If the child’s jaw develops correctly, then the replacement of teeth occurs as follows: first, the roots of the baby teeth dissolve, then the teeth fall out of the gum tissue, after which new, already permanent ones grow in their place. This is a natural process that does not require intervention.
If everything goes well, then by a certain age all baby teeth will be removed from the mouth, and straight and healthy permanent teeth will grow in their place. However, the picture does not always look like this. Sometimes parents notice that their child’s second row of permanent teeth grows even before the baby tooth falls out.
You need to pay attention to this, since new teeth can be impacted, that is, partially remain in the gums. And retention, in turn, can lead to inflammation, fever and sometimes even suppuration. Therefore, at the first signs that the child’s second row of teeth is growing, you should immediately contact a pediatric dentist.
What is hyperdontia
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), the diagnosis of “supernumerary teeth” is assigned code K00.1. When answering the question about what hyperdontia is, it should immediately be noted that normally a child should have 20 milk units, and after the formation of a permanent dentition their number will increase to 32. With the development of hyperdontia, a person develops supernumerary, that is, extra elements. Most often, this diagnosis is made towards the end of the formation of the mixed dentition, when most of the incisors, canines and molars have erupted.
Sometimes extra teeth grow along with the baby incisors and canines. The pathology is more often observed in males, while in girls and women it is diagnosed in 35% of cases of the total number. In 85% of cases, 1-2 more teeth appear in the mouth, but other patients may experience the appearance of 3 or more extra elements. Moreover, they can be located outside the jaw arch, including in the lingual area and on the hard palate1.
With hyperdontia, a person develops extra teeth
Usually, excess elements erupt near the incisors of the upper jaw; less commonly, the anomaly occurs in the lower jaw. At the same time, the teeth themselves may have a deformed shape; they often differ in structure and color. Many of them take on the shape of a cone, remain incompletely developed, dystopic and impacted.
Tests and diagnostics
The most demonstrative method for identifying hyperdentia is x-ray examination. Moreover, most often supernumerary teeth are discovered by chance during a routine medical examination.
To present the most complete picture of a dental anomaly, intraoral radiography in several projections, orthopantomography of the maxillofacial area and dental (cone-beam) computed tomography are performed. In this case, it is important to determine the location, structure, distribution and evaluate the relationship of supernumerary teeth with adjacent tissues.
Reasons for the development of the anomaly
Experts still cannot name the exact reasons for the development of pathology. However, scientists still managed to identify several theories according to which hyperdontia may be a consequence of the following prerequisites:
- atavism: the development of an anomaly is provoked by genetic memory, and then unnecessary elements arise as a consequence of a return to our ancestors. For those, the number of incisors on each jaw reached 6 pieces,
- splitting of the rudiment: this reason leads to the appearance of single defects. According to the theory, at the stage of intrauterine development, a certain malfunction occurs in the mother’s body, due to which the already formed rudiment splits, and instead of one incisor or molar, two erupt.
- serious illness of the mother and the environmental situation: the cause of the problem may be severe pathology during gestation, its aggressive treatment with medications or extremely unfavorable environmental conditions,
- genetics: a hereditary factor cannot be ruled out, since often in children with a similar diagnosis, parents also encountered a similar problem.
The cause of the problem may be severe pathology during gestation.
The appearance of excess elements in the embryonic state is usually observed in a child if his mother suffered a serious illness or its complication during pregnancy. Environmental conditions and heredity are also important factors.
Consequences
Untimely or improper treatment of hyperdontia can cause serious consequences, the correction of which may take a long time:
- severe malocclusion;
- speech defects that cannot be corrected;
- constant injury to soft tissues leads to chronic inflammation with a high risk of developing benign and malignant neoplasms in the oral cavity;
- Impacted teeth are a common cause of chronic osteomyelitis of the jaw.
The lack of correction of hyperdontia in children is especially dangerous, since it often causes disturbances in the correct formation of jaw tissues. Supernumerary teeth can cause the death of the rudiments of permanent teeth or their improper eruption.
Therefore, if there are any signs indicating the appearance of excess dental elements, or if impacted teeth are detected, you must urgently seek advice from a dentist!
What are the signs to recognize the problem - characteristic symptoms
The main symptom is the presence of extra teeth in the mouth, which can be located outside the jaw arch. They cause not only aesthetic inconvenience, but also impair diction and complicate the process of chewing food. At the same time, pathology manifests itself differently in children and adults.
In childhood
The anomaly develops almost immediately after the baby is born or within a few months after birth. The mother may experience increased pain during breastfeeding and may notice scratches and cracks on her nipples. The baby has difficulty latching on and sucking.
Pathology can occur in newborns
If the pathology develops along with the appearance of baby teeth, then the child experiences symptoms characteristic of this period, but in a more intense form. Among these, experts identify severe swelling and soreness of the mucous membrane, increased salivation, high temperature, up to low-grade fever, as well as difficulties with nasal breathing. Subsequently, the child’s bite may be deformed and diction may be impaired.
Supernumerary teeth in adults
In adults, this pathology manifests itself with the same symptoms as in childhood, but also has some distinctive symptoms. Often, supernumerary teeth are dystopic and impacted. They can be strongly curved and rotated around their axis, stopping at the eruption stage. Their palatal or lingual localization is most often observed. Adjacent units may become mobile, and the jaw bone may sometimes protrude in the area of the abnormal element. In this case, inflammation of the gums, severe deformation of the jaw and other abnormal phenomena are observed.
In adults, palatal or lingual localization is most often observed
Diet after removal of supernumerary teeth during polyodontia
Postoperative diet
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 21 days
- Terms: 1-6 months
- Cost of products: 1300-1500 rubles. in Week
After surgical interventions in the oral cavity, patients are recommended to adhere to a special diet, but they should not:
- too hot, hard, hot or spicy food;
- sugar and confectionery;
- coffee, cocktails and sweet drinks.
Considerable attention should be paid to rinsing and hygiene procedures, as well as enriching the menu with such products as:
- dairy products;
- cheeses;
- seafood;
- stewed dietary meat;
- fresh and boiled fruits and vegetables;
- porridge.
Frequently associated pathologies
Against the background of hyperdontia, curvature of correctly growing units and their roots, deformation of the entire row, and the appearance of large threes and diastemas with an open or deep bite are often observed. As mentioned above, in adults, supernumerary elements are most often accompanied by dystopia and retention - let’s look at these phenomena in a little more detail.
Dystoped elements
This anomaly involves the curvature or incorrect position of individual units. It is observed in adults, when extra elements grow in an already formed bite. The pathology has the following characteristic features:
- appearance of teeth on the hard palate or lingual areas,
- their incorrect rotation, tilt and severe curvature,
- abnormal shape, often cone-shaped.
Dystopic teeth occur when the bite is already formed.
The gums and the mucous membrane become inflamed, and on x-rays one can sometimes observe clear signs of deformation of the jaw bone and the root system of the supernumerary elements. It should be noted that in addition to functional disorders, patients face serious psychological discomfort. Its prolonged influence leads to disruptions in the functioning of the nervous, digestive and endocrine systems.
Retention as one of the common accompanying phenomena
This term implies partial eruption of crowns, when they remain half or even completely in the bone tissue. Often the patient does not experience any discomfort, and may not even be aware of the presence of this pathology. However, subsequently this phenomenon leads to the development of the following symptoms:
- swelling and redness of the mucous membrane in the area of the defect,
- loosening of apparently healthy incisors and molars,
- the appearance of subcutaneous protrusions when the causative element is localized near the edge of the jaw,
- aching pain for no apparent reason.
Teeth may not completely erupt.
Particularly difficult are cases when excess impacted elements appear near wisdom teeth, which is why they cannot erupt freely. This situation is fraught with the development of severe inflammation with suppuration, curvature of the entire row and damage to the roots of neighboring healthy molars.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of polyodontia is carried out exclusively by a specialized doctor - an orthodontist, who conducts a preliminary examination of the oral cavity and dentition, refers the patient to x-rays (orthopantomography) and analysis of anthropometric casts of teeth made of plaster. Such models are made for a more detailed study of a specific anomalous phenomenon, on the basis of which a diagnosis is then made and treatment is prescribed.
Table of normal human teeth. Deviation from the norm - polyodontia
When examining plaster models made on the basis of dental casts, the doctor measures the size of the teeth, and then analyzes the data obtained based on a special table by Wetzel and Ustimenko. The length of each row of teeth must be measured. This indicator may fluctuate depending on such characteristic individual characteristics of a person as crowding of teeth or the presence of large gaps between them. In the first case, the length will be less than normal, and in the second, a little longer. To diagnose asymmetry, the distance from the midline of the palate (or hyoid frenulum) to the far point of the dentition in one direction or the other is determined.
Types of hyperdontia
Based on the nature of the manifestation of the anomaly, several main types are distinguished. Each of them has its own characteristic features - let’s consider different options for the clinical picture.
Typical shape
Excess elements erupt exclusively within the jaw arch. More often, such crowns are smaller in size and have obvious signs of underdevelopment. Statistics show that the cause of the anomaly is usually a hereditary factor.
Teeth grow exclusively within the jaw arch
Atypical shape
Supernumerary teeth may appear outside the jaw arch, that is, outside the row. They are localized on the hard palate or grow from the lateral surfaces of the gums, including in the lingual area. This form is considered the rarest.
True hyperdontia
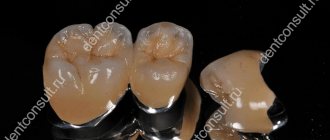
This diagnosis is made when there are excess root buds or when roots are split at the stage of their formation. Up to a certain point, “twins” may not cause much discomfort, but if one of them undergoes carious processes, its treatment can be seriously difficult due to the close intertwining of root systems. The same reason greatly complicates the procedure for removing one of the elements.
The photo shows hyperdontia
False hyperdontia
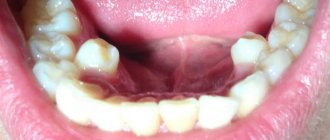
It occurs at the stage of formation of a permanent bite, when one crown has already erupted, but the milk element has not yet fallen out. With regular monitoring by a pediatric dentist, the doctor can promptly recognize the prerequisites for the anomaly and exclude its occurrence. In any case, the defect is eliminated immediately after the primary incisor falls out or is removed.
“My granddaughter’s molar went on top, but the baby tooth has not yet fallen out. Moreover, he didn’t even really wobble, that is, I definitely wouldn’t have risked tugging on him myself. We went to the dentist, he said we need to wait. Then I had to go again and pull it out. They sent me to an orthodontist. He said, as soon as the others appear, we’ll make a record.”
Lyubov Viktorovna, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
False hyperdontia is a fairly common phenomenon. Therefore, it is so important to pay increased attention to the process of bite formation at each of its stages, regularly examine the baby’s oral cavity and respond in a timely manner to suspicious changes.
The photo shows missing baby teeth
What treatment is required
Treatment of hyperdontia can be carried out in several directions. The choice of a specific method or their combination depends on the patient’s age and the clinical picture as a whole. For children, therapy usually involves eliminating symptoms and correcting pathology. Severe cases in adults may require surgery.
How to relieve teething symptoms
If the child is still very small, under the age of 3 years, he is prescribed antipyretic drugs to normalize the condition and relieve acute symptoms of teething. For very young infants, products in the form of suppositories or suspensions are recommended. To relieve pain, medications with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, such as Kalgel, Soloxeril or Dentinox, can also be prescribed. Until a certain age, serious interventions are contraindicated, so myogymnastics methods are usually used as therapy.
Antipyretics may be used to relieve teething symptoms.
Orthodontic correction
Correction using orthodontic removable and fixed structures begins only after removal. Timely treatment stimulates proper growth of the jaw system, corrects existing defects and provides favorable conditions for the eruption of permanent incisors, canines and molars.
Braces are installed only after removing unnecessary elements
For children with primary occlusion, removable soft-action devices are prescribed, for example, elastopositioners or orthodontic plates. At the age of 12-14 years, permanent braces are installed, which can be supplemented with elements that increase the pressure of the system.
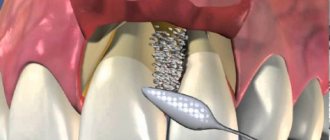
When is removal prescribed?
The removal operation is performed when supernumerary units have a negative impact on the formation of the jaw system. Be sure to remove dystopic and impacted elements, especially those with pronounced instability. However, extraction can be avoided if the extra teeth do not affect aesthetics or functionality in any way.
What does the cost of treatment depend on?
The cost of treatment is determined by various factors, including the complexity of the anomaly and the method of its correction. If the patient does not show signs of deformation of the jaw arch, then simple removal will be required:
- extraction of one supernumerary element costs around 1,500 rubles,
- with its dystopia and retention, complex removal is required, and the cost of the procedure will vary from 3,500 to 15 thousand rubles.
The need for orthodontic correction significantly increases the cost of treatment. Here the price will depend on the specific technique, type of corrective structure, its materials and additional procedures.
During what period can supernumerary teeth erupt?
The anomaly can appear both before or after a change in the primary dentition, and at a later age, which is especially typical for cases where heredity is a prerequisite. It is worth noting that pathology is usually diagnosed in the upper jaw, while its manifestation in the lower jaw is 5-6 times less common.
Since experts have not yet identified the exact causes of the development of hyperdontia, prevention of the pathology remains conditional. It is important that during pregnancy the mother closely monitors her health and, if possible, avoids serious illnesses. If one of your relatives had similar problems, parents should pay increased attention to the condition of the child’s oral cavity, especially during periods of change in bite. Don’t forget to visit your dentist every six months for preventive maintenance and follow basic hygiene rules.
1According to WHO statistics.