This article is devoted to answering questions from patients planning dental implantation and who have undergone an initial examination, during which the doctor determined that dental implantation is possible in your case. In this article you will find general information about upcoming implant prosthetics; your attending physician should provide you with more specific instructions. It is important to remember that you are a full-fledged member of the implantation team, and the service life of dental implants depends on following the doctor’s recommendations.
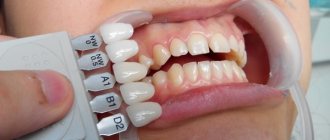
What is a dental implant?
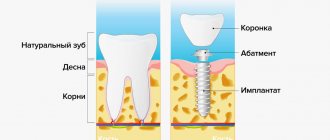
A dental implant consists of a titanium “root,” which is screwed into the jaw during surgery, and a titanium abutment, which is the transition piece between the implant and the crown or bridge. The installation operation is usually carried out in two stages. The first stage is installation of the implant in the jaw. After healing, the second stage is carried out - installation of the abutment. After final healing, osseointegration or fusion of the implant with bone tissue occurs. The final stage is prosthetics on implants. After dental implants, your dental implants have the function and appearance of natural teeth.
Alternative methods
Modern surgery is constantly progressing, but with the advent of new technologies, hand sutures continue to enjoy the same popularity. One of the new technologies is the application of titanium staples (skin staplers). Such a stapler is applied and removed using a special device - an endoscopic stapler.
Another type is staples that dissolve some time after surgery.
Despite simplifying the wound healing process, this method has 2 main disadvantages:
- High price for equipment and the implementation itself.
- Lack of participation of the surgeon himself. Hand sutures and direct involvement of the fingers of an experienced surgeon are more reliable and safe. A competent specialist feels the wound, selects the thickness of the suture and the proportions of the nodes.
Stages of dental implantation
Primary examination
During this visit, the doctor, after conducting the necessary research and interviews, will determine whether dental implantation is indicated for you.
Further examination
After the initial examination, you will undergo more in-depth examinations. You may need to consult related specialists: periodontist, orthodontist, hygienist, etc. You will be offered a treatment plan for the remaining teeth or gums (if necessary), a schedule for dental implantation and final prosthetics. All dental problems must be resolved before dental implantation begins.
Operation I: implant installation
Duration of the procedure: 40-60 minutes, anesthesia - local (in most cases), or general (anesthesia or sedation). During this procedure, a dental implant is screwed into the jawbone. The implant surgeon uses a special drill to drill a hole, creating a bed for the dental implant. After this, the implant is screwed into the hole and stabilization is achieved. To replace a completely toothless jaw, it is necessary to install 6 to 8 dental implants. If there are several teeth on the jaw, then doctors decide how many implants are needed during the examination. After the operation is completed, you can return home. If you are replacing a completely toothless jaw and wore removable dentures before implantation, then on the upper jaw the denture can be returned immediately after the operation, on the lower jaw - a week after the operation.
Healing stage I (care after implant placement)
Complete healing requires an average of 6 months for the upper jaw and 3 months for the lower jaw. Such a noticeable difference in duration is characterized by the structure of the jaws and the characteristics of the bone tissue. During the healing period, it is necessary to observe a gentle regime of load on the jaws. During the first month after surgery (minimum 2 weeks), you must follow the diet prescribed by your doctor. If you notice the following symptoms: chafing from the prosthesis, swelling or tenderness in the area of the installed implants, contact your doctor immediately.
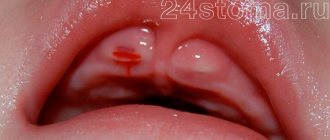
Minor swelling or slight pain during the first week after dental implantation is considered a normal reaction. The sutures are removed a week after the procedure, and the gums will return to their normal state 1-2 days after the sutures are removed.
It is important to examine the oral cavity daily in order to promptly notice redness or swelling in the area of the implants. Brush your gums with a soft brush, use prescribed rinses, and follow hygiene procedures prescribed by your doctor or hygienist. Dentures should be cleaned using a soft brush and low-abrasive toothpaste.
Operation II: installation of abutment
After the first stage of healing, surgery to install abutments is performed. During this simple procedure, the surgeon removes the cover screws and screws the abutments in their place. This is where all manipulations associated with surgery end.
Healing stage II (care after abutment placement)
The second stage of healing is much shorter and lasts approximately 1 week. At this stage it is important to pay attention to the areas around the abutments. Pain may be observed during the first days after surgery; if pain increases or swelling appears, be sure to consult your doctor. Hygienic care begins 1-2 days after surgery using a soft toothbrush. In addition, you can use rinses prescribed by your doctor.
Important information! Be sure to contact your doctor if you experience the following symptoms:
- Severe pain in the implant area that is not relieved by prescribed medications. The pain increases rather than decreases.
- The gums in the implant area are swollen and continue to swell for 2-3 days.
- You have noticed strange changes in the seam area. Some fluid is oozing from the gums around the abutments.
- General poor health, body temperature increased.
- A dental implant protrudes from the gum.
Prosthetics on implants
Dental implants have taken root in the bone, abutments have been installed, and the gums have healed. You are ready for the final stage - prosthetics. At this stage, the joint work of the orthopedic dentist and dental technician comes to the fore. The process begins with taking impressions of the jaws, which are needed to create a model of new teeth. At all stages of the work, you will be tried on a denture structure several times, which in the future will become your new teeth. Adjustment will occur until the doctor and patient are completely satisfied with the result of the prosthetics. The final stage, including the production of the prosthesis, takes an average of 2-4 weeks. After dentures are completed, you can enjoy new teeth and restored functionality of your jaws.
Types of postoperative sutures
Depending on the location of the operation, sutures are placed on the walls of the internal organs, or connect external tissues.- Depending on the nature of the operation, sutures can be surgical or traumatological. The techniques can be different, the only difference is that traumatological sutures are applied promptly, during the operation to eliminate defects resulting from external trauma. In surgery, surgery and localization of sutures is a deliberately planned event.
- The type of postoperative suture directly depends on the type of damaged organ, characteristics of blood vessels and tissues, and the depth of the postoperative wound.
- Seams can be made from various materials and performed using various techniques, depending on the brands and tools used.
| 1. If possible, self-excretion | Characteristics |
| Absorbable sutures | Application is possible only for tissues and organs that grow together within a period of up to 4 months. They are eliminated from the body independently and completely. |
| Non-absorbable sutures | Must be removed after complete healing of the postoperative space |
| 2. By thread type | |
| Natural threads | Silk, ketchut, cotton, linen have a number of disadvantages. Non-absorbable sutures are placed on their basis. Linen and silk are practically not used due to the high degree of conductivity of pathogenic microorganisms into the body. |
| Synthetic threads They differ in material:
| They are able to be eliminated from the body independently due to biodegradation. It is possible to use absorbable sutures. The main disadvantage is the unpredictability of the material. Stitching with catgut is extremely dangerous - it is unknown how long the material will hold the tissue. If such material ruptures before the tissue heals, it can cause deterioration in the patient. |
Reference! The patient is not informed which sutures the doctor will use in his work. The choice is made based on personal preference and operating situation.
- Differences in thread structure: braided and monofilament (monofilament). The choice is based on the need to stitch the wound less or more tightly: monofilament is much weaker, rope braid is correspondingly stronger.
- Cosmetic sutures and sutures for connecting internal organs
Cosmetic sutures connecting the patient’s skin must not only complete the operation correctly, but also not create problems in later life. Ideally, the seam should not remain, or be more or less visible. For these purposes, a continuous intradermal cosmetic suture or metal staples are most often used.
Sutures for connecting internal organs have different techniques, depending on which organ the operation was performed on.
Care of dentures on implants
The importance of high-quality hygienic care has already been mentioned above, but it is worth repeating that the end of the implantation process does not mean the end of good hygienic care. The lifespan of dental implants is now in your hands.
Do not neglect good hygiene care, regularly visit your doctor for routine examinations and a hygienist for professional cleaning of your teeth and dentures. The first of these visits will take place one week after the completion of the prosthetics. You can discuss with your doctor the functioning of your new teeth and any possible problems. Your doctor and hygienist should check that you are taking proper care of your teeth. Other visits are recommended after 1, 3 and 7 months, after a year you should come for an examination once a year if no problems have occurred.
Hygienic care after dental implantation is carried out using a soft toothbrush, a soft mono-beam brush, interdental brushes of a designated size, dental floss and rinses. It is best to discuss the use of all care products with your doctor or hygienist.
When should sutures be removed after surgery?
How long it takes from surgery until the sutures are removed depends on many factors. First of all, take into account:
- speed of regeneration;
- age category of the patient;
- presence of wound postoperative complications;
- type of operation performed;
- features of the surgical intervention area and its trophism.
Depending on all these factors, the surgeon
individually determines the time of suture removal.
The approximate time frame that specialists rely on when carrying out most operations is 5-7 days. However, when performing surgery on the chest or when performing amputations, the removal of sutures
is postponed until approximately the 10th day.
If the operation was performed on an older person or a patient whose body is weakened by infections or internal pathologies, they will need to remove the postoperative sutures later - approximately two weeks after the operation.
It is worth mentioning that the postoperative scar is hyperemic, the sutures cut into the wound, tissue necrosis occurs - the sutures must be removed as quickly as possible.
The sutures must also be removed if suppuration occurs, which makes it possible to prevent the development of dangerous complications.
It should also be noted that in some cases, even with rapid wound healing, it is recommended to remove the sutures in several stages, with an interval of at least one day.