2657
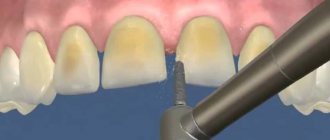
Preparation is a dental procedure that is based on grinding down a damaged tooth.
A manipulation is carried out to create additional space, which will then be used for the installation of an orthopedic structure.
Grinding is a mandatory procedure, without which it is impossible to properly fix the prosthetic structure.
The essence and purpose of the procedure
During turning, the surface layer of enamel is removed using special equipment equipped with high-speed burs with diamond tips.
Only with an ideally processed dental surface will the installation of the prosthesis be accurate and tight, which, in turn, will allow further avoidance of its rejection or the development of complications.
During preparation, the tooth is prepared for its further restoration. It takes on a cone-shaped shape (which simplifies the placement of the product), the remains of the carious cavity and old fillings are eliminated.
The procedure is considered by patients to be one of the most unpleasant in dentistry, so many of them do not decide to undergo prosthetics and end up losing their teeth.
But today, preparation technology has changed somewhat. The advent of new devices has made it possible to improve the technique, so there is virtually no pain or discomfort.
In addition, local anesthetics are used, which reduce the level of human sensitivity.
How is tooth preparation done?
The choice of preparation method directly depends on:
- clinical situation,
- technical equipment of the dental clinic,
- client's wishes.
Grinding of pulpless teeth is carried out without anesthesia (except for those cases when the doctor has to use special threads to move the gums back). If the procedure is performed on living (vital) teeth, the patient may require local anesthesia.
Grinded teeth are necessarily protected with temporary crowns. This allows you to keep damaged dental tissues in an acceptable condition until they are covered with a permanent prosthesis.
Teeth preparation should be carried out only in specialized medical institutions that have positively proven themselves in the dental services market. Only a professional and competent approach to the procedure allows not only to achieve the desired result, but also to avoid the development of complications.
Indications
The procedure is required in almost all cases when restoration is carried out in the oral cavity, namely:
- To restore or replace worn-out filling material;
- When reconstructing a dental element after a fracture;
- To correct a congenital defect of the coronal part;
- When installing veneers, crowns, etc.;
- To carry out other restoration activities as one of its stages.
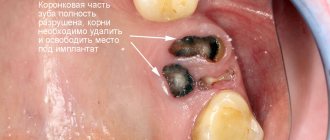
Preparation is also necessary if caries is discovered during the removal of the enamel layer.
In this case, to prevent the spread of pathogenic microorganisms to neighboring units, carious tissue and infected dentin are removed.
Rules for the use of glass ionomer cement for fixation of crowns and bridges, composition and properties of the material.
Come here if you are interested in reviews about ceramic inlays for teeth.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/koronki-np/nuzhno-znat-o-titanovyih.html together we will calculate the price of titanium crowns for teeth.
Options for manufacturing cast crowns –
Solid crowns can be made not only entirely from one metal, for example, a cobalt-chromium alloy. Their surface can also be sprayed with a yellow tint, or the front surface of the crowns can be lined with a more aesthetically acceptable material, for example, plastic. Also, cast crowns can be combined with metal-ceramic ones in one bridge prosthesis (we will also talk about this prosthetic option below)
- One-piece crown without sputtering (Fig. 1, 2, 4) - we have already said above that such crowns will look like the most ordinary well-polished metal.
- Solid crown with sputtering (Fig. 3) – if the patient is not satisfied with the color of shiny polished metal, then it is possible to spray such crowns with a “gold” look. These are already so-called metal crowns with spraying. However, it should be noted that spraying may have some negative effects on the oral mucosa due to the occurrence of electrochemical reactions (microcurrents). This phenomenon is called "galvanosis".
- One-piece crown with veneer (Fig. 5) - a one-piece crown with veneer has an overlay made of plastic or ceramic on the front surface (which is visible when smiling). However, it should be noted that such crowns often have chips of plastic/ceramics. The cost of a cast crown with ceramic lining will not be much lower than that of a metal-ceramic crown, lined with ceramic on all sides. A cheaper option is also possible: veneering with plastic (such crowns are called “metal-plastic”).
- Combined bridges (Fig. 6) - when making a bridge with supports for the 5th and 7th teeth, it is not necessary to make the entire bridge from 3 crowns - entirely from metal ceramics. You can make metal-ceramic only teeth that fall into the smile line, for example, only 5 or 5-6 teeth (as in Fig. 6). The remaining crowns will be made without ceramic veneer, i.e. solid cast.
Techniques
Not long ago, a special drill was used to treat problem units. Today, grinding technology has improved significantly.
Several new techniques have been developed that have made the manipulation more comfortable, as painless and safe as possible:
Ultrasonic
Grinding occurs using ultrasonic waves , which are emitted by a high-precision device. The advantages of the procedure include:
- absence of negative feelings;
- minimal risk of damage to hard tissues;
- pulp safety;
- painlessness;
- no heating of dentin and enamel.
Laser
This technique is based on the process of heating water in dental tissues using a pulsed laser. Its effect allows you to easily remove the affected areas with an air-water flow.
The advantages are considered to be high precision of processing, silent operation of the device, absence of damage and heating of tissues.
Disadvantages - there is a minimal risk of infection, the technique can only be used for surface treatment.
Air abrasive
Here, instead of a drill, a mixture of abrasive substance and air is used , supplied under pressure. This force is enough to remove the required amount of enamel and dentin.
The advantages of the technique are:
- safety;
- speed of manipulation;
- minimal heating of tissues;
- processing accuracy;
- no vibration;
- preservation of the maximum volume of healthy tissue;
- painlessness.
But at the same time, air abrasive grinding cannot be used as an independent technique due to the fact that it can only act on surface layers.
Can be used in combination with other methods of preparing teeth for prosthetics.
Chemical
Preparation involves the use of chemically active substances (for example, acids), which, through their action, soften the desired area of enamel.
The positive aspects of the technique are painlessness, safety for healthy tissues, and the absence of heating.
The only drawback is the length of the process (on average, it takes about 30 minutes to process one unit).
Tunnel
This technique is the most common due to its ease of implementation and the ability to accurately control the thickness of the surface being removed.
It is carried out using a special diamond tip (or metal) with high rotational ability.
The only advantage of tunnel preparation is the high precision of processing.
The method has significantly more disadvantages:
- strong heating of the enamel;
- need for pain relief;
- high probability of tissue damage;
- there is a risk of infection.
It is impossible to single out the best method from the entire list. All of them are selected individually for each patient , based on the condition of the oral cavity, examination results, and in accordance with the specific type of defect.
Types of ledges
A ledge is the part of hard tissue remaining after preparation on which the future prosthetic structure is planned to be secured. There are three varieties of it:
- Rounded . Used under metal-ceramic prosthesis. Allows you to preserve the maximum amount of hard tissue. Thickness varies from 0.8 to 1.3 mm.
- Knife-shaped. Designed for solid metal crowns. Ideal for turning inclined pieces. The width ranges from 0.3 to 0.5 mm.
- Brachial. It is the most reliable and durable when securing orthopedic products, but is uneconomical in terms of removing a large volume of tissue. The width is about 2 mm. Requires removal of the nerve from the tooth (depulpation).
If you do not create a ledge before prosthetics, the quality of the fit of the prosthesis will decrease significantly. This circumstance complicates oral care and increases the likelihood of developing recurrent caries.
Rules for grinding teeth
- The doctor must prepare the patient: explain that you cannot move sharply during preparation, and if necessary, you need to give a sign with your left hand.
- Grinding of living teeth under a metal-ceramic crown is carried out only under anesthesia.
- The preparation is carried out as sparingly as possible: the doctor should not grind off hard tissue more than is required to restore the tooth with a crown while maintaining its anatomical shape.
- It is impossible to grind teeth continuously: during processing there should be frequent breaks, during which the tooth is irrigated with water to avoid overheating of hard tissues.
- Before work, the dentist must check the technical serviceability of the drill and the fixation of the burs in the grinding tip.
Tactics
The entire grinding process can be divided into two stages:
- Elementary. The dentist determines the amount of tissue to be removed (for this he makes grooves - special notches).
Be sure to clean the tooth of damaged enamel and dentin, and remove “extra” tissue from the lateral convex surfaces. Such actions allow you to create the optimal size of the unit and give it the desired shape. - Final. Includes removal of carious areas (if any) and “old” fillings, pulp protection, as well as final treatment of the tooth cavity and walls.
At the end of all manipulations, the doctor evaluates the quality of the turning and the degree of sealing before applying the composite.
What modern dentistry offers for increased wear of hard dental tissues, and how effective the treatment is.
In this publication, we will discuss how to prevent metal allergies from occurring in dentistry.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/ottisknyih-materialov-ortopedicheskoy-stomatologii.html we suggest you familiarize yourself with the classification of impression materials in dentistry.
Some nuances
Each orthopedic product has its own rules and requirements for its installation. Depending on the type of prosthesis, the preparation stages differ.
Under the crown
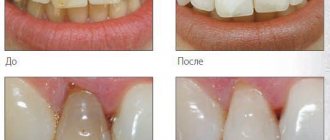
When it is planned to install a solid cast structure, grinding begins from the side surfaces to avoid damage to adjacent units.
For metal-ceramic crowns, about 2 mm of enamel is removed from the sides of the tooth, and a ledge is created that matches the type of product selected. To ensure a tight fit, the enamel is not polished, but is left slightly rough.
When a porcelain crown is installed, the tooth is ground down to a cylinder or cone shape, however, the ledge must be 0.1 cm into the gum.
If the prosthesis is made of zirconium, the ledge is formed with clear boundaries of a round or shoulder-shaped shape.
In the video, watch the process of preparation with a ledge for installing a crown.
Under veneer
Since a veneer is an overlay on the outer side of a tooth, when turning, special attention is given to the front surface
.
The sides are processed in two ways:
- leaving contact between teeth;
- with output to the inner side of the ledge boundaries.
Another point is that if the veneer is made of ceramic, the preparation is carried out to the gum. If a composite is used, no preparation is carried out (the layer is left slightly rough to improve adhesion to the material).
For tab
An inlay is a partial prosthesis, so when grinding it is important to make the side walls parallel and maintain the dimensions of the corners. Compliance with these conditions will ensure tight insertion and reliable fixation of the insert in the cavity.
Important! To eliminate the likelihood of developing repeated caries, the cavity of the tooth being restored is slightly expanded.
Under a prosthesis
In this case, preparation is carried out with the aim of shortening the prosthetic elements. During treatment, all thin and sharp walls, dentin and enamel protrusions are removed. The best option is to give the cavity an oval shape.
Under special circumstances, the pulp is first removed.
When splinting
Splinting is a procedure that secures units in a row and prevents their further loosening. The procedure involves minimal grinding of the enamel.
Typically, dentists adhere to the technique used when installing metal-ceramic crowns.
Plastic crowns - indications, preparation features
Speaking about the indications for the use of artificial crowns in general, we partially discussed the issue of indications for the use of plastic crowns. In addition to this, we consider it necessary to note the following. While distinguished by good aesthetic properties, plastic crowns are inferior in strength to other types of similar prostheses. However, with a correct assessment of the clinical picture, competent preparation of the abutment tooth and good technical performance of the prosthesis, high quality can be achieved.
The general indication for the use of plastic crowns is aesthetic requirements, but there must be certain clinical conditions, in the absence of which it is better not to make this prosthesis. In particular, with a low wide clinical crown, pathological abrasion of teeth, allergies, deep bite and absence of lateral teeth, which are relative contraindications. The presence of defects in the lateral parts of the dentition, especially Kennedy classes I-II, is also a relative contraindication.
Features of tooth preparation. Considering the need to make a more durable plastic crown, the tooth tissue should be ground to a greater thickness. The initial reference point can be a tooth prepared for a stamped crown (Fig. 185). It should be borne in mind that when applying a stamped crown, the space between it and the abutment tooth is filled with fixing cement. When making a plastic crown, the volume is almost completely restored by the prosthesis material. Between it and the hard tissues of the tooth there remains only a thin layer of cement, which is necessary for fixing the artificial crown. It is better to prepare a tooth with a shoulder. However, this method requires a lot of skill, so orthopedists often do it without a ledge. Although this technique is indicated when the cervical part of the tooth is affected by caries and it is impossible to make a ledge.
A layer of tooth tissue up to approximately 1.5 mm thick is removed from the chewing surface or cutting edge. Particular care is taken to remove hard tissue from the palatal surface of the front teeth, where there is a danger of opening the tooth cavity. Separation from antagonists should be within 1-1.5 mm. The side walls of the tooth are additionally ground so as to obtain a barely pronounced cone (inclination no more than 3-5 degrees). With a more pronounced cone, there is a danger of worsening fixation, and with insufficient inclination, a crown with thin walls is obtained. At the end of the preparation, sharp corners are carefully smoothed out and the degree of separation of the prepared tooth from the antagonists is checked both during central occlusion and during lateral movements of the lower jaw. Then they begin to take impressions. When making plastic crowns, the best results are obtained from an impression made from alginate materials or a double one. The color of the plastic is determined, and this ends the first clinical stage.
Did you like the article? Share with friends
0
Similar articles
Next articles
- Plastic crown manufacturing technology
- Finishing, grinding and polishing of a plastic crown
- Application and fixation of a plastic crown
- Metal-plastic crowns
- Metal-plastic crowns on a stamped base
Previous articles
- Fixing a stamped crown on a tooth
- Whitening, grinding and polishing of a stamped crown
- Fitting stamped bits
- Methods for stamping artificial crowns
- Making a metal stamp
Add a comment
Answers to frequently asked questions
Since the term “dissection” is not widely used among patients, many of them are keenly interested in information regarding this procedure itself.
- What layer of fabric is removed? The amount of grinding depends on the type of structure being installed, the characteristics of the tooth surface and its original volume.
Usually no more than 2 mm of hard tissue is removed. But this volume depends on the type of prosthesis being installed. So, before placing the inlays, only 0.5 mm is ground on each side. - How much does it hurt ? Modern technologies allow the procedure to be performed absolutely painlessly. When processing “live” units, local anesthesia is administered.
- How long does the process take? The duration of the process depends on the technique chosen by the doctor. On average, processing takes from half an hour to 2 hours.
- Is it possible to do prosthetics without preparation? Unfortunately, it is impossible to fix the product in a high-quality manner without grinding. If this manipulation is skipped, a person may face a number of negative consequences in the future.
- Can this be done for children ? This procedure has no restrictions regarding the patient's age. Children usually undergo chemical preparation.
- Why do my teeth and gums hurt, and what can be done ?
The cause of pain may be too deep grinding, as a result of which the dentist left a very thin tissue layer, and the nerves in the pulp react quite painfully when eating hot/cold foods. Another common cause of pain after turning is inflammation. In any case, the manifestation of this symptom is a reason to immediately seek medical help.
Possible complications
Complications arise only if the dentist performed the preparation poorly. In such a situation, the following most often develop:
- inflammation of the gum tissue (in case of infection);
- secondary caries (with incomplete cleaning of the cavity from carious tissues).
If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, complications will subsequently lead to premature loss of supporting elements.
To avoid the negative consequences of grinding, you should contact only a highly qualified dentist.
To do this, having read the reviews and ratings in advance, you need to contact a center that provides quality services to its patients in accordance with all norms and rules, and strictly adhere to all medical recommendations and prescriptions.
Turning for metal-ceramics: is it painful to prepare a tooth?
In modern dentistry there are atraumatic methods and anesthetics that make grinding for crowns painless. Most often, anesthetic drugs are used to grind living teeth to relieve pain during preparation.
If the patient is allergic to painkillers, the dentist selects the most suitable treatment method: laser, chemical method, ultrasound.
Sometimes patients complain that the tooth hurts after grinding for a crown. As a rule, symptoms are short-lived and disappear a couple of days after the procedure.
The main reasons why teeth may hurt after grinding:
- Grinding away a large layer of hard tissue under metal-ceramics without first removing the nerve fiber from the pulp. The tooth becomes sensitive to temperature conditions or pressure. The pain goes away on its own after a few days.
- Trauma due to retraction cord. This is a special thread that the doctor uses to form a ledge between the teeth and the prosthesis - this is how the crown “sits” tightly on the teeth and is securely fixed with cement. The injured gum may turn red and even swell slightly, but the symptoms quickly subside.
- Inflammatory process. Pain in the teeth due to developing pulpitis and periodontitis does not go away after a couple of days, but only intensifies. In such cases, you should immediately consult a doctor for treatment. If the pain began after the crown was installed, it will require subsequent replacement.
Reviews
Modern methods of tooth preparation have made it possible to carry out prosthetics almost painlessly, quickly and with better quality.
This is evidenced by numerous reviews from patients who have undergone the process of restoring teeth with prosthetic structures.
You can share your experience of restoring teeth with orthopedic structures, talk about the impressions and feelings you experienced before and after the procedure, by leaving a comment on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags fixed prosthetics prosthetics
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
The importance of timely detection and elimination of hidden caries
Next article
What can lead to darkening of teeth and how to correct the situation