From this article you will learn:
- why do gums bleed during pregnancy,
- what is pregnancy gingivitis,
- how to carry out treatment correctly.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
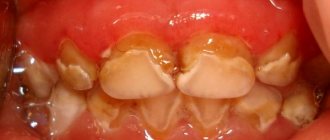
Inflammation of the gums during pregnancy is a process characterized by bleeding gums, as well as hypertrophy of the gingival papillae, which occurs due to an increase in the concentration of estrogen and progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman. This condition is usually called the term “gingivitis in pregnant women”, and according to statistics, it is observed in 75% of women - for a period of 2 to 8 months. Most often, gingivitis occurs in the area of the front teeth, and it affects only the gingival margin at the necks of the teeth (including the gingival papillae).
Clinical studies show that more than half of all women with gingivitis during pregnancy already had a mild form of chronic catarrhal gingivitis at the beginning of pregnancy, which is practically asymptomatic. Thus, an increase in the content of estrogen and progesterone in most cases led to an exacerbation of pre-existing gingivitis, and was not the root cause of its development. We will tell you more about the causes of inflammation below, because... there are other factors to consider.
Chronic catarrhal gingivitis –
But pregnant women can experience not only gingivitis, but also a more serious gum disease, in which inflammation spreads from the superficial part of the gums to deeper tissues. This disease is called periodontitis, and with it there is destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth, destruction of the dental-gingival attachment, suppuration from periodontal pockets, and over time, tooth mobility also occurs. And this disease already indirectly affects the fetus, which requires mandatory treatment.
Why does gingivitis occur during pregnancy?
Tens of millions of microorganisms live in the oral cavity. Slight swelling of the gums leads to an increase in periodontal pockets, which become an excellent reservoir for the life and reproduction of bacterial microflora. In addition, microorganisms do not lack nutrition, since pregnant women like to pamper themselves with sweets, and carbohydrate foods are the best substrate for the development of bacteria.
Swelling of the gums, leading to an increase in periodontal pockets, excessive salivation, an acidic environment in the mouth, an increased feeling of hunger - these features that accompany pregnancy are the main factors contributing to the rapid growth of oral microflora. And this, in turn, provokes inflammation of the gum tissue - gingivitis.
Diet of the expectant mother
For the health of the unborn child and good health, women need to monitor their diet. It is recommended to eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, fresh herbs and vitamins.
But an excess of vitamins can be dangerous, so it is advisable to consult with your doctor and, if necessary, prescribe a suitable diet, taking into account individual characteristics.
A low-carbohydrate diet has a beneficial effect on the condition of the body as a whole. Spicy and fatty foods that can irritate the mucous membranes in the mouth should be avoided.
It is very important to compensate for calcium deficiency. Sauerkraut, blackberries, onions, kiwi, and broccoli are especially useful for ginginitis.
Whims or symptoms of gingivitis during pregnancy?
The first symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women begin to appear between 8 and 12 weeks. Expectant mothers, as a rule, suffer from two forms - catarrhal and hypertrophic; ulcerative gingivitis develops less often.
Catarrhal gingivitis
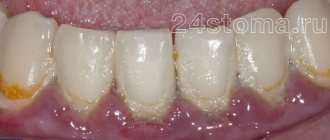
This form of the disease is manifested by the formation of a fairly large amount of soft yellow plaque on the surface of the teeth, swelling of the gums, their soreness and significant bleeding when pressed with a sharp object. Catarrhal gingivitis is characterized by the spread of inflammation over the entire surface of the gums, sometimes the process affects the tissues of both the upper and lower jaws.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
The first symptoms of hypertrophic gingivitis usually appear no earlier than the twentieth week of pregnancy. Inflammation affects the lower jaw, gums in the area of incisors, canines and small molars. The hypertrophic form of gingivitis is characterized by an increase in the volume of gum tissue, an inflammatory process in it and bleeding. Gum pockets also appear - grooves formed between the tooth and gum due to the growth of gum tissue.
Ulcerative gingivitis
The most severe form of gingivitis occurs in pregnant women. It occurs against the background of serious health problems accompanying pregnancy, in the last trimester, or under the influence of stressful situations. The main signs of ulcerative gingivitis are severe itching, burning, bleeding of the gums, swelling and ulceration.
Causes of gum problems from the beginning of pregnancy
In many patients, symptoms of inflammation and bleeding gums begin already in the second month of pregnancy; in the absence of proper treatment, they can continue until the end of pregnancy, causing undesirable effects on the course of such an important period in the life of every expectant mother. Experts associate the causes of the occurrence with a restructuring of the hormonal system, which provokes sluggish inflammatory processes that took place even before pregnancy.
| Prices and methods of treating bleeding gums during pregnancy | |
| Professional cleaning | from 3000 R |
| Drug therapy | from 1000 R |
An increased concentration of female hormones and toxicosis cause disturbances in the blood supply to the gums, as a result, the development of pathological bleeding. In parallel, a noticeable increase in the papillary endings and growth of the marginal part of the gum may develop. Inflammation itself, which results in bleeding, is caused by the development of microbial flora, the accumulation of soft and hard deposits in areas adjacent to the gums.
Safe treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women
The dentist is included in the list of mandatory specialists to visit during pregnancy. He will be able to detect the disease in time and prescribe safe treatment for gingivitis. The peculiarities of therapy for pregnant women are that measures aimed at eliminating gingivitis include only the removal of tartar and plaque, anti-inflammatory therapy and the prevention of re-development of inflammation, that is, therapeutic measures only imply relief of symptoms.
The first stage of treatment that the dentist will perform will be professional teeth cleaning. Dental plaque will be removed mechanically using Air Flow or ultrasound. The idea that ultrasound, which is used in this procedure, harms the fetus is absolutely groundless: throughout pregnancy, a woman undergoes scheduled ultrasound examinations at least three times. As an anti-inflammatory therapy, the doctor will select drugs that can act as gently as possible on the vulnerable body of a pregnant woman. Their use comes down to a local effect on the gum tissue: rinsing, baths, irrigation.
Treatment
If your gums become inflamed, bleeding or swollen, it is important to consult a doctor immediately and follow the prescribed hygiene measures. The doctor will prescribe treatment, perform the necessary manipulations and prescribe procedures that can be performed at home.
Depending on the intensity of the disease, various medical interventions are required - from simple cleaning to tissue removal.
In the early stages of pregnancy, it is highly not recommended to carry out treatment with potent drugs and carry out dental cleaning procedures with laser or ultrasound.
During the first trimester, you can visit a doctor who will determine the need for immediate intervention or prescribe a treatment plan for a later period.
The safest time for treatment is considered to be the second trimester. The last trimester is also suitable for carrying out procedures, if the patient is feeling well, there is no dizziness and problems with low blood pressure.
Therapy in a clinic setting
Any modern clinic has good equipment and professional specialists who are ready to treat both simple and complex cases.
The sooner you contact a dentist, the faster you can receive qualified services and save yourself from unpleasant symptoms of the disease. The help of a periodontist in the fight against gingivitis can be divided into several stages:
- Initial examination and determination of the shape, location and degree of gum damage.
- Professional removal of plaque and stone.
First of all, a procedure is carried out to remove deposits and clean plaque. To do this, they first disinfect and anesthetize the diseased areas, and then clean out the deposits manually or using modern equipment. - Disinfection of the oral cavity with solutions, for example, Chlorhexidine.
- Anti-inflammatory procedures. To restore proper vascular-tissue permeability, lotions are applied to the gums. They last from several minutes to several hours. Ointments that are harmless to the child are used as effective remedies.
- Electrophoresis and vacuum massage procedures. To reduce swelling and normalize the functioning of blood vessels, one to five procedures are performed.
At the end of the treatment, the periodontist prescribes an individual system of care and hygiene, which includes rinsing, cleansing and diet.
Home and folk recipes
To provide first aid and prevent gingivitis, there are a number of measures that can be taken at home to mitigate the signs of the disease and eliminate severe pain.
Among these methods, the most effective is rinsing the mouth. It is recommended to carry it out with special solutions:
- decoctions of herbs (lingonberry, chamomile, oak bark);
- means "Rotokan" or "Maraslavil";
- soda solution;
- hydrogen peroxide (diluted with water);
- kefir (infused for at least 3 days).
Gels of the “Metragil-Denta”, “Lakalut”, “Cholisal” series and other preparations are also used for oral care.
In order to stop bleeding and remove inflammation, you can use folk recipes. Fir oil and a paste of honey and sea salt should be applied to problem areas.
Linden infusions, Kalanchoe juice or brewed oak bark also alleviate pain and inflammation. It is important to apply the products using gauze or straining the decoctions so that small leaves do not fall between the gums.
Recommendations to help avoid problems
In order not to become one of the pregnant women suffering from gingivitis (and, according to statistics, there are more than 60%), you must adhere to simple rules.
- Carry out the necessary hygiene procedures regularly: brush your teeth using a toothbrush with soft bristles, and do this as thoroughly as possible, use floss and antiseptic rinses.
- Avoid excessive amounts of sweets and consume sweets, chocolate and cakes in moderation. It is strongly recommended to refrain from chewing toffee and caramel, since the remains of viscous delicacies can accumulate in the periodontal space of swollen gums, provoking particularly active proliferation of microorganisms.
- Eat more vegetables and fruits, paying special attention to foods containing vitamin C.
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women cannot be postponed until later. Occurring due to changes in hormonal status and the growth of microbial microflora, it provokes even more active proliferation of bacteria, which in the most severe cases can cause intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Fact #4: If gingivitis is not treated, periodontitis will develop.
If your gums bleed during pregnancy, you should be especially careful about this phenomenon and consult a doctor. After all, one of the complications of untreated gingivitis is periodontitis. This is a disease that is characterized not only by superficial inflammation of the gums, but also by the fact that it affects the deeper layers of hard tissue, reaching the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth. It also gradually destroys bone tissue, causing the gradual loss of all teeth.
In rare cases, women expecting a baby may develop periodontal disease. This is a systemic disease, but, unlike periodontitis and gingivitis, it does not cause bleeding gums.
Read the article on the topic: 5 differences between gingivitis and periodontitis and periodontal disease.
If left untreated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis and lead to tooth loss
Prevention of oral diseases
To prevent inflammation of the gums around the tooth, various preventive measures should be taken.
The following measures will help prevent bleeding:
- Performing a gum massage using a soft brush;
- Taking vitamins for expectant mothers;
- Reducing intake of sugary foods;
- Timely treatment of caries;
- Treatment of mouth diseases;
- Visiting the dentist once every trimester;
- Drinking high-quality clean water;
- Diet;
- Regular dental care.
If you follow the rules presented, you will not have to look for information on forums on how to deal with the problem. In addition, you will prevent the occurrence of diseases both in yourself and in your baby.
At what stage of pregnancy is it recommended to treat teeth?
There are no time or deadline restrictions. If your teeth are sick, you need to treat them immediately. But if the situation is not critical, it is better to wait until 14 weeks (i.e. after the first trimester) and during this period go to the doctor.
It is forbidden to use anesthesia in the first months of pregnancy
, since at this time vital organs are formed.
In the period from 14-15 weeks, the baby’s life is already protected by the placenta. During this period, it is allowed to take anesthetics containing minimal amounts of adrenaline.
X-rays are allowed (in particularly difficult cases).
In the third trimester, the fetus already puts significant pressure on the aorta, which should be taken into account when choosing a position in the dentist's chair. Positioning on the left side will help prevent fainting; a drop in pressure will help.
Video about dental treatment in general and implantation in particular
Features of gum treatment after childbirth
If a woman has a wisdom tooth coming out after childbirth or her gums are swollen for other reasons, she needs comprehensive treatment. First, you should visit your dentist. He will prescribe anti-inflammatory and antiseptic medications.
If there is no improvement, problems with the immune system can most likely be diagnosed. Then the specialist prescribes general strengthening medications that will not harm the baby.
After giving birth, you should definitely go on a special diet.
It is recommended to eat foods rich in vitamins:
- in the morning you can drink carrot juice;
- Corn, peas, beans, and bread should be included in the diet (they contain vitamin E);
- It is very important to eat cabbage, spinach, tomatoes and citrus fruits. They are high in vitamin C;
- Milk, rye flour and apples contain vitamin B.
For severe bleeding in the mouth, you can use special pastes and decoctions. They should contain sage, oak bark or chamomile.