Tartar is not only an aesthetic defect, but is also one of the reasons for the development of dental pathologies.
Using the information on proper hygiene and at-home softening and cleaning methods presented in this article, you can not only get rid of mineralized deposits on your teeth, but also prevent their formation.
How does tartar appear?
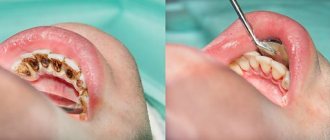
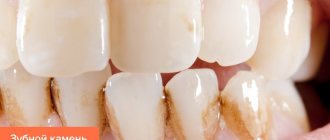
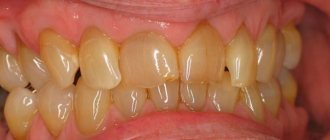
Deposits on teeth in the form of a dense formation (stone) are hardened mineralized plaque. It often forms in the cervical area of the dental crown and causes aesthetic discomfort in humans. But the unattractive appearance of your teeth while laughing or talking is not the worst thing. Compacted dental mineralized deposits provoke gum disease and caries. Mineral deposits are not as rare a problem as they seem. This defect occurs in 80% of people, and even in childhood.
Composition of sediments:
- calcium and iron salts;
- particles of food residues;
- polysaccharides, proteins;
- particles of skin epithelium, mucous membranes, lips;
- microbes, coccal bacteria and others.
Mineral deposits are almost 90% inorganic. According to ICD 10, dental growths are characterized as a disease under code K05.6.
For what reasons do growths begin to be deposited on the crowns of teeth? This process depends on the composition of the salivary fluid and the quality of oral hygiene. For some people, stones appear in 3-4 months, for others the hardening process takes 9-10 months.
First, a thin protective film (pellicle) appears on the crowns, the purpose of which is to protect the enamel from the aggression of chemical compounds. The film forms almost immediately after brushing your teeth. After a couple of hours, plaque begins to accumulate on the pellicle, consisting of food components, bacteria and components of salivary fluid. If this formation is not removed within two days, a thickened plaque will appear. It gradually becomes denser due to the addition of new components and mineralizes (hardens). After 2 weeks, hard tartar will appear at the site of the plaque.
Due to the plaque that appears, the surface of the crown becomes rough, which allows for the accumulation of new deposits: it is easier for them to adhere to the convex surface. Bacteria are attracted to plaque and produce toxic substances during their life. Due to constant toxins, the mucous membrane around the tooth begins to become inflamed. The process of tissue inflammation is accompanied by the release of periodontal fluid, which is attractive to microorganisms. This liquid also contains protein, which attaches to the plaque that has already formed.
Causes
The most important reason for the formation of growths is poor oral hygiene or lack thereof. If plaque is not removed in a timely manner, it will quickly turn into a hardened formation with bacteria. To prevent this process, you need to thoroughly clean all your teeth in the morning/evening and rinse your mouth after each snack. It is advisable to use not only a toothbrush, but also dental floss, mouthwash, and irrigator.
Other reasons that contribute to the formation of stones:
- unhealthy diet;
- bad habits;
- composition of saliva;
- malocclusion;
- defective chewing;
- endocrine diseases;
- disruption of the salivary glands;
- fixed orthodontic structures.
Not all toothpastes effectively clean plaque on teeth: the abrasiveness index (RDA index) must exceed 50 units.
Unhealthy eating includes baking, drinking lemonade, and soft carbohydrate foods. In order for saliva to cleanse teeth of plaque, you need to give preference to solid foods: raw vegetables and fruits, crackers. Chewing raw carrots or apples promotes the active secretion of saliva, which prevents plaque from depositing on the walls of the teeth. Eating crackers after meals also contributes to this.
Bad habits include smoking, frequent drinking of strong coffee and tea. These substances contribute to the rapid formation of dental plaque. Smoking is especially dangerous: tar deposits on the teeth, and hot smoke irritates the gums.
The composition of saliva also affects deposits. When the acid-base balance is disturbed (in the direction of increasing acidity or alkalization), rapid mineralization of plaque occurs. High acidity provokes hypermineralization, and low acidity promotes demineralization of the enamel - it becomes porous and vulnerable to deposits.
Diseases
The composition of saliva is different for all people. If it contains an increased concentration of minerals (calcium, fluorine), then they settle on the surface of the dental crowns. This promotes rapid mineralization of dental plaque. The formation of growths is also affected by the amount of saliva: there may be too much or not enough.
Incorrect bite and crooked teeth also negatively affect the formation of tartar. This is due to the incorrect positioning and curvature of the teeth: there is more space for the formation of tartar in the interdental space.
Inadequate chewing increases the risk of formation of growths. This defect is typical for people with partial edentia. A person has to chew only on one side (where all the teeth are), as a result, the opposite side is not washed with saliva. Accordingly, more plaque accumulates on it, which is a favorable environment for the formation of growths.
Fixed orthodontic appliances also contribute to the formation of build-up, as plaque accumulates in the gaps between them and the teeth. It is not always possible to thoroughly clean teeth with installed implants. Therefore, instead of a toothbrush, it is better to use a irrigator.
Endocrine and other diseases of systems and organs require constant use of medications. Some antibiotics negatively affect the composition of saliva and its density: this leads to the formation of plaque and stones.
How to quickly soften and remove stones from teeth using folk remedies?
Traditional medicine methods are widely popular, allowing you to effectively and quickly remove tartar at home.
In addition to their high therapeutic effect, they are easily accessible means, the use of which does not require professional skills.
The most effective means that can be used to treat tartar include:
- Salt is used with extreme caution and must be finely ground
Hydrogen peroxide. Used for various procedures. Preparation of lotions: moisten a cotton pad with 3% peroxide and apply to the teeth for a couple of minutes, which allows you to dissolve the stone. Afterwards, remove the softened plaque with a brush. For the mask, mix 5 drops of lemon juice, 20 drops of peroxide and 5 g of baking soda. Apply the mixture to your teeth for 2 minutes and then rinse thoroughly.
Important! The frequency of manipulations using hydrogen peroxide should not exceed 1 time per week. Frequent use of such a product will lead to destruction of tooth enamel.
- Baking soda. Most often it is mixed with toothpaste or warm water, which is used to clean teeth. It can also be added to various mixtures to remove hard plaque.
- Salt. It is used with extreme caution and must be finely ground. Using it and a soft brush, you brush your teeth and massage your gums every morning and evening to not only remove plaque, but also prevent oral diseases.
- Ash. A powder without large particles is used, which is rubbed into the tooth enamel with your finger. You should first blot your teeth with a dry cloth, leave for a couple of minutes after application and rinse your mouth thoroughly.
- Clay. Use a medium-hard toothbrush using any organic clay powder to clean your teeth daily. In case of any periodontal damage, clay applications can be made to the affected area.
- Honey rinse. It is carried out daily before bedtime for 1.5 - 2 months. To prepare the solution, you need to mix 35 g of linden honey and 0.25 liters of warm water.
- Herbal decoctions are used for rinsing the mouth or for oral use. The most effective means that dissolve the stone are: Celandine. Pour 15 g of dried flowers into 200 ml of boiling water and leave for an hour. Use the strained infusion to irrigate the oral cavity twice a day.
- Beans with burdock. Mix crushed burdock root with 2 dried bean pods. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and simmer over low heat for a couple of hours. Cool, filter and rinse your mouth 4 times a day.
- Beans and burdock. Mix the ingredients in equal proportions. Pour 20 g of the finished mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave for 12 hours. Drink 100 ml warm in the morning and evening.
- Horsetail Pour 20 g of dried flowers into 0.25 liters of boiling water and leave for an hour. Filter and divide into two doses. Drink 100 ml of warm infusion orally.
- Walnut bark. Pour 40 g of crushed raw material into 0.25 liters of hot water and simmer over low heat for a quarter of an hour. Filter and moisten the toothbrush in the medicinal broth to cleanse the tooth enamel. To enhance the therapeutic effect and strengthen periodontal tissue, you can rinse your mouth with the prepared decoction.
Symptoms
You can independently determine the presence of hardened deposits using your tongue. You need to run the tip of your tongue over your teeth next to the gum. If roughness is felt, it means that deposits have already formed. On the frontal part of dental crowns, deposits are visible when talking and smiling. If a person is addicted to black tea, coffee or cigarettes, the deposits will turn dark.
The next symptom is bleeding gums. If deposits have accumulated in hard-to-reach corners of the interdental space and periodontal pockets, they will make themselves felt by inflammatory processes in the gums. Sometimes these processes are accompanied by slight bleeding: when brushing your teeth, when biting off solid food (apple, carrot).
Soreness on contact is the next symptom. Mineral growths on the enamel provoke inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth, so when pressing or brushing, a slight pain is felt. Sometimes pain is felt even when chewing food.
If plaque is not removed in time, deep periodontal pockets may form, exposing the cervical area of the crown. In this case, the teeth will react to changes in food temperature: hot-cold/sour-sweet.
Types of tartar
Depending on the location of the growths, two types are distinguished:
- subgingival tartar;
- supragingival calculus.
There is another variety - a stone bridge. This formation involves several dental units at once. Most often, a bridge is formed on the lower front teeth on the tongue side.
Supragingival
Patients themselves notice supragingival deposits. They are localized above the gum level, on dental crowns. Most often they appear on the lingual side of the teeth, as a person does not pay enough attention to oral hygiene. Another name for these stones is salivary stones.
These growths are unsafe: they can destroy the structure of the soft tissue of the gums and penetrate deep into periodontal pockets. They also have a detrimental effect on the composition of the enamel: they soften it, as a result of which caries begins to develop.
Timely and high-quality oral care prevents the formation of tartar.
Is it possible to remove supragingival deposits? This can be done by the person himself if he cleans the oral cavity properly. Salivary stones are also removed at the dentist's office.
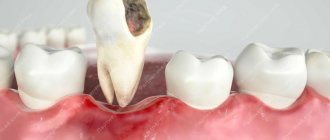
Subgingival
These growths cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are located in periodontal pockets. That is, hidden under the gums. You can guess the presence of subgingival deposits by the pain when chewing and brushing your teeth, as well as by periodic bleeding of the gums.
These growths are much more dangerous than supragingival ones, as they provoke inflammatory processes in the gums - periodontitis, periodontal disease. As a result, the periodontal ligaments are destroyed, the level of the gums rises, and teeth become loose and fall out.
It is impossible to remove these growths on your own; you need to contact a dentist or periodontist. In addition to cleansing the crowns of your teeth from mineralized plaque, you also need to treat your gums.
Why are stones dangerous if you don’t get rid of them?
Patients who seek professional cleaning are usually guided by aesthetic considerations: the stones are noticeable to others and spoil the smile. Less often, patients are bothered by an unpleasant odor or inflammation of the gums.
But neglected pigment and mineralized deposits are more dangerous than they seem. If they are not cleaned in time, they lead to the following consequences:
- halitosis – calcifications contain colonies of bacteria, whose activity causes bad breath;
- demineralization of enamel - microbes contained in plaque attract fluoride and calcium ions more intensely than dental tissues: as a result, they do not receive minerals in sufficient quantities and become porous and fragile;
- caries - microorganisms in stones release toxins and hydrochloric acids, which gradually corrode the enamel, after which the pathogenic flora penetrates the tooth and starts the process of its destruction;
- gingivitis - superficial inflammation of the gums, occurs due to the accumulation of plaque, stone and pathogenic microorganisms contained in them;
- periodontitis - as the stones increase, they penetrate under the gums, form periodontal pockets and cause inflammatory processes;
- gum recession – as infection spreads and plaque accumulates, the edge of the gums drops and exposes the necks of the teeth;
- looseness of units - in the final stages of periodontitis, destruction of the periodontal ligaments occurs, the crowns no longer adhere tightly to the sockets and fall out;
- diseases of the oral mucosa - an abundant accumulation of pathogenic flora in plaque and calculus causes inflammation of the epithelial membrane and leads to the development of stomatitis, candidiasis, ulcers, foci of necrosis, etc.;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases: toxins released by bacteria during the accumulation of dental plaque penetrate the systemic bloodstream and worsen the course of cardiovascular pathologies, arthritis, diabetes, etc.
Therefore, it is so important to carry out professional oral hygiene as plaque accumulates: on average, once every six months.
Tartar leads to exacerbation of chronic diseases
How to remove deposits at home
Dense growths cannot be removed from teeth; a dentist will help with this. But soft (partially mineralized) plaque can be removed.
To remove tartar you need:
- Electric Toothbrush;
- ultrasonic brush;
- irrigator.
The principle of operation of an electric toothbrush: breaks up deposits and then cleanses teeth of them. To do this, you need to use the desired rotation mode. A pulsating rhythm is suitable for breaking up deposits; a reciprocating rhythm is used to cleanse broken deposits. An ultrasonic brush quickly destroys partially mineralized growths and plaque.
An irrigator is a device for cleaning teeth using a jet of water under pressure. The advantage of an irrigator over an electric brush is that it does not harm tooth enamel. A jet of water under pressure gently removes plaque on the surface of the crown, in the interdental spaces and in shallow periodontal pockets. Irrigators can use herbal or medicinal solutions.
Traditional methods
Is it possible to remove growths using improvised means? This is dangerous for the health of the enamel, because homegrown methods are based on the use of either abrasives or acid. Both have a negative effect on the enamel, thinning its layer and softening its structure.
Abrasive agents (soda, salt, ash, chalk) aggressively attack the enamel surface, leaving scratches on it invisible to the naked eye. Pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate these cracks and cause carious lesions.
Acid (citric acid, vinegar) softens tartar and along with it the enamel. As a result, the protective coating of the teeth becomes vulnerable to the aggression of microbes and pathogenic microorganisms. Inept use of hydrogen peroxide is also dangerous. If you exceed the percentage of peroxide when diluted with water, you can burn the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat.
Removing tartar on your own will damage the enamel and mucous membrane of the gums.
The use of herbal infusions (including alcohol) will only lead to staining of plaque and pigmentation. If you use celandine juice, you can burn the oral mucosa and even get poisoned. Because celandine juice is a poison.
If you try to remove plaque using tweezers and other metal objects, you can cause irreparable damage to the enamel. This is absolutely not possible. Iron objects can damage not only the enamel, but also injure the mucous membrane with careless movements.
Methods for removing plaque in a dental clinic
Dentists practice several methods of cleansing enamel from mineralized plaque:
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- using ultrasound;
- sandblasting;
- using a laser;
- combined.
Mechanical method
Cleaning plaque manually using tools. This is an outdated method, but it is still used in government clinics. The doctor uses metal instruments and treats each tooth separately. Cleaning is also carried out using a drill and special attachments.
The advantages of this method are price and prevalence. There are many disadvantages: pain, risk of damage to the enamel and mucous membrane, long rehabilitation period, bleeding gums.
Ultrasonic cleaning
A modern method of removing stones. The device creates ultrasonic vibrations that mechanically destroy dense mineralized structures. There is another method - using an antiseptic liquid. In this case, ultrasonic waves create many bubbles in a liquid medium, which destroy dense structures upon contact with them (explode).
The advantages of the method are effective cleansing, absence of unpleasant sensations, low trauma. Pain medication is only required when cleaning periodontal pockets. Disadvantages - enamel injury due to improper use of instruments; cannot be used by patients with fixed orthodontic structures (fastenings are damaged). The cost of the service is several times more expensive than mechanical cleaning.
Air Flow Method
Air Flow (sandblasting) is the removal of formations using a water-air jet under pressure. Abrasive particles of specially treated soda are added to the solution. They destroy hard formations on the enamel. The solution is also flavored with lemon or mint extract.
The advantages of the method are the absence of painful sensations, can be used with installed orthodontic structures,
After sandblasting, virtually no plaque is formed: food debris does not stick to the smooth surface. The enamel brightens by 1-2 tones.
The disadvantage of this method is that it only removes small, partially mineralized plaque and is not suitable for removing large hard formations. This method cannot treat gum pockets more than 5 mm deep. The sandblasting method is used in addition to laser or ultrasonic cleaning.
Laser cleaning
The principle of laser cleaning of tartar is the evaporation of moisture from the neoplasm, due to which dense structures are destroyed. During the procedure, the enamel layer is not affected, since it does not contain water (moisture less than 1%). The laser method is the most gentle, painless and effective. In addition to cleansing, the laser beam destroys pathogenic microflora and activates tissue regeneration processes. The effect of enamel whitening is also noticeable.
After removing mineralized formations, the enamel surface remains rough, which can provoke the rapid accumulation of a new layer of plaque. Therefore, after cleaning, sandblasting is carried out, after which a perfectly smooth surface remains.
However, the laser technique has many contraindications:
- age 18+;
- periodontitis;
- installed fillings;
- presence of braces, implants;
- pregnancy, lactation;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- enamel pathologies;
- dangerous infections.
The disadvantages of this method include the high cost of the dentist’s work. However, the result justifies the cost. After grinding the enamel, fluoridation can be done—coating the crowns with a protective layer. This procedure significantly reduces the risk of re-formation of dense plaques. For fluoridation, special varnishes and gels are used. The procedure is completely painless and inexpensive.
When is curettage justified?
If there are a lot of deposits, they are located deep under the gums and the methods listed above do not allow you to completely get rid of them, then the doctor resorts to a procedure such as curettage. To carry it out, curettes are used - special instruments at the end of which there is a hook that engages the stone.
There are two types of curettage - closed and open.
Closed is used when periodontal pockets are less than 5 mm in depth. Actually, to carry it out you only need curettes and an ultrasonic scaler.
With closed curettage, periodontal pockets are cleaned with special hooks
An alternative to closed curettage can be the use of the Vector ultrasound device, whose impulses penetrate deep under the gums, eliminate the risk of injury and have a gentle effect on the roots of the teeth. The hardware method has a beneficial effect on tissues, improves their nutrition, and has a massage and disinfecting effect.
Open curettage is necessary if the periodontal pockets are deeper, which usually happens with progressive periodontitis, but here we are talking about a full-fledged surgical manipulation, since first the doctor exfoliates the gums, then cleans and polishes the roots, and then sutures the mucous membrane. If necessary, bone grafting is performed during surgery. After the procedure, drug support and anti-inflammatory therapy are required for rapid tissue healing.
With open curettage, before cleaning. peel off the gums
If there is a lot of plaque under the gums, then any procedure to remove it can be painful, so superficial or local anesthesia is first applied (with open curettage). Gels with lidocaine are often applied as a superficial “freeze”, which can cause an allergic reaction, so warn your doctor in advance if you are prone to allergies.
Bottom line
Tartar is most often the cause of caries and gum inflammation. These dense structures consist of dental plaque, mineral components contained in saliva and bacterial waste products. Regular professional cleaning of enamel from stone will protect teeth from caries and gums from inflammatory processes.
Sources used:
- Kuryakina N.V., Kutepova T.F. Periodontal diseases. — M.: “Medical Book”, 2003
- Lukinykh L.M. Periodontal diseases. Clinic diagnostics, treatment and prevention / L. M. Lukinykh, E. N. Zhulev, I. N. Chuprunova. - Nizhny Novgorod: publishing house NGMA, 2005.
- Smoking and periodontal disease // Australian Dental Journal. — 2009.
- The American Academy of Periodontology
Is it painful to remove subgingival calculus?
When cleaning stone in subgingival pockets, in most cases, mild pain occurs. This is explained by the fact that the stone is attached directly to the periodontium. Even a thin layer of enamel significantly reduces tooth sensitivity; it simply does not exist in the subgingival zone. Therefore, discomfort during the procedure is a completely reliable and expected phenomenon.
Subgingival stone must be removed, as it causes the development of putrefactive bacteria and contributes to the occurrence of caries and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.