Improper and irregular oral care means there is a high probability of getting some kind of infection, which can lead to gum disease. Gum papilloma is a form of oral disease that requires immediate treatment. It may also occur on the lips, tongue, larynx, and throat. Papillomas can be quite painful, and their development threatens inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Causes
The appearance of growths on different parts of the body is due to the presence of a virus in the body. HPV is considered an extremely common infection with three main routes of transmission:
- sexual;
- contact and household;
- generic.
Localization of papillomas on the oral mucosa is a common phenomenon diagnosed in adults and children. This type of growth occurs mainly due to the actions of 6 and 11 strains of papillomavirus .
Transmission of these types occurs through direct contact with an infected person and usually occurs in household settings.
Among the reasons due to which the virus can appear on the oral mucosa:
- using other people's hygiene items (towels, toothbrushes, etc.);
- eating food from poorly processed dishes of the patient;
- kissing an infected person;
- unprotected oral sexual contact.
In this case, a factor predisposing to infection is damage to the oral mucosa. Even a small amount of virus particles trapped in microcracks is enough to secure HPV in the body.
Which people are susceptible to papillomas?
Based on the information we provided above, we can distinguish several “risk groups”, people in which are susceptible to the development of growths and neoplasms on the tongue and body.
The appearance of a process on the tongue is possible:
- In a situation where a person has reduced immunity as a result of stress, the presence of parasites in the body or ongoing inflammatory processes.
- If a patient with a growth in the mouth suffers from autoimmune diseases.
- In a person with HIV infection.
- In people who are promiscuous.
- In the event that a person has bad habits. Smoking and drinking alcohol especially contribute to the appearance of neoplasms in the form of growths on the tongue.
- If there was any trauma to the tongue or damage to the mucous membrane occurs systematically.
Types and forms
Doctors divide emerging papillomas into two forms: single growths and multiple ones (papillomatosis). The number of tumors may gradually increase as the disease progresses. Their size also becomes larger over time.
Based on the type of origin, growths are divided into 3 groups:
- Traumatic. Appear after injury to the oral mucosa due to mechanical or chemical influences. The peculiarity of this type of growth is that their growth usually stops after the cause is eliminated.
- True. Formed due to disruption of cell functioning. Their growth and division mechanisms stop working as usual. Typically, such growths are localized in distant areas of the cheeks, which can make self-diagnosis of the disease difficult.
- Viral. This type occurs directly due to the action of the papillomavirus. After infection, it can take from several weeks to several years, so it can sometimes be difficult to determine the cause of papillomas.
Scheme of human papillomavirus infection
Regardless of the type of growth, the patient should be tested for the presence of HPV in the body.
About virus infection
Papillovirus or HPV is a common disease. Statistics show that more than 70% of people of different ages and genders suffer from this virus. A sign of infection with the virus is new growths on the skin, but this does not always happen. Warts appear only when the patient's immune system weakens. Most often, papillomas appear in people who have undergone surgery or are suffering from illness, as well as in individuals leading an unhealthy lifestyle. Warts also occur due to hormonal imbalance in women who are pregnant or taking hormonal pills. The average incubation period is from two to six months, but the virus can remain dormant for several years. Most people become infected with papillovirus for the following reasons:
- The virus enters the body through small cracks. Damage to the oral mucosa can occur during dental surgery.
- You can also damage the mucous membrane by eating an overly hot or spicy culinary masterpiece.
- The virus is transmitted from person to person. Papilloma on the oral mucosa is transmitted through kissing an infected person, or through oral sex with him. The virus can also be picked up indirectly by using other people’s hygiene products. Therefore, doctors advise avoiding using other people's toothbrushes, even if they belong to relatives or loved ones. You can become infected simply by eating ordered food in a cafe, because the delicacy was served on a plate that had previously been used by someone infected with papillovirus;
- The disease is transmitted from mother to child if the mother was infected with papillovirus and refused to undergo the necessary medical procedures. During the passage of a child through the birth canal, the child is attacked by viruses. Most often, such a child will suffer from the most terrible type of warts - papillomas that grow in the throat. In this case, removal of papillomas is carried out without shelving, since there is a high risk of death.
Papillomas can cause problems with the speech apparatus, digestive system, and even lead to nervous disorders.
Kiss is a method of transmitting the virus
What they look like
Papillomas are a small round-shaped neoplasm with a small stalk and a wide surface. Their size, as a rule, does not exceed 2 cm , but in advanced cases this figure may increase. The color of papilloma is usually pale pink or flesh-colored. The mucous membrane does not change its color, but in some cases it may become paler. This occurs due to keratinization of the epithelium. External trauma, such as biting, can cause the papilloma to change color to darker due to the hemorrhage that occurs.
When palpating the growth, the patient does not feel pain; his health is usually normal. If papillomas are constantly injured, lesions may appear on them, indicating the possibility of oncology.
Prevention
The Cleveland Clinic offers the following preventive measures.
- Limiting the number of sexual partners throughout life.
- Vaccination of children and young people. Both existing vaccines protect against HPV type 16, among other things.
- Regular screening (visiting a doctor) increases the likelihood of early diagnosis of cancer.
- Visiting the dentist. This specialist is often the first to diagnose oral or pharyngeal cancer.
- Limit alcohol consumption and smoking. Conventional cancer risk factors also play a role.
It is important to know that the HPV vaccination benefits both sexes and not only women. In the United States, the National Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends HPV vaccination for boys aged 11–12 years. Currently, it is believed that the vaccine will be beneficial if vaccinated before age 26.
Locations in the mouth
Growths can appear throughout the oral mucosa, affecting a variety of places:
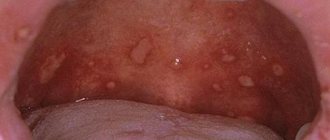
- Papillomas on the tongue. Usually it is the tongue that first suffers from the effects of the papillomavirus. Small bumps or white granularity begin to appear on it. The growths can be either multiple and small, or single but large. In the latter case, the patient may experience not only discomfort, but also pain.
[Show slideshow]
On the tongue, papillomas can appear on the tip or on the sides. Growths located under the tongue are also common. Much less often, neoplasms can be seen on the vine. The color of the growths can vary: from pale pink to deep red.
- Papillomas in the throat. In this area, diagnosing the presence of a problem is quite difficult, since the growths do not cause pain in patients and do not interfere with the flow of food. A distinctive feature of these neoplasms is frequent soreness and some discomfort, which is rarely paid attention to.
If the papilloma in the throat begins to enlarge, it can lead to difficulty swallowing food. Sometimes this is reflected in the patient’s voice, which gradually becomes quieter. The neoplasm here looks like a small bump, rough to the touch. Most often it appears in the tonsil area.
- Laryngeal papilloma. The most dangerous type of growths is in the mouth area. Such papillomas interfere with breathing, as a result of which the patient may experience oxygen starvation.
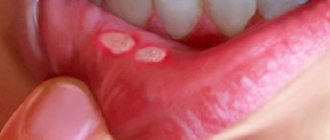
- Papilloma on the lip. The growth that appears in this area is not life-threatening, but it causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient. The tumor is located in a conspicuous place, so the person experiences problems of an aesthetic nature. In addition, the papilloma, which increases in size, can be injured while eating or accidentally touched by hands.
- Papilloma on the gum. This variety usually does not cause any inconvenience to the owner and can go unnoticed for a long time. However, the growth can be injured during brushing, which will lead to negative consequences in the future.
The presence of some types of papillomas is difficult to diagnose independently. Therefore, if you suspect a problem, you should contact a specialized specialist.
How to avoid relapse of the disease?
After the growth has been removed from the patient's tongue, the person should not relax. Typically, single papillomas do not recur, but with multiple formations, the reappearance of growths on the body occurs quite often.
Therefore, after surgical removal of papillomas from the surface of the tongue, you should:
- Take precautions and limit risk factors (see above).
- Take a course of antiviral treatment as recommended by your doctor.
- Seasonally take immunomodulatory drugs and vitamin complexes, which your doctor will also help you choose.
- Maintain oral hygiene and avoid tongue injuries.
One of the main conditions for achieving a favorable outcome in the fight against papillomas is choosing the right medical center, since much in the procedure for removing a tumor depends on the actions of the doctor. We hope that the recommendations of specialists from the LeaderStom network of dental clinics helped you clarify the picture of the growth that has developed on your tongue, and now you can solve this problem without unnecessary emotional distress.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease begins with collecting anamnesis and external examination of the oral mucosa. Based on this, a preliminary diagnosis can be made, which must later be confirmed using a special study.
If the nature of the growth is viral, strains of papillomavirus will be detected in the patient’s body. Their presence can be checked using PCR diagnostics, aimed at determining the strain and viral load on the body. In some cases, a histological examination is prescribed to determine the good quality of the material taken.
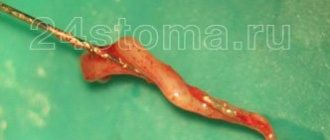
Removal methods
Removing papillomas in the mouth area requires special delicacy. Traditional removal methods, cryodestruction and electrocoagulation, are not recommended for such growths, as they can injure the mucous membrane and affect healthy tissue.
The best option is laser removal, which can be performed anywhere the papillomas are located.
This also applies to laryngeal tumors, which are considered quite difficult to remove. The area of action of the laser beam is very limited, due to which local destruction of growths is carried out. This method is considered safe and the most progressive to date. Before the operation, anesthesia is first administered so as not to cause great discomfort to the patient.
In severe cases, surgical methods can be used. Such operations are typical for large papillomas that cause significant pain to the patient. They can merge into associations, which makes them difficult to remove with targeted techniques.
How to remove papilloma on the tongue, see our video:
Treatment
The goal of any treatment is not only to get rid of unwanted growths. In addition, therapy performs such tasks as:
- strengthening the immune system;
- reduction of viral activity;
- reducing the risk of relapse.
For this, the patient is prescribed antiviral drugs, used topically, if the papillomas are located on the lips. As a rule, this is Acyclovir ointment in combination with various mouthwashes - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, etc. This helps reduce the concentration of the virus in the affected area.
Immunomodulatory therapy is necessary to correct the state of the immune system, which is responsible for naturally containing the virus. Such drugs include Isoprinosine, Allokin-alpha, Panavir, etc.
It is important to combine drug therapy with the removal of all existing tumors. Otherwise, the treatment will give a temporary effect with a high risk of reappearance of papillomas.
Methods for treating papilloma on the inside of the cheek
A papilloma that appears on the cheek in the mouth should alert a person, although it is usually benign. Immediately after its detection, you need to contact an ENT specialist, dentist or therapist for diagnosis and effective treatment. A timely response to this growth will help to avoid malignant processes and prevent you from putting your life in danger.
Treatment of papilloma on the inside of the cheek with medications
In the photo there are preparations for papillomas on the inside of the cheek
First of all, you need to strengthen your immune system by drinking special immunostimulants . Among them, Immunal, which costs about 250 rubles, best copes with its tasks. (120 UAH). It is sold in liquid form, making it easy to use. It can be replaced by Lymphomyosot, also available in the form of drops. You can also recommend taking Echinacea purpurea, which is the most economical option. Treatment of papilloma on the buccal mucosa should be carried out for at least 2-3 weeks.
In parallel with taking immunostimulants, it is recommended to take antiviral drugs - Likopid, Kagocel or Tsitovir-3. On average, they need to be taken for 5-10 days; taking it longer is not recommended in order to avoid suppression of the intestinal microflora.
Among external agents, it is recommended to use Miramistin , which perfectly reduces the activity of bacteria, viruses and infections. They need to rinse their mouth 2-3 times a day for 2-3 minutes. It costs about 200 rubles. (90 UAH).
It has a good analogue - Chlorhexidine . Both are antiseptics, but the latter is recommended to be used 2-3 times a day. Successful treatment of papilloma on the buccal mucosa will take at least a week.
Traditional medicine for papilloma on the inside of the cheek
The most famous remedy is calendula tincture , which should be used to wipe the papilloma 3-5 times a day. To do this, you can use an ear stick or a piece of cotton wool, moistening them in the composition.
Instead, sea buckthorn oil ; it needs to be lubricated with the formation twice a day for 7-10 days.
You can also rub the cone with peeled garlic, treat it with the juice of celandine and aloe, potato and lemon.
, tincture of walnuts , prepared with the addition of 50 g of this component along with crushed green shells and the use of vodka, which is taken twice as much, is also very helpful All this is mixed and left in a jar for 2 weeks, kept in a dark place. After this time, the composition must be filtered, soak a cotton swab in it and wipe the growth. This must be repeated 3 times a day, treatment is carried out for about 2 weeks.
To combat papilloma on the oral mucosa, castor oil , which is recommended to be heated beforehand. They treat formations with an ear stick 2-3 times a day. For this to help, treatment should be carried out for at least 10 days.
It is useful to rinse your mouth with a soda solution , for the preparation of which you should add this component (2 tsp) to 200 ml of warm water and stir well. This procedure must be carried out 5 times a day for 2-3 minutes.
No less useful will be lubricating the growth with propolis , which has strong cleansing and anti-inflammatory properties.
Also, when treating papilloma on the buccal mucosa, you should pay attention to an infusion of wormwood and chamomile , of which you need to take 2 tsp per 250 ml of water. The composition must be kept covered for 2-3 hours, filtered and used to rinse the mouth 3-4 times a day. This treatment should be carried out for at least 10 days.
The child has
Symptoms of human papillomavirus development in children are the same as in adults. However, they do not yet have the immune defense that inhibits the development of the virus. As a result, tumor growth can be very rapid and aggressive. If the child is very young, diagnosis is difficult due to the lack of complaints, and the disease can only be identified thanks to the vigilance of the parents.
Children of different ages are characterized by the development of laryngeal papillomatosis if the mother is infected with HPV.
During natural childbirth, the risk of transmitting the virus to the fetus is very high. And, as a rule, papillomavirus manifests itself in the mouth area.
It is important to understand that high-quality removal of growths is only possible under the supervision of a specialist. Independent attempts to remove papillomas can lead to trauma to the sensitive oral mucosa.
Consultation with our practicing dermatovenerologist:
Causes of papillomas in the oral cavity
Oral papillomatosis occurs as a result of infection and factors that provoke it. A neoplasm may appear on the mucous membrane:
- after using someone else's toothbrush or towel;
- when consuming food from poorly washed dishes, if they were previously used by an infected person (catering provides a high risk);
- after kissing or oral sex with a carrier of the virus.
It has been established that approximately 80% of people have dormant HPV. The carrier of the virus does not always know about it himself; he can infect people, but not have symptoms himself due to his strong immunity. Activation of HPV in such people can occur years later, under the influence of certain factors:
- colds and infections;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- hormonal disorders;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- exhaustion;
- obesity;
- disruptions in the functioning of the circulatory system;
- taking antibiotics and chemotherapy;
- severe stress;
- physical fatigue;
- pregnancy.
There have been cases of infection of a child from the mother during childbirth and activation of HPV in adolescents during hormonal changes.