: Are there any signs of gum inflammation (swelling, redness, metallic breath)?
Question 4: Has the child become nervous, capricious, or sleeping poorly?
Question 5: Do you have diarrhea?
All drugs approved by regulatory authorities for use in such situations are highly safe, tested in rigorous clinical trials, and therefore can be purchased without a prescription. However, they have either only an analgesic or anti-inflammatory effect. Therefore, doctors, as a rule, recommend Dentokind, specially created for babies, which, in addition to analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, calms the nervous system and stabilizes sleep.
Teethers are also a very good remedy - plastic rings or special toys that the baby can scratch his gums on and reduce itching, but which he cannot swallow. To remove excess saliva, regularly wipe your baby's face with tissues or a towel. This will prevent skin irritation. When your baby is sleeping, place a napkin under his head to absorb saliva so you don't have to change soiled bedding every day. An irreplaceable way to alleviate the baby’s condition is your attention to him, affection, care, constant distractions from pain and discomfort in the gum area.
Specific pungent odor
Parents should be alarmed by the specific smell from the baby’s mouth, which does not go away after hygiene procedures. Limit your baby's consumption of sweets and heavy protein foods, and ensure he drinks plenty of fluids. Usually, after these events, children's halitosis goes away.
Below we will tell you which smells should cause an instant reaction from parents.
Acetone (acetic, solvent)
The smell of acetone or a chemical solvent emanating from a baby, especially against a background of elevated temperature, should cause maximum concern for parents. It appears in acetonemic syndrome, a dangerous condition that is quite common in children of all ages. If you suspect its occurrence, you must immediately call an ambulance, before the doctors arrive, and give the baby boiled water often and in small quantities (a teaspoon).
A slight acetone smell can be a sign of kidney disease, malfunction of the pancreas, helminthiasis (worms), dysbacteriosis, and diabetes. In any case, it is advisable to consult a doctor immediately.
Putrefactive
Appears with insufficient oral hygiene, the occurrence of ENT diseases (sore throat, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, in parallel, the child has a white tongue, a stuffy nose, a cough), stomatitis, caries, low acidity of the stomach (the baby often has a stomach ache), the presence of diseases of the esophagus . You should consult a dentist, ENT specialist, gastroenterologist, systematically brush your teeth with a children's toothbrush and toothpaste, and ensure drinking regime.
Purulent
A pungent purulent odor accompanies chronic inflammation and proliferation of lymphoid tissue in the baby’s nasopharynx. The tonsils become covered with purulent plaque, plugs form, emitting an unpleasant odor. The child has a high fever, a sore throat, a runny nose, and a coated tongue. Contact your pediatrician; antibiotic treatment may be necessary. After recovery, your breath will become fresh again.
Another reason for bad breath against the background of copious discharge of dense yellowish snot can be the presence of some object in the baby’s nostril. Contact your ENT specialist to examine your baby's nose.
Sourish
If your baby has a sour breath, this may indicate increased acidity and an inflammatory process in the stomach. It is necessary to contact a gastroenterologist and check the baby for the presence of gastritis. The second cause of bad breath is reflux, or the entry of gastric juice into the baby’s esophagus. In this case, the patient suffers from heartburn and pain in the hypochondrium.
Sweetish
Does the baby have a cloying sweet aroma from the mouth? There is reason to suspect liver problems. It is important to promptly visit a gastroenterologist - the symptom occurs with hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver.
Chemical
If your toddler smells of chemicals, it is advisable to check the condition of the digestive organs, especially the gallbladder; this symptom is characteristic of biliary dyskinesia.
Chlorine
The specific smell of chlorine mixed with metallic notes appears with increased bleeding gums and periodontal disease. Contact your dentist and check the condition of your baby's teeth and gums.
Yoda
The appearance of the smell of iodine is a reason to urgently contact an endocrinologist, as it may indicate an excess of iodine that accumulates in the baby’s body. This condition can occur after a long stay at sea, after taking iodine preparations, or in the presence of thyroid pathology. In infants, an iodine tint appears when infected with Klebsiella, a bacterium that enters the child's body with unwashed fruit and affects the stomach and intestines.
Bile
If a newborn's breath smells like bile, this may indicate poor bile flow. Consult a doctor, do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, and take general tests.
Gland
The presence of a metallic taste and iron smell from the baby's mouth may indicate the occurrence of iron deficiency anemia. You should take a blood test to determine your hemoglobin level, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, take vitamin complexes with a high iron content.
The second reason is the presence of gastritis, high acidity, dysbiosis, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Urine
An ammonia smell indicates kidney pathologies, as well as diabetes. The reason for its appearance is a decrease in insulin levels and impaired carbohydrate metabolism.
Kala
It is extremely rare. It is mainly associated with poor heredity, appears with metabolic disorders, and sometimes accompanies acute intestinal dysbiosis. Diagnosed by an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist.
Rotten eggs
Belching, the smell of rotten eggs, and a white coating on the tongue are symptoms of gastritis, ulcers, liver disease, and impaired bile flow. If you find halitosis in a newborn or older child, you should contact a gastroenterologist.
Yeast
If a baby smells of yeast, this is a reason to suspect candidiasis. Often a sick stomach is also expressed by a yeasty aroma. An experienced general practitioner will be able to recognize the true cause, and he will also refer you for examination if gastrointestinal diseases are suspected.
Is it possible to get rid of the smell of caries?
Unfortunately, it will not be possible to completely eliminate the smell of current caries until the disease is completely cured, because cariogenic bacteria will continue to destroy the tooth. If it is not in a too advanced stage, it is possible to reduce the intensity of the smell during caries. You must adhere to certain rules. Here's what experts advise in this case.
Regular cleaning
It is advisable to brush your teeth after every meal. However, this should not be done immediately, but approximately 20-30 minutes after eating. The minimum number of cleanings is two per day. Remember that brush movements should be vertical, from top to bottom and vice versa. It is better to select the bristles of the brush that are not too hard, and carry out the process for at least two minutes. You can use a toothpaste with sodium bicarbonate, which actively eliminates the buildup of caries bacteria along the gum line.
Using rinse aids
After brushing your teeth, use an additional mouthwash. Many of them contain essential oils of menthol, thymol, eucalyptus, and methyl salicylate. They effectively prevent the formation of microbial plaque on the surface of teeth and destroy bacteria that provoke their destruction. The mouthwash removes odor for a while and is also a good preventative against gum and dental diseases.
Flossing
This method is especially relevant when the structure of the teeth is such that food often gets stuck between them. It is especially convenient to use dental floss (floss) and then mouthwash in the workplace - brushing your teeth in the office bathroom is not always inconvenient. It is the leftover food that bacteria feed on, then causing the process of rotting and the corresponding smell.
Tongue cleaning
This is important to do in case of dental diseases, when plaque forms on the tongue, which also spreads an odor, including caries. Daily care of your tongue, along with your teeth, cleans it of bacteria and also helps:
- get rid of bad breath for a while;
- remove plaque in which bacteria multiply;
- avoid the active development of caries, preventing microorganisms from destroying teeth.
In addition, a clean tongue perceives the taste of food and drinks much better. For this procedure, special accessories and products are sold: gel, scraper, attachment for a brush or for an irrigator. With their help, you can effectively and gently cleanse your tongue of plaque to reduce the risk of bad breath.
Causes of halitosis in children
The appearance of halitosis in children of any age can be caused by a variety of reasons, ranging from insufficient oral hygiene to the presence of a foreign body in the nose. It is important to correctly diagnose, determine the true cause of osostomy and, if possible, eliminate it.
Lack of moisture in the body
Causes increased viscosity of saliva, poor digestion, which can cause bad breath. An infant newborn receives the main liquid from mother's milk; in hot weather it is necessary to give boiled water to drink. A 4-5 year old child should drink approximately 1.5 liters of liquid per day, not limited to juices and teas. It is important to give your toddler drinking water, which helps improve digestion.
Poor oral hygiene
With the appearance of the first tooth, the baby should be accustomed to oral hygiene procedures. Children under two or three years old should have their teeth brushed by one of their parents. From the age of three, children should be taught to brush their teeth correctly on their own. Improper and insufficient cleaning of plaque contributes to the appearance of halitosis, which resolves after thorough brushing of the teeth.
Poor nutrition
If a child systematically overeats, eats fatty fried foods generously seasoned with onions and garlic, a heavy odor from the mouth will haunt him constantly. It is important to adjust the baby’s nutritional system according to his age needs, observing the drinking regime.
Stressful situation
Strong emotional shock, stress, and vivid emotions are a real test for a newborn. They cause dry mouth, which contributes to halitosis. In a stressful situation, you need to give the child a drink of water or sour juice, suck a slice of tangerine or lemon; such simple steps promote active salivation and make the child’s breathing clean and easy.
Unpleasant smell in the morning
Babies may experience bad breath after sleep. It is caused by the fact that saliva is not released at night during sleep, bacteria multiply, causing halitosis. It is enough to brush your teeth with a brush and toothpaste - and the unpleasant phenomenon disappears on its own.
Chronic nasal congestion
If your baby's mouth smells like snot, you need to pay attention to the condition of the mucous membrane of the nose. With chronic rhinitis, nasal breathing is difficult, and dry crusts form in the nasal passages. It is necessary to moisturize the surface of the mucous membrane, monitor humidity, ventilate the room well and carry out wet cleaning.
Presence of a foreign body in the nasal passages
A strong putrid odor accompanied by thick yellow discharge from the nasal passages should alert you. These symptoms are characteristic of a foreign object entering the nasal passages - beads, buttons, a piece of fruit. You should consult a doctor or emergency room as soon as possible to remove the foreign body. Otherwise, serious complications are possible, including suffocation.
Diseases of teeth and gums
Caries, stomatitis, gingivitis and other dental diseases can cause bad breath. A careful examination will reveal a carious lesion in the baby’s mouth. Even if there is no visible damage to the tooth enamel, it is necessary to consult a dentist to rule out the presence of oral diseases.
Upper respiratory tract diseases
Sore throat, tonsillitis, adenoiditis, bronchitis provoke the occurrence of halitosis in children. The pus that accumulates on the surface of the tonsils, in the lacunae, on the back wall of the throat has an unpleasant smell. The cause of the disease should be treated, rinse with an antiseptic solution, and in difficult cases, antibiotic therapy is necessary.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
When a little person’s mouth smells like solvent, sour milk, vinegar, and there is an upset stomach and diarrhea, this indicates problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Consult a gastroenterologist; sometimes it is enough to adjust the baby’s diet, and the problem disappears without a trace. In more complex cases, special treatment is indicated.
Teething odor
When a baby is teething, temporary halitosis may occur, caused by inflammation of the gums and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. The baby's gums are red, painful and swollen. The dentist will recommend special medications that reduce the baby’s discomfort during teething.
Oral hygiene
The importance of regular dental care cannot be overstated. Daily and regular oral hygiene should be carried out from the moment the first tooth emerges , this is the only way to prevent dental damage from caries.
- From six months to one year, teeth are brushed every day 1-2 times, from one year onwards at least twice a day. It is also advisable to rinse your mouth after each meal or simply give them a drink of water. You can do without a toothbrush for up to a year by carefully cleaning your mouth with a soft cloth or gauze moistened with water.
- Since the year You need to choose a toothbrush that is suitable for this age. The use of special gels or pastes is not required until the third birthday.
Important! Up to three years of age, parents should brush their child’s teeth; then the child himself can be involved in the process under parental supervision.
- At three years old, you can buy children's toothpaste, preferably high quality, one that can be swallowed. At first, it will be difficult for your baby to spit it out entirely.
Rules for using toothbrushes for babies
- Your toothbrush should be changed every 2-3 months.
- The brush should have soft bristles and a head without traumatic corners to protect the delicate mucous membrane.
- The use of fluoride toothpaste and whitening pastes is prohibited; they are contraindicated for the delicate enamel of baby teeth.
- Mouthwash should only be used after consultation with a specialist.
Treatment of unpleasant odor
In most cases, osostomy does not require special treatment. It is enough to systematically thoroughly brush your teeth and gums, review your diet, limit your consumption of sweets, give him enough liquid per day, and the unpleasant symptom will disappear on its own. If after a few days it does not disappear, you need to consult a specialist, undergo an examination and determine the cause of halitosis.
Parents should be especially concerned about the smell of acetone emanating from the baby - in this case, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance or take the baby to the hospital to prevent the occurrence of acetone syndrome.
Preventive measures
To promptly prevent the appearance of halitosis in your baby, you must follow a few simple rules:
- Brush your baby's teeth thoroughly twice a day, starting when the first tooth emerges. It is necessary to teach your child how to use a brush and toothpaste correctly to remove plaque from the surface of the teeth.
- Adhere to the age-specific nutrition system, introduce vegetables, fruits, and foods rich in phosphorus and calcium into your child’s diet.
- Eliminate sugar, chocolate, and other sweets from your diet and replace them with honey.
- Give your child plenty of fluids, especially drinking water.
- Visit your dentist regularly to prevent the development of caries.