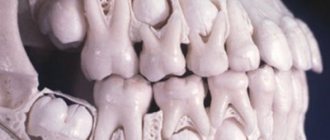
Tooth numbering systems: ISO (FDI), universal, Zsigmondy-Palmer (+ visual illustrations)
There is probably no student of the Faculty of Dentistry who at one time would not have been confused by various tooth numbering systems. Where did they come from? For what? And how to convert tooth numbers from one system to another? We will answer the first two questions in text, and the illustrations given in this material will help you with the third.
What is better - implantation or prosthetics?
A removable denture and a bridge supported on adjacent teeth are financially economical options, but they have a number of disadvantages:
- the jawbone underneath continues to atrophy, which leads to subsidence of the structure;
- the main load goes on the supporting teeth as a result of which they are destroyed;
- short service life - 5-7 years (for comparison, crowns on implants last 15 years or more, and titanium roots themselves last a lifetime);
- look unnatural;
- removable dentures cause discomfort due to the presence of an artificial palate, they press and rub;
- the presence of metal in the frame can cause an allergic reaction.
What does the dental formula look like in a medical record?
The dental formula of an adult, as well as a child, in the medical record of a dental patient looks in the form of a schematic table (Fig. 5), which will reflect only the serial numbers of permanent or baby teeth. Directly in this formula, the doctor will mark the missing teeth (in this case, the number is crossed out with a cross), which teeth are affected by caries, pulpitis or periodontitis, as well as which of them have crowns or bridges.
Dental formula in the form of a table in the medical record –
How many implants need to be placed?
In the absence of three adjacent units of the dentition, the following are placed:
- 2 implants - are introduced along the edges of the defect, serve as support for a permanent bridge prosthesis consisting of three welded crowns (two of them are fixed to titanium roots, and the central one is hinged);
- 3 implants - replace each lost tooth and, after healing, are covered with separate crowns.
Which option will be chosen and which orthopedic structures will be used depends on the location of the defect.
Front teeth
Implantation of three adjacent incisors has a number of features due to increased aesthetic requirements:
- white zirconium abutments are used that are not visible through the gum;
- if necessary, plastic surgery of soft tissues is performed;
- smaller implants are selected for installation in the narrow bone of the frontal jaw;
- Crowns made of lightweight materials with bite relief are placed as temporary prostheses.
If three teeth in a row are missing from the front, both restoration options are suitable (2 and 3 titanium roots), however, the installation of three implants followed by prosthetics with single crowns is preferable. In this way, identity to natural teeth is achieved, an even gingival contour is formed, which guarantees maximum aesthetics.
Chewing teeth
When replacing three adjacent units of the lateral jaw, high demands are placed on the functionality of the structures. They must be securely fixed, withstand severe chewing loads, and prevent atrophic processes.
In such cases, we choose the option of installing three implants with single crowns, since a bridge on two titanium roots does not provide uniform pressure on the bone and leads to its resorption.
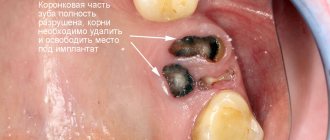
When implanting several teeth in a row, three or more, it is important to assess the condition of adjacent units. If they previously served as supports for a bridge, then, as a result, they are destroyed and cannot be restored - they will have to be removed and work with a more extensive defect.
Implantation of 3 teeth, E.max ceramic crowns
Attending doctor
Strigin Vladimir Igorevich
Sign up
Viola scheme
Literally since 1971, the Viola human formula began to be used in dentistry and is in great demand to this day. As already mentioned, it is the Viola table that is recommended by WHO for use in specialized educational institutions. The peculiarity of this formula is that each tooth located in the oral cavity has an individual number. A two-digit dental formula is also characterized by the fact that the teeth in it are designated by two numbers.
Let us consider the described human formula in as much detail as possible. Each tooth in the mouth has a number from 1 to 8. This number, in accordance with the formula, is indicated in it second. In the first place is the number that marks the tooth in the quadrant of the jaw. Note that in the human mouth there are 4 quadrants of the jaw. Both the upper and lower jaws can be conditionally divided into 2 parts: the right one belongs to the second quadrant, the left one to the first.
The Viola scheme is also used for numbering baby teeth. The theory itself has a slightly different form for the reason that the quadrants have completely different numbers - 5, 6, 7, 8.
How are permanent teeth numbered?
The numbering of permanent teeth differs significantly from the numbering of milk teeth (for more details, see the article: numbering of teeth in dentistry and their location diagram). The jaw is divided into 4 parts, each of which has an individual name:
- The first part is tens. This part begins with the upper incisor on the right and this tooth is designated by the number 11.
- The second part is characterized by twenties. Here the left upper incisor, numbered 21, protrudes first.
- The third part is called thirty. This part is located on the lower jaw on the left side, and the first canine in it is tooth number 33.
- The fourth part is forties. This part is located on the right side of the lower jaw. That is, the countdown starts from fang number 41.
To remember segmentation well, it is extremely important to define the reference point as required. Then it is recommended to move clockwise.
Baby Teeth - Children's Formula
As for the children's dental numbering system, it is slightly different from the one described above. To understand what principles of calculation the baby teeth have, you need to study how they are replaced by permanent teeth (we recommend reading: which baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth first?). In general, the process of changing teeth in children is as follows:
- at the age of 6-8 years, children initially change their central incisors above and below (numbers 32 and 42),
- the next to change are the upper lateral incisors, which occurs at approximately 9 years of age,
- at the age of 10, new lower canines appear,
- at approximately 11 years of age, the fours that are located on top also change,
- even before the child turns 12 years old, he should have fives on top, fours on the bottom, upper canines, and premolars,
- With the onset of adolescence (12-13 years), the primary molars fall out and numbers 17, 27, 37, 47 appear in their place.
How is root canal treatment performed?
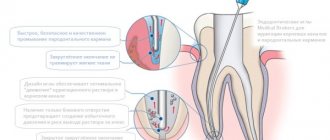
Filling cavities inside the root is one of the main conditions for the successful treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis. The stages of a doctor’s work are as follows:
- Determination of length. The doctor removes the pulp and, using special, thin instruments, measures the length. In good clinics, the process is carried out under the control of an apex locator - a device whose display reflects the moment the instrument reaches the root apex.
- Treatment for expansion, preparation for filling. The procedure is done manually or using an endodontic handpiece.
- Medical treatment using disinfectants administered through a thin needle.
- Filling with gutta-percha material. The pin is selected according to the size of the expanded space, it is filled with paste, the pin is installed and secured.
- X-ray quality control.
- Removal of excess, installation of temporary filling.
Tools for processing channels.
Standards for the provision of dental care do not allow simultaneous filling of canals and dental cavities. The crown should be restored at the next visit.
Root canal treatment is considered one of the most difficult dental procedures. There is even a special branch that deals with this problem - endodontics.
The main purpose of this procedure is to treat the inside of the tooth - the root canals, which are filled with pulp. The pulp is a soft tissue that includes nerve fibers, lymphatic and blood vessels, and connective tissue.
The complexity of the procedure lies in the fact that the canals are difficult to access by the dentist’s instruments, and it is also problematic to visually monitor the progress of the procedure.
Among the main indications for this type of dental treatment are inflammatory processes that lead to damage to soft tissue in the canal cavities.
Diagnosis to determine the need for treatment is carried out using x-rays or visually.
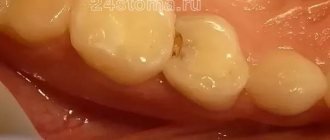
The cause of such inflammatory processes can be various dental diseases, most often pulpitis or caries. Also, with periodontitis, root canal treatment may be necessary.
Symptoms of the need for root canal treatment are usually the following: toothache or swelling of the gums near a tooth. Although in the chronic form of the disease, pain may not be observed, treatment of the canals will still be required.
Treatment of dental canals consists of the following stages:
- injecting anesthesia (usually through an injection into the gum near the affected tooth);
- separation of the tooth from the rest of the oral cavity using a cofferdam (a special rubber film that is attached to the tooth using small hooks);
- Opening the tooth using a drill to gain access to the inflamed pulp (on incisors, the hole is made from the side of the tongue or palate, on molars and premolars - on the chewing surface);
- The affected pulp or its remains are removed very carefully using a special tool, and the canals are simultaneously treated with medications;
- Drying the canals using special paper points;
- Filling canals with various materials, usually gutta-percha (rubber resin) is used.
The duration of the entire treatment procedure directly depends on the complexity of the underlying clinical situation, as well as on which teeth are being treated, since they all have a different number of canals. On average, the procedure takes from half an hour to an hour.
The success of this procedure will depend on how well the dental canals were cleaned, as well as how tightly they were sealed.
After canal treatment is completed, the crown part of the tooth is restored using various materials, most often with filling.
In cases where the dental crown is sufficiently damaged, filling is carried out using dental pins. To do this, the dentist removes part of the gutta-percha from the canal in order to obtain an area for installing a pin. After which the pin is attached to the tooth canal using special dental cement. After this, filling material is placed around the pin and the anatomical shape of the tooth is restored.
The filling of the tooth crown is carried out immediately after the canals are filled or at the next appointment.
After the procedure
After the root canal treatment process, the patient may experience toothache for some time, especially when pressing on a filled tooth, as well as general malaise and an unpleasant feeling of discomfort in the oral cavity.
In some cases, after the procedure, for several days, increased sensitivity of the teeth to temperature and chemical irritants is possible. Therefore, it is not recommended to subject the treated tooth to heavy loads. After a few days, all discomfort should disappear.
If the pain is intense enough, you can take painkillers.
If the pain does not disappear for a long time, then you need to contact your dentist again, since there is a possibility that the treatment was not carried out correctly, and this may also cause any complications.
For example, this may be a sign of an allergic reaction to the components of the material used for filling. In addition to pain, in such cases other signs of an allergic reaction appear: the appearance of a rash, itching. If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to determine which component caused the reaction, and then replace the filling with a new one that does not contain the allergen.
Also, if the filling was placed recently, then there is a possibility that it may fall out due to poor preparation of the cavity. The reason for this may be that the walls of the tooth were under-dried or, on the contrary, over-dried. In addition, the filling is likely to be damaged when chewing if the patient neglected the doctor’s recommendations and ate earlier than two hours after the procedure. Therefore, it is very important to follow all instructions from your dentist.
For any dental manipulations with the roots of teeth, a control x-ray examination is required.
Thanks to the capabilities of modern dentistry, even severely damaged teeth can be saved from extraction. Maintaining the integrity of the dental arch is very important to ensure even distribution of stress when biting and chewing food. This helps protect the jaw joints from deformation and the teeth from rapid wear.
It is important to eliminate caries in a timely manner so that no infection gets into the tooth pulp. If the inflammatory process affects the internal soft tissues, the nerve endings in the canals become irritated, and toothache begins. If the infection moves deeper into the canal, it can cause the following diseases:
- dental cyst - the immune system isolates a colony of pathogenic microorganisms in a dense sac near the apical opening;
- periostitis - the inflammatory process involves the tissue of the periosteum;
- osteomyelitis - pathogenic microorganisms enter the bone tissue and begin to cause damage to it.
In order to prevent such consequences, tooth canal treatment is carried out in a timely manner. To do this, the dentist performs the following actions:
- drills the tooth down to the pulp;
- An x-ray is taken of the desired section of the jaw in order to find out the number and exact location of the roots and canals of the tooth;
- injects a paste-like preparation that contains an anesthetic and paraformaldehyde;
- during the next visit, when all the nerve endings have already lost their vitality, the cavity of the dental roots is cleaned with special needles from soft and dead material;
- the internal space of each root is sterilized and filled with filling material;
- a picture is taken to control the quality of the development of the root system;
- the appearance of the tooth is restored.
Sealing of canals must be carried out in strict compliance with all sanitary standards. It is very important to locate and clean all the canals of the tooth, otherwise the patient will face complications after treatment.
The development of dental pathologies can be prevented only by following the advice of qualified doctors and observing the rules of oral hygiene.
So, for prevention purposes, dentists recommend:
- do not abuse the rules of hygiene, brush your teeth only in the evening and in the morning. More frequent exposure to tooth enamel contributes to its wear;
- hygiene procedures should be carried out half an hour after eating;
- use rinses to destroy germs remaining in the mouth after brushing;
- Cleaning should be carried out for at least 3 minutes, performing circular movements.
The main rule is that if the first signs of the disease are detected, you should immediately contact your dentist. This will help prevent further development of pathology and preserve teeth.
An important step in the process of treating root cavities is determining the working length of these canals. Not everyone knows the definition of tooth root length. So, the working length of the root canal is the distance from the edge of the frontal units to the apical constriction preceding the apical foramen.
Endodontics treats tooth root canals. When an endodontist treats a root canal, he performs the manipulations in the following sequence:
- diagnostics;
- X-ray;
- preparing the dental cavity for treatment;
- anesthesia;
- chemical treatment of instruments;
- opening of the tooth cavity;
- determination of the working length of root canals;
- medicinal treatment, cleaning and expansion of root canals along the entire working length;
- filling a tooth cavity.
Diagnostic methods
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=faBO3RuUahc
The first stage of tooth root canal treatment is diagnosis, which will help the doctor make the correct diagnosis and decide on a treatment method. To do this, the patient needs to undergo an x-ray to examine the part of the crown that the doctor cannot see. This procedure allows you to understand how many roots and canals the tooth cavity has. If the X-ray examination is ignored, then the cavity of the diseased tooth will have to be opened again.
Why do you need a dental formula?
The location of the dental units and their number are recorded by the doctor in the form of a table, which fully reflects their condition. The formula allows you to simplify the task of correct diagnosis of diseases in the oral cavity (caries, pulpitis, etc.) and the most specific recording of information in the patient’s outpatient record.
When visiting a dentist, especially with acute pain, the patient can rarely accurately indicate the causative factor. By looking at the chart and assessing the dental formula, the doctor will understand what he will be working with.
Reasons for creating a dental formula
Human teeth, despite their visual similarity, have certain differences. Each tooth is individual and designed to perform its function. Thanks to numbering in the dental field, examination of the patient's oral cavity is optimized to the maximum.
Clear and concise markings help to accurately record information in the patient's chart. In this case, the use of the same numbering system is observed. This is necessary so that the new doctor can decipher the medical history and past treatments that were performed by another dentist. Different dentists cannot use an individual calculation system, as this will change the patient's hospital history.
International two-digit Viola system
In practical dentistry, such designations are rarely used, and the teeth of a person’s jaws are simply numbered from incisors to molars (from 1 to 8).
International two-digit Viola circuit
The scheme was adopted by the World Health Organization in 1971 and is used throughout Europe [3]
All teeth are divided into 4 sectors (counterclockwise when viewed from the inside):
- The teeth of the upper jaw are on the right (respectively, the central incisor is 11, the second incisor is 12, the canine is 13, the first premolar is 14, the second premolar is 15, the first molar is 16, the second molar is 17, the third molar or wisdom tooth is 18).
- The teeth of the upper jaw are on the left (21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, similar to the right side) [4].
- Lower jaw teeth on the left (31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38).
- Lower jaw teeth on the right (41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48).
For children's teeth, a similar numbering is used from 51 to 85, or they are indicated in Latin numerals.
Haderup scheme
This scheme also uses the division of the jaws into segments, and individual numbers are assigned to the teeth. These numbers are calculated as in the international system - from the center of the jaw to its edge and have digital values from “1” to “8”. However, in this case, instead of the digital designation of segments, the signs “+” and “-” will be used. Here, a positive value indicates the upper jaw, and a negative value indicates the lower jaw. Showing the left and right sides of the jaws is very simple. You just need to place the desired sign to the left (for the left side) or to the right (for the right side) of the number that indicates the tooth. [3]
Haderup numbering scheme
| permanent teeth | |||||||||||||||
| top right | top left | ||||||||||||||
| 8+ | 7+ | 6+ | 5+ | 4+ | 3+ | 2+ | 1+ | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 |
| 8− | 7− | 6− | 5− | 4− | 3− | 2− | 1− | −1 | −2 | −3 | −4 | −5 | −6 | −7 | −8 |
| bottom right | bottom left | ||||||||||||||
| baby teeth | |||||||||||||||
| top right | top left | ||||||||||||||
| 05+ | 04+ | 03+ | 02+ | 01+ | +01 | +02 | +03 | +04 | +05 | ||||||
| 05− | 04− | 03− | 02− | 01− | −01 | −02 | −03 | −04 | −05 | ||||||
| bottom right | bottom left | ||||||||||||||
| baby teeth (alternative system) | |||||||||||||||
| top right | top left | ||||||||||||||
| V+ | IV+ | III+ | II+ | I+ | +I | +II | +III | +IV | +V | ||||||
| V− | IV− | III− | II− | I− | −I | −II | −III | −IV | −V | ||||||
| bottom right | bottom left | ||||||||||||||
Zsigmondy-Palmer scheme
The system was first used in 1976. It is also called square-digital.
To indicate that a tooth belongs to any segment, a special icon is placed next to the number (in one of the four corners) - “corner”. It seems to indicate a piece of the crown, showing how it grows - down or up. [3]
Zahnschema nach Zsigmondy
| permanent teeth | |||||||||||||||
| top right | top left | ||||||||||||||
| 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| bottom right | bottom left | ||||||||||||||
| baby teeth | |||||||||||||||
| top right | top left | ||||||||||||||
| V | IV | III | II | I | I | II | III | IV | V | ||||||
| V | IV | III | II | I | I | II | III | IV | V | ||||||
| bottom right | bottom left | ||||||||||||||
Upper canine
Average age of teething: 10-12 years
Average age of root formation: 13-15 years
Average length: 26.5 mm
As the longest tooth, the canine has an imposing shape designed to withstand strong occlusal forces. Its long crown with a thick layer of enamel is subject to abrasion by the cutting edge. As she ages, she often has deep cervical erosions.
The access cavity corresponds to the shape of the lingual surface of the crown and is oval. To obtain direct access, the cavity must be expanded incisally, but not so much as to weaken the actively functioning cusp. The initial access is made in the middle part of the crown from the palate. If the pulp cavity is deeper, a No. 4 or 6 ball-shaped extended bur may be required. A sweeping motion with this bur will open up the oval pulp cavity.
As it moves through the cervical portion and down apically, it remains oval. Thorough cleaning of this oval-shaped canal is difficult, so attention must be paid to targeted file processing.
The root canal is quite straight and long. Most canines require instruments 25 mm or longer in length. The last 2-3 mm of the top often bends in some direction.
The morphology of the canines rarely changes radically, and lateral and accessory canals are less common than in the upper incisors.
The vestibular cortical plate over the apex of the tooth root is often destroyed to form a fenestration. The apical foramen is usually located close to the anatomical apex, but can be located laterally, especially if there is an apical bend of the root.
Types of teeth
The human dental system belongs to the heterodont type. According to the norm, there are 32 teeth, but their number can be 28. Each has its own purpose. Dental formulas help distribute molar processes into groups based on their shape, location, and purpose.
Such numbering greatly facilitates the work of specialists. For permanent and baby teeth, various conditional expressions (formulas) have been created, slightly similar in the systematics of construction.
Understanding a dentist is not so difficult; it is enough to understand the dental formula and remember its diagram.
Rows of dental crowns are arches located on the upper and lower jaws, consisting of:
- 4 incisors (2 lateral, 2 central);
- 2 fangs;
- 4 premolars;
- 6 molars (possibly 4).
If we talk about molars, their number can be four, which corresponds to the norm. Molar wisdom teeth are considered a defect and are removed. As dentists say, this is a relic of the past. For ancient people, they were indispensable for grinding hard food; the shape of the jaw allowed them to cut through without problems.
Video about dental anatomy:
Until the age of three or four, children have a limited number of teeth to twenty. Their eruption starts at about six months.
The functions performed are identical to the permanent ones, while the teeth differ in their characteristic features:
- they are much smaller in size, have a delicate, bluish tint;
- dentin is not so developed, and the pulp is noticeably enlarged;
- the content of mineral compounds in enamel is much less.
To calculate the required number of teeth in children of different ages, a separate formula has been created:
N – required number of teeth n – child’s age in months
For example, 14 - 4 = 10 - in a year and two months the child will have 10 teeth. This system has a significant drawback - it has a limited period of use; after the child reaches two years of age, it is no longer suitable.
Children's arches number ten teeth:
- 4 incisors – 2 lateral, 2 central;
- 2 fangs;
- 4 premolars.
Numbering in pediatric dentistry
Due to the nuances of the anatomy of the children's jaw, numbering in dentistry for children is carried out differently. A child’s milk teeth, which usually appear between 4 months and six months, erupt simultaneously with the formation of the roots of permanent teeth. Because of this, both permanent and temporary teeth will be visible on the x-ray. The constants already have their own numbers, so children's teeth are counted from the next tens.
On a note! To count temporary teeth in children, there is a special formula in which the letter N indicates the number of teeth, and n indicates the child’s age. The formula is as follows: N = n – 4
X-ray of a child's teeth
Understanding the numbering of teeth and deciphering the formula of adult teeth will help the patient better understand their dentist. With the help of generally accepted values, the meaning of treatment becomes clear and the diagnosis recorded in the hospital record is clarified.