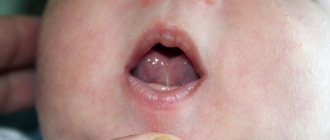
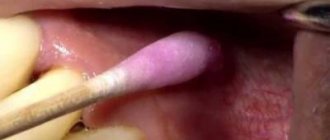
The elastic folds of the oral mucosa that connect the lips to the jaw are called frenulums. There are two such jumpers - lower and upper. The third frenulum is located under the tongue, connecting it to the floor of the mouth.
Normally, the folds of the oral mucosa do not interfere with speaking and chewing food. But there are a number of pathologies associated with their structure, which are accompanied by discomfort and can lead to impaired diction and bite. If the frenulum of the upper lip in a child or adult has an abnormal structure, it is trimmed.
At what age is it best to have surgery?
Trimming the frenulum of the upper lip is a relatively easy operation, but the optimal age for it, according to most doctors, is 5–7 years, when the permanent incisors begin to emerge. If you carry out the procedure during this period, you can avoid the formation of a diastema and further manipulations to correct the bite by the orthodontist. But according to indications, it is not too late to perform plastic surgery in adolescence, and even in adults.
“I took my child to this operation. My son was 8 years old at the time. He already understood everything that was said to him, and at the same time he was very afraid. Before the operation, we sat and calmed down in the doctor’s office for about 15 minutes. I want to say that the child’s psychological attitude is very important here. About the operation itself: it didn’t hurt, my son didn’t cry. But after the anesthesia began to wear off, he complained that his gums hurt, but this problem was solved with Nurofen syrup. Already on days 4–5, the trace of the wound was almost invisible, although it was done with a scalpel. But in children everything heals quickly.”
Lada, review from the dental portal gidpozubam.ru
The operation is best performed at the age of 5-7 years
Trimming the lip frenulum in children
The optimal period for plastic surgery is 3-6 months. The need for frenulum correction is determined by the doctor. An “adherent” or thick fold in infants is not always a pathology, so its removal or dissection must have clear medical indications:
- excessive rigidity of the frenulum, which will not be able to self-correct (stretch);
- dysfunction of sucking.
You need to pay attention to the cords of the upper and lower lips at the age of six. At this time, the formation of permanent incisors and molars occurs - the most important “mechanisms” of the human body. They participate in the functioning of the digestive tract and support the facial muscles. In addition, in the period from 6 to 9 years, stable speech skills are developed, which are subsequently quite difficult to correct.
The operation, carried out on time, provides a number of advantages:
- the freed space is quickly and, most importantly, independently closed with new teeth;
- To correct the dentition, you will not have to resort to orthodontic treatment.
Types and technologies of upper frenuloplasty
Before the procedure, it is important to carry out a complete sanitation of the oral cavity, treat diseased teeth and stop acute inflammatory processes, remove bacterial plaque - all these are sources of infection, which can subsequently provoke postoperative complications. You should also eat before surgery, as hunger can impair blood clotting.
There are several techniques for performing the procedure. The doctor decides which one to use depending on the patient’s age, the location and attachment of the frenulum. Let's list all the technologies that exist today:
- frenotomy, or frenulotomy: involves transverse dissection of the frenulum if it is very narrow and thin. This is the so-called minor operation, which is considered the least traumatic. The purpose of the manipulation is to relieve the tension of the ligament. The procedure can be performed on newborns, as well as older children,
- frenectotomy: this is a more complex operation, during which the frenulum of the upper lip is trimmed and part of the tissue located in the space between the central incisors is removed. The procedure is performed if the frenulum is thick, as is often the case in adolescent and adult patients,
- frenuloplasty: the doctor releases the ligament and moves it to the area where it should be.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
Each of the listed operations is performed on an outpatient basis, under local anesthesia. Traditionally - using a scalpel. Afterwards, the doctor applies self-absorbing sutures and sends the patient home. Everything lasts about 10–15 minutes. Next, the patient receives clear recommendations on how to behave during the rehabilitation period. 1 and 3 days after the operation, you need to visit the doctor again for follow-up examinations.
Today, plastic surgery of the upper frenulum can be performed using a laser, which allows the procedure to be carried out quickly, without pain and blood, and to disinfect the operated tissues. This also reduces the likelihood of developing postoperative complications (swelling, pain, inflammation, scars). A big advantage is that when using laser equipment there is no need to apply stitches.
Laser frenulum trimming is the least traumatic
The rehabilitation period takes about 10–14 days. During this time, the patient is not recommended to eat food that can irritate the operated tissues (cold, spicy, hot, hard). It is also necessary to rinse your mouth with an antiseptic and apply wound-healing ointments (for example, Solcoseryl).
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 3 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
prevention
- Alimirzoev F.A. Dental anomalies in childhood and their diagnosis // Achievements of university science. – 2014.
Consulting specialist
Geraskina Inna Igorevna
Doctor rating: 9 out of 10 (2) Specialization: Dentist-therapist, orthodontist Experience: 11 years
Treatment with traditional methods
Alternative medicine is often used as an adjuvant therapy.
The greatest therapeutic effect is achieved by:
- Sage.
Used to prepare a decoction. To do this, 30 g of raw material is crushed, 0.5 liters of boiling water is poured in and boiled over low heat for 10 minutes. Afterwards, let it brew until it cools completely, filter and use for irrigating the oral cavity and as a lotion on the bump.
- Sea salt. Antiseptic solutions for rinsing the mouth are prepared on its basis. For 0.25 ml of warm water 1 tsp. salt.
- Propolis. Can be used in the preparation of a mouth rinse solution. Also based on it, ointments are made that improve nutrition and tissue regeneration, stopping the growth of pathogenic microflora. To do this, mix crushed propolis and butter in equal quantities.
- Calendula. On its basis, a tincture is made, which is subsequently used as a lotion or for irrigation of the oral cavity.
- Tea tree oil. Used to prepare compresses for the bump, which are kept overnight. To do this, mix 0.5 tsp. oils with 1 tsp May honey.
Comments
Which doctor can give a referral for this operation?
Marina (06/14/2020 at 07:28 pm) Reply to comment
- You can get a referral after an examination by a dentist or periodontist, orthodontist, speech therapist, or neonatologist (for newborns). The operation itself is performed by a dental surgeon.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (06/17/2020 at 09:07) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Possible complications
The most difficult thing in the postoperative period is the quiet healing of tissues. Unlike other organs, the penis cannot remain motionless due to a person’s volition. A slight erection is enough to disrupt the integrity of the seams and cause them to separate. In addition, the organ contains the largest percentage of sensory receptors compared to other parts of the body. Taking into account all this specificity, the following complications of the postoperative period can be identified:
- pain syndrome – expressed due to the high receptor sensitivity of the organ (relieved by analgesics);
- suture dehiscence and bleeding require regular monitoring by a specialist;
- swelling of the penis;
- infections and inflammatory processes are prevented with the help of antibacterial therapy;
- scarring of sutures;
- poor external aesthetics.
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is a degenerative process that affects all periodontal structures. Its distinctive feature is the absence of inflammation on the gingival margin and periodontal pockets. The course of periodontal disease is always chronic.
According to severity they are distinguished:
- a) mild – exposure of tooth roots up to 4 mm;
- b) average – 4-6 mm;
- c) heavy – more than 6 mm.
The prevalence of periodontal disease is generalized.
Flap surgery is a periodontal operation that involves cutting out and folding a mucoperiosteal flap, followed by careful treatment of the surfaces of the roots of the teeth, bone pockets and the inside of the flap.
The advantages of this operation are the complete removal of pathologically altered tissues under full visual control.
Operation stages:
- the mucoperiosteal flap is cut out and folded back,
- subgingival dental plaque and granulation tissue are removed using an ultrasonic tip and curette,
- antiseptic and antibacterial treatment of periodontal tissues,
- if necessary, implantation of bone tissue,
- the flap is then placed in place and secured with sutures.
- Next comes the application of a healing bandage.
- After a week, the sutures are removed.
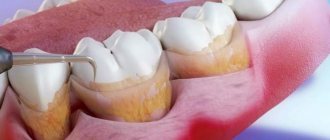
Curettage is the removal of pathological tissues around the tooth (supragingival and subgingival calculus and granulations). There are closed and open curettage. The essence of these manipulations is to clean periodontal pockets using special instruments - curettes.
In this case, pathological tissues are removed mechanically (with constant irrigation of the surgical field with antiseptic liquids), which are irritants that support inflammation.
It is important to realize that if pathological tissue is not removed, the process will worsen due to the presence of that same irritant. Ultimately, this will lead to the loss of a tooth, which, by the way, may be completely healthy.
Splinting of teeth is a manipulation aimed at combining mobile teeth into a single block, the so-called “splint”. Splinting is most often carried out in the area of the lower incisors, because It is they who suffer more during the generalized process of periodontitis or periodontal disease. To do this, a special wire or an orthodontic retainer is glued to the composite material on the inner surface of the teeth undergoing splinting.
Before installing a splint, it is necessary to carry out professional oral hygiene - remove stones, plaque and thoroughly polish the surfaces of the teeth.
Gumplasty is an operation to correct changes in the appearance of the gingival margin, in the form of excessive growth, or vice versa - recession (reduction in the volume of the gum, accompanied by exposure of the tooth root). Gum plastic surgery is often performed to achieve maximum aesthetic effect. For example, in orthopedic dentistry to increase the clinical height of the crown, when forming an ideal smile. Also after patch surgery, implantation, surgical treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis, etc.
Recession is a decrease in gum volume, accompanied by exposure of part of the root. Recessions can be localized or generalized.
Recessions arising from:
- structural features of the jawbone - when the teeth have a massive root, and the bone in this area is thinned.
- negative microbial flora – the presence of supragingival and subgingival dental plaque. To avoid this, it is necessary to carry out professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year.
- chronic trauma to the gingival margin. This occurs more often due to improper brushing of teeth (incorrect brush movements, use of brushes with hard bristles, often the use of electric brushes).
- bad habits - using toothpicks, matches to clean the contact surfaces of teeth, biting pencils and other objects.
- external trauma of teeth in the form of dislocations accompanied by chipping of the edge of the socket.
- orthodontic pathology.
During recessions, patients mainly complain about an aesthetic defect and also about increased sensitivity of the teeth. The problem of recession can be solved either orthodontically (if the cause of recession is orthodontic pathology) or surgically.
Surgical methods for treating recession include various types of plastic surgery:
- Moving the pedicle flap
- Relocation of the free flap, with the autograft most often taken from the palate.
- Moving the gingival trapezoidal flap coronally to the defect area.
After surgery, a healing period begins and in less than a month, the patient sees the result.