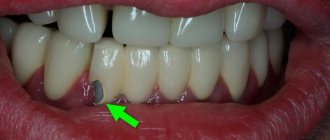
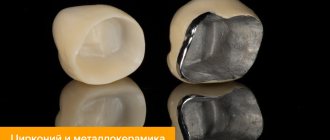
Reasons for chipping ceramics in metal-ceramic structures
At the junction of the metal frame of the denture and the ceramic coating, strong stresses often arise, which in stressful situations lead to the formation of cracks, chips or spalls in the ceramics.
The main reasons for ceramic chipping are:
- Mismatch between the thermal expansion coefficients of ceramics and the metal alloy from which the frame is made.
- Unreasonable choice of metal ceramics as a material for a fixed prosthesis in some patients (for example, those suffering from bruxism).
- If the intermediate part of a metal-ceramic bridge is too long, the frame of which is made of precious alloys (which have lower rigidity than non-precious alloys), chewing loads on it can lead to chipping of the veneer.
- Incorrect tooth preparation, for example, insufficient taper, can lead to stress in the framework of the metal-ceramic crown and subsequent chipping of the veneer.
- Chips often occur when performing orthopedic work (especially large-scale ones) without an articulator and a facebow.
- When fixing a metal-ceramic prosthesis with excessively thick cement, or when foreign bodies get between the tooth stump and the crown.
- Chips may be a consequence of incorrect modeling of the metal-ceramic frame of the future prosthesis:
- insufficient height of the frame, which necessitates the layering of an excessive amount of ceramics - unmodeled tooth relief - non-compliance with the technology of mechanical and chemical processing of the metal frame - holes in the metal frame, which technicians close with ceramics. Subsequently, after cementing the crowns, tension arises here, since the cement presses evenly on all walls and later a chip forms in this place and rapid decementing of the structure.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
- The cause of chipping may be stress in the ceramics or metal frame, resulting from non-compliance with technological rules for working with ceramics:
- overheating of the metal during firing of ceramics - violation of temperature relationships during successive firing and cooling of ceramics - violation of the rules for working with ceramic masses offered by manufacturers - non-compliance with ceramic processing technology.
- Careless or careless handling of the patient with prosthetic metal-ceramic structures. The fragility of ceramics under inadequate loads, and less often during sudden temperature changes, should be taken into account. We also recommend that you read the article about installing ceramic crowns at 32Dent dentistry.
Review of plastic dental crowns – stages of their manufacture, indications for installation and current prices
Article navigation
- Short description
- What types of plastic crowns are there?
- Materials
- Manufacturing methods
- Indications and contraindications
- Pros of crowns
- Flaws
- Stages of dental restoration
- Installation Features
- How long can you wear it?
- Life time
- Price
Question for a specialist
Today dentistry has a variety of materials for prosthetics.
Among others, plastic stands out, which has fairly good aesthetic characteristics and low cost. Should I wear plastic crowns permanently? Of course not. But some types can be used for quite a long time. Next, we will talk about the features of dental crowns made of plastic, the pros and cons of these orthopedic structures, their service life and prices.
Materials used in metal ceramics
In metal-ceramics, a metal frame is used as a base, which solved the problems of excessive fragility of ceramics. Ceramic is applied layer by layer to the outer surface of the metal and held firmly in place by sintering. As a result, a metal-ceramic crown is reliable, durable and very beautiful. Plus, it looks like a real healthy tooth.
To effectively protect teeth from destruction under crowns, teeth are treated with a protective paste that releases fluoride into the tooth tissue. Modern dental cements are used to fix metal-ceramics, which makes it possible to achieve the strongest fixation. A high-quality metal-ceramic structure lasts for decades. The average service life of cermets on base alloys is 10-12 years. On gold-platinum alloy 15 years or more.
Brief description of products
Plastic crowns are artificial dental crowns in the form of single caps made from dental plastics. They are used to protect a tooth when it is severely damaged, as well as to restore the aesthetics of a smile. The “cap” is attached to the abutment tooth, core inlay or implant (more precisely, to the abutment on the implant). Externally, it imitates a natural tooth quite well, because plastic can be easily painted to the desired shade. What the prosthesis looks like is shown in the photo below. Plastic crowns are classified as non-removable. To restore several teeth in a row, plastic crowns are combined into a bridge.
Materials for production
Plastic dental crowns are usually made from materials obtained by mixing two components - liquid and powder. As a result, a plastic mass is formed from which the prosthesis is already made. But some manufacturers produce ready-made paste in small dispensers. There are acrylic monomer and non-monomer materials - for example, Tempron from GC (Japan). As well as plastic composite non-monomer compositions - for example, DentaCrown from Itena (France), Protemp 4 from 3M ESPE (USA). There are also initially solid PMMA (thermoplastic plastic) blocks. Telio CAD from Ivoclar Vivadent is also such a material.
There are plastic crowns in which the plastic is specially reinforced at the production stage - for greater strength and wear resistance of the structure. For example, this could be reinforcement - strengthening a plastic cap with a metal or fiberglass mesh. There are also metal-plastic products - they are based on a metal cap, which is covered on top or only on the side with a layer of light synthetic material1.
The nuances of installing metal-ceramic dentures: consultations with Berezki dentists
Patients who decide to restore the fullness of their dentition with metal-ceramic products should know that there are different types of structures. They differ from each other in terms of strength and reliability, aesthetic characteristics, service life and price.
You need to understand that to achieve a positive effect, it is not enough to simply choose the most expensive products. It is very important to carry out the preparatory procedures correctly and efficiently:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- treatment and filling of root canals if they are preserved;
- grinding of dental units.
After therapeutic manipulations, a control X-ray examination is required to prevent negative consequences. Only after making sure that the preparatory stage has been completed flawlessly does the doctor begin taking impressions from which the crown is made.
Methods for making dentures
The production of plastic dental crowns can be carried out in two ways:
- direct: in the dentist's office, i.e. in the presence of the patient. Very fast method of prosthetics,
- indirect: in a dental laboratory based on previously taken impressions of the patient’s dentition. It takes longer, but as a result the product “sits” more accurately on the support and adheres to it without gaps.
Plastic crowns can be made using cold or hot polymerization (hardening of plastic compounds). There are also stamped and milled plastic "caps". The latter are distinguished by the highest production accuracy, because are cut on computerized machines, which eliminates any errors.
Another option is standard, that is, templated plastic crowns. These are used in removable or adaptive dentures on implants. Essentially, these are just ready-made teeth that are inserted into an acrylic base.
Alloys in cermets
To make a metal-ceramic crown, the dental technician first makes a metal frame that exactly matches the contours of the tooth prepared for prosthetics. The frame is the most important part of the design of a metal-ceramic crown.
There is a saying: “the mouth is the beginning of the stomach, saliva is the first “stomach” juice.” Saliva is rich in a variety of enzymes. As a result of a chemical reaction, the metals that make up the alloy of the metal-ceramic prosthesis are “washed out” by saliva into the oral cavity in microdoses. Next, saliva with microdoses of metals is swallowed, absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and enters the liver. This causes slow poisoning of the body.
The ceramic layer covering the outside surface of the metal frame is a good barrier to saliva and is an excellent insulating material. The teeth are isolated from the metal with high-strength cement, which completely protects your tooth from harmful factors, but metal is still present in the structure, and no one can guarantee that subtle biochemical reactions between your body and the metal frame do not occur.
There is no “best alloy” that suits everyone; patients have different sensitivities to certain elements. The determining factor here is the degree of corrosion. The fewer components of the alloy are dissolved, the less danger there is of a pathological reaction of the body to metal-ceramics. It follows from this that the alloy should contain a minimum of base components, because they are more susceptible to corrosion compared to noble metals.
Determination of the allergic effects of the alloy is carried out using tests on animals. Direct transfer of results to humans is not shown, however, it is possible to establish the allergic potential of the alloy.
Indications and contraindications
Plastic crowns are suitable for installation on both chewing and front teeth. And also for implants. But, we repeat, this will be temporary prosthetics. However, you cannot do without it in the following cases:
- it is necessary to preserve or restore the aesthetics of the smile while a permanent prosthesis is being made: this becomes especially important when the upper front teeth are prosthetic - after all, the entire smile depends on their appearance,
- it is necessary to protect the ground teeth from infection from outside or from injury,
- you need to maintain the level of the gum before installing a permanent prosthesis: the point here is that the layer of enamel on the stump can be worn down quite strongly, plus the stump is ground down with a slight ledge near the gum. And if the permanent crown takes a long time to be made - more than 2-3 weeks, then the gum tissue will simply grow onto the ledge (bottom of the stump). Therefore, permanent installation will be painful, there will be bleeding, inflammation of the gums, pain and discomfort in wearing.
There are practically no contraindications to installation. But one can highlight the risk of allergies, especially if conventional plastics are used rather than composite monomer-free compounds. It is the monomer that most often causes allergies. At risk are children, people of retirement age and those who are already allergic to anything. Another contraindication is the inability to wear prosthetics at a given time. For example, if you have recently suffered a serious illness or in the coming weeks it will not be possible to maintain good oral hygiene.
How is a crown installed on a tooth?
If you decide to put a crown on a tooth, then it will be useful for you to know what stages of this process you will have to deal with. In the process of placing a crown on a tooth in dental clinics, the following stages can be distinguished...
Initial consultation with an orthopedist (prosthetist) −
During the initial consultation, the doctor, assessing the condition of the teeth externally and using x-rays, must offer possible prosthetic options, and the patient, accordingly, must approve one of the options. Based on this, a treatment plan is drawn up, which may take into account -
removal of non-viable teeth,- preparing teeth for crowns (filling, depulping),
- choice of the type of crowns, for bridges - the number of supporting teeth, etc.
- The cost of making crowns and treatment in general is calculated, the deadline for prosthetics is determined, after which the patient must sign a treatment plan and a contract for the provision of services.
Important: at this stage the patient must choose one of the types of artificial crowns offered to him. Choosing the type of crown is not easy for the average patient, and there are a lot of pitfalls that the dentist will never tell you about. Articles to help you choose -
→ Pros and cons of metal-ceramic crowns → How to choose crowns for front teeth
Preparing teeth for prosthetics −
In some cases, crowns can be placed on living teeth. This is preferable because dead teeth are more fragile, and therefore, if the teeth are left alive, this has a positive effect on the service life of the crowns. In what cases can teeth be left alive? As a rule, we are talking about large chewing teeth. This is due to the fact that large teeth have a greater distance from the surface of the enamel to the pulp of the tooth (than single-rooted teeth) and, therefore, the risk of thermal burn of the pulp when grinding the tooth for a crown will be much lower.
Moreover, under crowns made of metal-free ceramics, even the majority of single-rooted teeth can be left alive. This is due to the fact that under ceramics the tooth is ground down by 1.0 from the side surfaces, and under metal-ceramics – on the same surfaces by 2.0 mm. Therefore, metal-free ceramics also allows you to increase the service life of the tooth itself under the crown.
When using metal-ceramic prosthetics for single-rooted teeth, the nerve is almost always removed. If this is not done, then turning such a tooth can lead to a thermal burn of the dental pulp, i.e. neurovascular bundle. In this case, after some time, its inflammation will develop, and the crown will then have to be removed and the tooth re-treated. If the tooth under the crown is destroyed by a carious process (there is pulpitis or periodontitis), then planned depulpation of the tooth and treatment of inflammation at the apex of the root are required.
When depulping a tooth, it is carried out -
- removal of a nerve from a tooth,
- instrumental treatment and expansion of root canals (Fig. 2),
- the canals are filled with gutta-percha (Fig. 3),
- after which a filling is placed on the crown part of the tooth (Fig. 4).
Important: if the crown part of the tooth is destroyed by 1/2 or more, the tooth must be strengthened with a pin fixed in the root canal (otherwise the crown can easily fall out along with the filling). There are 2 main methods for restoring severely damaged teeth.
What is the best way to restore a badly damaged tooth? –
The first option (Fig. 5) – patients also call it a crown with a pin or a crown on a pin. This is when a pin is screwed into an already filled root canal, and then, based on it, the crown part of the tooth is restored using filling material. Only after such restoration is the tooth ground down for a crown.
- The second option (Fig. 6-8) – the crown part of the tooth is restored using a stump inlay.
Such an inlay is cast from metal in a dental laboratory and consists of a root part (which is fixed in the canal) and a crown part, which has the shape of a tooth that has already been ground for a crown. This method provides greater reliability, strength and longer service life of the crown. Making a core inlay for a crown –
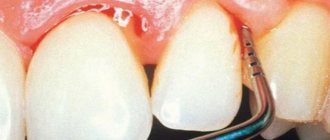
Preparation of teeth for crowns −
In common parlance - grinding teeth. The preparation process is carried out by an orthopedic surgeon, who (using a drill and a set of diamond burs) gives the tooth a certain shape. Preparation is a painful process if living teeth are ground down. In this case, local anesthesia is required. When dead teeth are ground down, anesthesia is given only if the doctor needs to strongly press the gum away from the tooth during preparation.
The tooth tissue is ground down by the doctor to the thickness of the future crown (Fig. 9-11). Crowns made of metal-free ceramics (for example, zirconium dioxide or E.max glass ceramics) require less grinding of the tooth tissue - approximately 1.0 to 1.5 mm on different tooth surfaces. But under metal-ceramics, the teeth are ground down on all sides by 1.5-2.5 mm - as a result of which almost nothing remains of the tooth. As a result of preparation, the tooth crown takes on the appearance of a “stump”.
Tooth preparation for metal ceramics –
Important: high-quality tooth preparation for a crown is a very complex and time-consuming process. The most difficult thing here is to create a ledge in the gingival part of the tooth crown. The reliability and service life of your crown largely depends on the correct formation of the ledge. It must be admitted that most doctors make a lot of mistakes at this stage. How the ledge is formed is clearly shown in the video below.
Grinding front teeth for crowns: video
Taking impressions, making plaster models of teeth –
Impressions are taken from the ground teeth using special impression compounds (Fig. 12). Subsequently, based on these casts, plaster copies of your teeth are created in a dental laboratory (Fig. 13). Such plaster models depict the patient’s teeth with very high accuracy, including those ground for crowns, and it is from such models that they are manufactured.
A very important question here is what kind of impression material you will use to take impressions. Good impression compounds are “A-silicone” or, better yet, “polyester compound”. But usually, in order to save money, alginate masses or C-silicone can be used, which will affect the quality/accuracy of crowns for the worse. As a result, crowns may not fit the ground teeth, may not fit well around the neck of the tooth, and the latter will inevitably lead to rotting of the tooth under the crown.
Taking an impression of your teeth is usually a tolerable procedure that is not accompanied by pain. However, sometimes the doctor needs to insert a retraction thread deep into the gingival sulcus in order to move the gum away from the ground tooth and thereby obtain a better impression of the teeth at the gingival margin. Gum retraction is quite painful and is best performed under anesthesia. Gum retraction also has a disadvantage - very often gum avulsion can lead to the appearance of a periodontal pocket.
But there is also a group of patients for whom taking impressions is a very big problem. For example, if you have an increased gag reflex. Of course, before the actual impression is taken, you may be sprayed on the root of your tongue with Lidocaine spray (an anesthetic), but this still does not help much. In this group of patients, it is advisable to additionally use sedatives before the procedure itself.
How dental impressions are taken in dentistry: video
Making crowns in a dental laboratory –
So the casts were taken, plaster models were made. The dental technician begins to make your future crowns based on these models. Because While the manufacture of metal-ceramics and ceramics may take several weeks, while permanent crowns are being made, temporary crowns are usually made of plastic. They will not only restore aesthetics, but also protect sharpened teeth from destruction by the aggressive environment of the oral cavity.
The most important thing at this stage is that we recommend getting dentures only in those clinics that have their own dental laboratory (located directly in the clinic itself). This is necessary so that the orthopedic dentist has direct contact with the dental technician at the stages of making crowns, and the dental technician can always come to the office when trying on crowns.
The latter is very important if you want to get good aesthetics of the crowns, well-formed contact points with neighboring teeth, etc. Of course, none of this will help if your prosthetist's hands are growing out of a bad place, but at least it will improve your chances of receiving quality service.
Trying on crowns –
Before the dental technician finishes his work, it will be necessary to try on the unfinished work.
For the first time, the frame of the crowns is usually tried on, which can be either metal or made of metal-free ceramics. The second time they try on an almost finished crown, on the surface of the frame of which (after the first fitting) layers of ceramic mass, as well as dyes, were applied. It is at this stage that you can still say that you don’t like something (color, shape), and it can be corrected. Those. It is at this stage that the color is finally agreed upon, and if you have agreed on it and, moreover, signed the medical record that everything suits you, then it will be too late to make a claim. Therefore, our advice: if you are not satisfied with anything and you are ashamed to point it out to the doctor, be sure to say so, and do not sign anything until you are really satisfied with the results of the work.
After the final fitting, your crown is sent back to the laboratory where it goes through the glazing process to achieve its final look and shine. At your next visit, you will have ready-made crowns fixed with permanent or temporary “cement.”
Video of fitting of E.max ceramic crowns –
Temporary / permanent fixation of crowns –
In principle, there is no need for temporary fixation as such. It is necessary, and you should insist on it only if for some reason you are not sure of the quality of the work or something confuses you (the color/shape of the crowns, their visibility against the background of neighboring teeth). If the crowns are placed on permanent cement, they can only be removed by sawing.
If you insist on temporary fixation, and the dentist refuses you, this is also a signal to think about the quality of the work. Such cases and conflicts on this matter between the doctor and the patient are not uncommon, and here you must remember that it is you who pay the money and decide how everything should be - you too. Usually 1-2 days is enough to get used to the new crowns, determine how well the color matches the desired one, and after that come back to the clinic and have the crowns placed on permanent cement.
Advantages of plastic crowns
The advantages of plastic crowns lie in the characteristics of the material. After all, it is inexpensive, easy to process and has the color of natural enamel. The positive aspects look like this:
- you can quickly restore a damaged tooth: literally in 1 hour, maximum in 1 day,
- good aesthetics: plastic does not stand out from the dentition,
- low cost,
- allows you to protect the ground tooth, adjacent gums or tissue around the implant: while a permanent prosthesis is being made or while the implant is taking root,
- prevents neighboring teeth from moving towards the defect (“holes” in the row).
As for the ground teeth, if you leave everything as it is (and do not put a temporary plastic crown on the stump), then the remaining layer of dentin without enamel will be attacked by microbes, destroyed by acids or trauma. Since in general dentin is much weaker than enamel. This is reflected in pain throughout the tooth. The shape of the stump may be disrupted - i.e. the prosthesis being manufactured simply will not fit.
What shortcomings can be found
There are few disadvantages (in number) of plastic crowns on teeth, but they are quite significant. See for yourself:
- fragility of the material,
- a high probability of gum inflammation during long-term use due to a not very tight fit to the gum and support (this does not apply to milled dentures made using CAD/CAM technologies),
- there is a high probability of caries appearing under the prosthesis if the period of wearing it is exceeded,
- risk of allergies,
- rapid loss of color, darkening, pigmentation from food and other dyes: due to the presence of micropores on the surface.
Afterwards, the plastic prosthesis is replaced with a more durable, aesthetic, durable one - for example, ceramic, metal-ceramic, zirconium dioxide, ceramic composite. That is, a permanent one that will last for many years.
BEST REMOVABLE DENTURE - 20,000 rub.
All manipulations for the manufacture, installation and fitting of the prosthesis, including impressions, are included.
Save RUB 10,000! >> Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Stages of dental prosthetics with complete edentia
The production of a complete removable denture begins with an examination of the patient’s oral cavity, diagnosis of the condition of the dental system, and selection of a suitable design. The first impression is taken with a standard impression tray. Depending on which design is chosen, the impression mass is selected. The impressions are sent to the laboratory, where a dental technician casts plaster models and makes a wax base with occlusal ridges and custom impression trays.
On the second visit, using these trays, the doctor takes functional impressions, and using rollers, determines and fixes the occlusion. All information is transmitted to the dental technician. He makes the future prosthesis from wax with acrylic (plastic) teeth .
On the third visit, the structure in the oral cavity is checked, occlusion, fit, and the appearance of the patient’s face are assessed. The doctor makes the necessary notes and corrections and transfers the future design to the laboratory. The dental technician finally models the wax structure, plaster it into a cuvette where the wax is replaced with plastic. Next, he grinds and polishes the finished prosthesis.
At the next visit, the prosthesis is handed over. Finished structures are fitted, fit, occlusion and aesthetics are checked. The doctor will tell the patient how to use and care for the new prosthesis. During the adaptation period, additional corrections are possible.
What is included in the stages of dental restoration?
Making plastic crowns is not a very complicated process. However, the dentist and dental technician must observe all the nuances of production in order for the product to cope with its function. Prosthetics consists of the following stages:
- the best method of prosthetics is selected: first, the patient undergoes an examination by a doctor, then an X-ray diagnosis follows, then the option of a permanent prosthesis is selected and/or implantation is discussed,
- preparation: diseased teeth or their roots are removed, the enamel surface is cleared of plaque and stone, root canals are prepared, the enamel is ground, an implant or pin is installed (stump inlay),
- impressions are taken,
- making a plastic crown in the office or in a dental laboratory,
- installation of a temporary plastic prosthesis for the patient.
Read on the topic: what is better to choose – implantation or prosthetics, and why?
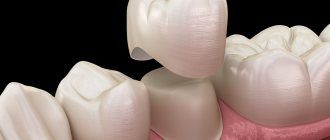
Stages of manufacturing a metal-ceramic crown
The traditional manufacturing process of metal-ceramic crowns involves the following steps:
- Determination of tooth color, characteristic features, structure of enamel, dentin, determination of the transparent layer, the presence of individual characteristics (enamel cracks, staining of fissures in the chewing group of teeth, the presence of chalky stains, enamel abrasion, etc.).
- Next comes the removal of the destroyed dental tissue and the process of preparation (grinding) of the tooth, which takes a very long time. In order to ensure that after installing a metal-ceramic crown there is no effect of the so-called “blue” gum or compression of the gingival dental papilla by the crown, the doctor must very carefully grind the tooth to create a gingival ledge (the angle on which the crown will rest). Only with this method will the work be successful.
- An impression is then taken and sent to the laboratory.
During the production of permanent metal-ceramic structures, a temporary crown is placed, which hides the defect and eliminates psychological discomfort.
- After the metal frame is made, ceramic masses are applied to it layer by layer, recreating natural teeth as accurately as possible. Next comes the artistic design of the metal-ceramic crown, taking into account the individual characteristics of the tooth.
- Then follows the fitting of an almost finished metal-ceramic crown (a metal frame with ceramics already applied, but not glazed). At this stage, the color of the crown is finally determined, because You can still make changes.
Finally, at the last visit, the permanent crown is placed. The entire process of manufacturing a metal-ceramic crown takes on average up to 10 working days.
Installation features - how to install and how to remove
The plastic crown is fixed using special cement, which quickly hardens after installation. But, at the same time, the cement is not as strong as that of fixed permanent dentures. Therefore, sometimes the plastic crown falls off - if there is no damage, the doctor will be able to put it back. Before permanent prosthetics, the dentist will easily remove the temporary cap and clean the support from excess “glue” using ultrasound or special compounds.
When using prosthetics on implants, screw fixation can be used; in this case, the prosthesis will be conditionally removable (since the dentist will be able to remove it without damage). Here a small hole is created in the crown, a small screw is screwed through it, and the groove is closed on top with a filling. If necessary, the filling is removed, the screw is unscrewed, and the prosthesis is removed, changed, cleaned, and put back.
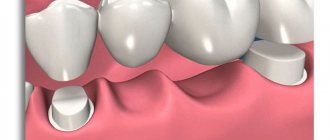
All-ceramic bridges
All-ceramic bridges have confidently taken the position of one of the most aesthetic and functional structures. This explains that manufacturing companies most often improve the methods of manufacturing just such prostheses. Computer modeling and milling are increasingly being introduced into the daily routine of dental practice. The development of such technologies makes it possible to increasingly reduce the production time of bridges, down to one visit to the dentist.
Methods of layer-by-layer application of ceramic masses with restoration of the smallest tooth structures help create prostheses that are as close as possible to the appearance of natural teeth. Due to the strength properties of modern ceramic materials, metal-free bridges have excellent functional characteristics, but this also has a downside.
While metal-ceramic dentures have some degree of compliance, all-ceramic dentures have a much lower elastic modulus. Because of this, loads leading to chipping of ceramics in metal-ceramic structures can lead to failure of metal-free “bridges” with the need for their complete replacement, while chipping of ceramics can be corrected in a clinical setting.
And, however, despite this drawback, all-ceramic bridge designs are the most progressive and will set the vector for the development of materials and manufacturing technologies.
Service life
The service life depends on the manufacturing method and the characteristics of the materials used. Thus, for those manufactured by the direct method, the service life is 1-2 months. For laboratory ones – up to 1 year. For those models whose walls are reinforced with fiberglass or metal thread, as well as those made by milling, the service life can be 1.5-2 years. But, of course, if you take good care of the prosthesis - clean it regularly and do not subject it to heavy loads.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS ON 6 IMPLANTS - 290,000 rub.
The price includes all manipulations for installing Osstem implants (South Korea), manufacturing, installing and fitting the prosthesis, including anesthesia and diagnostics.
Save RUB 30,000. >> Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Preliminary treatment
Dental treatment is an important point not only before prosthetics or implantation, but throughout life. Timely sanitation of the oral cavity preserves the health and integrity of the dental system, avoids possible complications, as well as the spread of infection throughout the body. Treatment of abutment teeth , hidden and obvious carious cavities, acute inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues or bones is mandatory before starting any prosthetics. This will allow not only to eliminate defects or diseases that have arisen in a timely manner, but also to extend the service life of the prosthesis. Also, some fixed structures require mandatory endodontic treatment.
How much does prosthetics cost?
The cost also depends on the manufacturing method, the quality of the plastic and its quantity, and the method of fixation. An ordinary plastic crown made in a doctor’s office costs from 1,000 rubles. The laboratory price is already higher - from 2000 thousand. The most expensive ones are milled ones; they can cost 3500-5000 rubles.
1Vyazmitina A.V. Materials science in dentistry, 2002.
Your questions and answers
QUESTION Hello, how long can I wear a temporary plastic crown on a tooth? Svetlana
ANSWER Hello, Svetlana. It all depends on what your dentist told you and what type of prosthetic treatment you are having. Ideally, if prosthetics are on your “native” tooth, then wearing a temporary plastic crown is not recommended for longer than 2-3 weeks. It is less common to walk with her for up to 12 months. For example, if you were given an implant with a temporary crown, and now it is healing. This is a slow process that requires some time. And after engraftment, it is necessary to change the temporary crown to a permanent one - made of ceramics, metal-ceramics or zirconium dioxide.
Author: Sambuev B. S. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
Types of alloys in metal ceramics
Gold-platinum alloy
The classic version with which orthopedic dentistry began. The first crowns were made from gold at the end of the 19th century.
Nowadays, many materials have appeared that, along with solving the problem of restoring chewing function, are quite durable and at the same time meet high aesthetic and cosmetic requirements. But gold, as a material for the manufacture of frames for metal-ceramic prostheses, is still relevant today.
Only a noble alloy can adhere so precisely to the treated tooth, which practically eliminates disintegration and recurrent caries. Gold almost never causes allergies.
The disadvantage of using a gold alloy is the limitation on the length of the intermediate (located between two supports) part of the metal-ceramic bridge (in the manufacture of metal-ceramic bridges), as well as the price: the cost of such a crown is from 10,000 rubles.
Sometimes, to improve color rendition, on a metal frame cast from other metals. a thin layer of gold is applied, which illuminates through a layer of ceramic mass with a warm yellowish color.
Nickel alloy
Most often, nickel-based alloys are used to cast the frame, which is the most accessible of the metals that can be the basis for metal-ceramics. With nickel alloys there are no problems when casting and fitting in the patient's mouth.
However, despite all the advantages, nickel has a serious drawback. This metal is a strong allergen.
Our body's daily need for nickel is thousandths of a gram, and the production of one metal-ceramic crown requires 2 grams of an alloy containing 1.3 grams of nickel. Thus, the metal is in contact around the clock with the oral mucosa, tooth tissues, and jaw. The result is allergic reactions and weakened immunity.
In Germany, they abandoned the use of nickel in dental prosthetics 10 years ago (as well as stainless steel back in the 30s).
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Cobalt-chromium alloys
The most optimal option taking into account biocompatibility and cost.
In cost, they are only 1.6 times more expensive than allergenic nickel alloys. The biocompatibility of the cobalt alloy is 36% (for the gold-platinum alloy it is 42%, and only one’s own teeth are 100% biocompatible), they are non-toxic and do not cause allergic reactions. Cobalt alloys are durable, and metal-ceramic bridges of fairly long length can be made from them.
Chromium alloys are not dangerous; only some of its salts are poisonous, but they cannot form in the oral cavity.
Molybdenum
A non-toxic metal, it is added to dental alloys in very small quantities to improve casting properties.
Beryllium
This metal is a carcinogen. It causes granuloma (a type of malignant tumor) in the lungs, liver, spleen and heart. Upon contact with beryllium, skin diseases develop and a severe weakening of the immune system is observed. In Russia, its use in dental alloys is prohibited.